Obama Commutes Sentences Of 111 Federal Inmates Convicted Of Non-Violent Drug Charges
WASHINGTON (AP) — President Barack Obama has cut short the sentences of 111 federal inmates in another round of commutations for those convicted of nonviolent drug offenses
Obama has long called for phasing out strict sentences for drug offenses, arguing they lead to excessive punishment and incarceration rates unseen in other developed countries.
White House Counsel Neil Eggleston says the commutations underscore the president’s commitment to using his clemency authority to give deserving individuals a second chance.
He says that Obama has granted a total of 673 commutations, more than the previous 10 presidents combined. More than a third of the recipients were serving life sentences.
Eggleston says he expects Obama to continue granting commutations through the end of his administration, but only legislation can ensure the federal sentencing system operates more fairly.
Prisoner applications are being reviewed by more than 1,000 attorneys at 323 law firms and organizations nationwide, pro bono. In the meantime, more than 35,000 inmates — about 16 percent of the federal prison population — have applied to have their sentences shortened under the Justice Department-led initiative. More her from the WashingtonPost.
This the program began under Eric Holder.
Obama has enacted his own SAFE Act, legislation that has not advanced, so he is using his pen and phone instead. Note the title ‘SAFE’….safe for who exactly?
The Safe, Accountable, Fair, and Effective (SAFE) Justice Act Rep. Jim Sensenbrenner and Rep. Bobby Scott
States Lead the Way in Corrections Reform
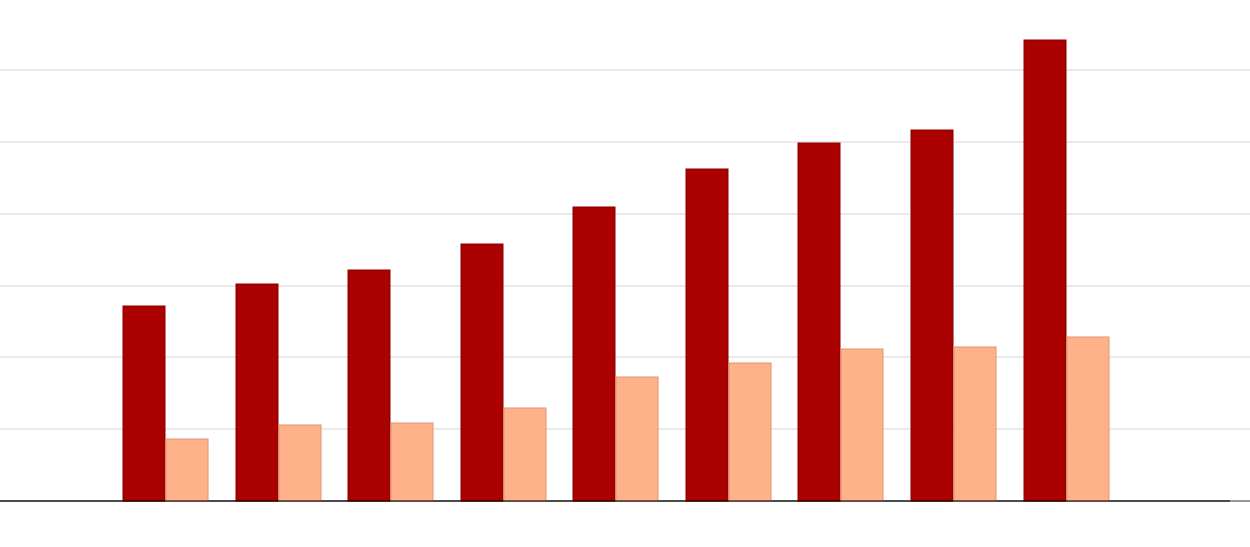
Since 1980, Congress has steadily increased the size and scope of the federal criminal code and with it the federal prison population. In that period, the federal government has added an estimated 2,000 new crimes to the books, while the federal imprisonment rate has grown by an astounding 518 percent. During the same period, annual spending on the federal prison system rose 595 percent, from $970 million to more than $6.7 billion, after adjusting for inflation.
Like the federal government, states also recorded sharp increases in imprisonment and associated costs over the past 30 years. During the past decade, however, the states have responded by reducing their imprisonment rate by 4 percent while the federal imprisonment rate jumped 15 percent. The state drop was driven in large part by comprehensive reform efforts in more than two dozen states designed to protect public safety while containing costs and preventing further growth in government programs.
These state reforms have returned dividends to taxpayers many times over: from Texas and Wisconsin to Rhode Island, from Georgia and South Carolina to New York, 32 states have reduced both their crime and imprisonment rates over the past five years. Cumulative cost savings in a subset of these states exceed $4.6 billion, and millions have been reinvested in prison alternatives better at breaking the cycle of recidivism.
