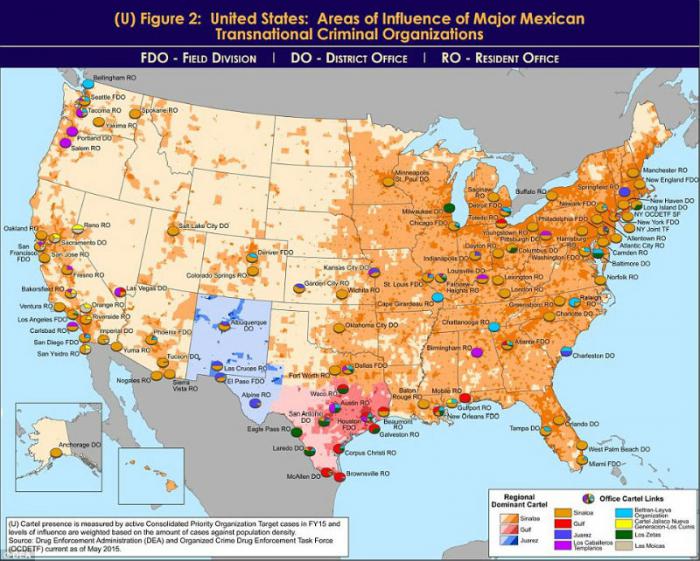
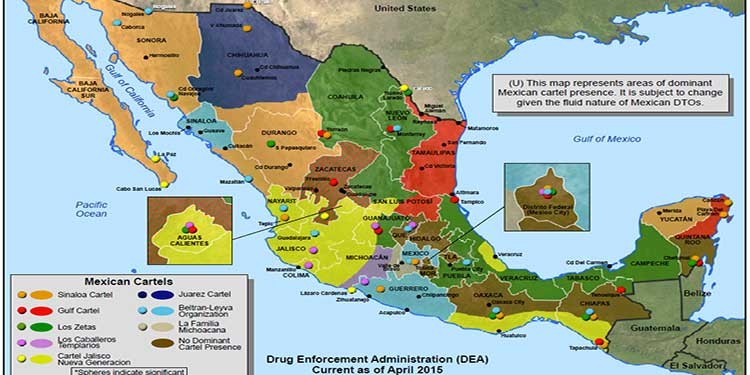
WHAT IS IN YOUR STATE?
NYPD, the premier law enforcement agency with a distinct terrorism division published a radicalization report in 2007, anyone take heed?
US terrorist database growing at rapid rate
ALEXANDRIA, Virginia (AP)— The U.S. government is rapidly expanding the number of names it accepts for inclusion on its terrorist watch list, with more than 1.5 million added in the last five years, according to numbers divulged by the government in a civil lawsuit.
About 99 percent of the names submitted are accepted, leading to criticism that the government is “wildly loose” in its use of the list.
Those included in the Terrorist Screening Database could find themselves on the government’s no-fly list or face additional scrutiny at airports, though only a small percentage of people in the database are actually on the list.
It has been known for years that the government became more aggressive in nominating people for the watch list following al-Qaida operative Umar Farouk Abdulmutallab’s failed effort to blow up an airplane over Detroit on Christmas Day 2009.
But the numbers disclosed by the government show submissions have snowballed. In fiscal 2009, which ended Sept. 30, 2009, 227,932 names were nominated to the database. In fiscal 2010, which includes the months after the attempted Christmas bombing, nominations rose to 250,847. In fiscal 2012, they increased to 336,712, and in fiscal 2013 — the most recent year provided — nominations jumped to 468,749.
What the FBI published on terrorism and the database. The searchable global terrorism database.
16 Southern California residents have been linked to Islamist terrorist activity since 9/11
 LATimes: The FBI announced Friday that it is investigating the mass shooting Wednesday in San Bernardino as an act of terrorism. Tashfeen Malik, one of the assailants, pledged allegiance to an Islamic State leader in a Facebook posting before the attack, two federal law enforcement officials said Friday.
LATimes: The FBI announced Friday that it is investigating the mass shooting Wednesday in San Bernardino as an act of terrorism. Tashfeen Malik, one of the assailants, pledged allegiance to an Islamic State leader in a Facebook posting before the attack, two federal law enforcement officials said Friday.
If the FBI declares the shooting an act of terrorism, it would be the first Islamic-terrorist attack in Southern California. But the region has experienced activities related to Islamic terrorism. The House of Representative’s Committee on Homeland Security said 16 Southern California residents have been tied to such activity since 2001:
Los Angeles
March 23, 2003
Hasan Akbar
Army Sgt. Hasan Akbar, who grew up in Watts, turned on his fellow soldiers while serving in Kuwait in 2003, shooting at officers and tossing grenades into their tents. Two officers were killed and 14 others wounded in the attack. In 2005, a military jury sentenced Akbar to death.
Read more »
July 27, 2005
Kevin James, Levar Haley Washington, Gregory Vernon Patterson and Hammad Riaz Samana
Law enforcement officials stopped a terrorist plot to attack religious institutions, military bases and airports. Officials said James, a former inmate at California State Prison, Sacramento, initiated the plot. While in prison, James headed a radical Islamic prison gang. After his release, he and Washington, another former inmate, recruited Patterson and Samana, from Washington’s mosque. All four were charged with conspiracy to conduct war against the U.S. government through terrorism. Washington and Patterson were sentenced to 22 years and 12 years, respectively. Samana was sentenced to 70 months in prison, and James was sentenced to 16 years. Read more »
May 22, 2015
Nader Elhuzayel and Muhanad Badawi
Elhuzayel and Badawi were arrested after expressing interest in traveling to Syria to join Islamic State. Federal authorities said they overheard a conversation between the two in which one proclaimed his desire to die as a martyr on a battlefield while fighting for the group. Elhuzayel was arrested at LAX before he boarded a plane for Turkey, and Badawi, who officials say purchased Elhuzayel’s ticket, was taken into custody at an Anaheim gas station. Both men have pleaded not guilty to charges of providing material support to a foreign terrorist organization. Read more »
Riverside
Nov. 16, 2012
Sohiel Omar Kabir, Ralph Deleon, Miguel Alejandro Santana Vidriales and Arifeen David Gojali
Deleon and Kabir were sentenced in February to 25 years in federal prison for a 2012 terrorist plot to travel to Afghanistan, join Al Qaeda and kill Americans. Vidriales and Gojali cooperated with authorities in the investigation and pleaded guilty to conspiracy charges. In March, Vidriales was sentenced to 10 years in federal prison; Gojali was sentenced to five years in federal prison. Read more »
Garden Grove
Oct. 11, 2013
Sinh Vinh Ngo Nguyen
Nguyen was arrested in 2013 while preparing to board a Mexico-bound bus in Santa Ana. He admitted to traveling to Syria the previous year to join opposition forces against the Bashar Assad regime. Authorities said Nguyen planned to become an Al Qaeda operative and lead an attack on coalition forces. He pleaded guilty to terrorism charges in December 2013. Read more »
Orange County
July 2, 2014
Adam Dandach
Dandach was arrested on July 2, 2014, at John Wayne Airport as he tried to board a plane headed to Istanbul, Turkey. He pleaded guilty in August to attempting to travel to Syria to join ISIS, and faces up to 25 years in federal prison. Read more »
San Diego
Oct. 9, 2009
Jehad Mostafa
An indictment was issued for Mostafa in 2009, alleging that he, a former resident of San Diego, conspired to provide material support to terrorists. Mostafa is currently believed to be in Somalia, possibly working with Shahab, an Islamist army with ties to Al Qaeda. Read more »
Aug. 26, 2014
Douglas McAuthur McCain
McCain, a San Diego resident, was reportedly killed while fighting for the Islamic State in Syria.
Read more »
April 16, 2015
Mohamad Saeed Kodaimati
Mohamad Saeed Kodaimati traveled to Turkey from San Diego in late 2012 and was in Turkey and Syria until he returned to the U.S. in March, according to prosecutors. Authorities allege that Kodaimati lied to federal officials about his links to Islamic State in Syria. He pleaded guilty to lying to the FBI and agreed to a prison sentence of eight years. His sentencing is set for Jan. 11. Read more »
Minneapolis is a Terror Axis, NPR