The Safe, Accountable, Fair, and Effective (SAFE) Justice Act
The SAFE Justice Act is bipartisan legislation that puts lessons learned in the states to work at the federal level. The legislation protects public safety and reins in escalating corrections costs by –
Curtailing overcriminalization – requires public disclosure of regulatory criminal offenses; allows victims of regulatory over-criminalization to contact the inspector general; restores discretion to judges to determine to what extent manipulated conduct that results from fictitious law enforcement “stings” may be considered in court; protects against wrongful convictions; creates procedures to simplify charging and safely reduce pre-trial detention; and eliminates federal criminal penalties for simple drug possession in state jurisdictions.
Increasing use of evidence-based sentencing alternatives – expands eligibility for pre-judgment probation; promotes greater use of probation for lower-level offenders; and encourages judicial districts to open drug, veteran, mental health and other problem solving courts.
Concentrating prison space on violent and career criminals – clarifies original Congressional intent by examining the role an offender plays in a drug offense and targeting higher-level traffickers for mandatory minimums and recidivist enhancements; applies life sentences for drug trafficking only in the most egregious cases; allows eligible offenders to petition for resentencing under new trafficking laws; modestly expands the drug trafficking safety valve; clarifies that mandatory minimum gun sentences can only run consecutively when the offender is a true recidivist; and expands compassionate release for lower-risk geriatric and terminally-ill offenders.
Reducing recidivism – expands earned time to encourage more inmates to participate in individualized case plans designed to reduce their likelihood of reoffending; seeks to boost success rates of offenders on probation and post-prison supervision by mandating swift, certain and graduated sanctions for violations and offering credits for those who are compliant; creates a performance-incentive funding program; creates mental health and de-escalation training programs for prison personnel; and mandates the use of performance-based contracting for half-way houses.
Increasing government transparency and accountability – requires fiscal impact statements for sentencing and corrections bills; requires sentencing cost analyses to be disclosed in pre-sentencing reports; adds a non-voting federal defender rep. on the U.S. Sentencing Commission; requires the calculation of good time as Congress intended; requires federal agencies to report on corrections populations and recidivism rates, among other indicators; reauthorizes the Innocence Protection Act and directs the Attorney General to develop best practices to reduce wrongful convictions; and encourages prison savings to be invested in strengthening safety measures for law enforcement.
The Research Foundation for the SAFE Justice Act
The SAFE Justice Act, like the comprehensive corrections reforms enacted in many states, draws from the large and growing body of research about what works to reduce recidivism, including the following principles:
To deter offending, use swift and certain responses – Research demonstrates that delayed, unpredictable, and severe responses are less effective than swift, certain, and fair sanctions. Swift and certain responses—both punishments and rewards—are more effective because they help offenders see the response as a direct consequence of their behavior and because offenders heavily discount uncertain and distant responses.
States that have implemented swift and certain responses include Washington, Georgia, and West Virginia.
Earned time policies can reduce recidivism – Research demonstrates that rewards and incentives can work to change offending behavior and reduce recidivism. The benefits of earned time policies for inmates and earned compliance credits for offenders under probation or post-release supervision include lower costs (through accelerated release) and lower recidivism (by shifting correctional resources to those offenders who continue to violate rules and break laws).
States that have built earned time into their prison systems include Kentucky, Maryland, and Louisiana. States that have built earned time into their supervision systems include South Dakota, Mississippi, and Arkansas.
For drug offenders, sentence strategically – The most vicious, predatory and high-level drug offenders warrant prison cells to avert the harm they cause to individuals and communities, but research shows that long terms of incarceration for the vast majority of mid-level couriers, distributors and dealers has little impact on public safety. While imprisonment may temporarily disrupt a drug market, the “replacement effect”—whereby new recruits quickly replace those imprisoned for mid-level roles—negates the impact of incarceration on drug price, availability, or related crime. Instead, prison time should be focused on violent or kingpin drug traffickers who are controlling the marketplace.
States that have recalibrated their drug sentencing systems to differentiate higher-level from lower-level offenders include South Dakota, Georgia, and South Carolina.
Focus on high-risk offenders – For many lower-level offenders, especially those whose criminal conduct is driven largely by substance abuse, alternatives like drug and mental health courts, treatment programs, and intensive supervision both hold offenders accountable and work better to reduce recidivism. In fact, research suggests that for many lower-risk and less serious offenders a prison sentence may actually be responsible for an increase in recidivism by encouraging anti-social ties and breaking bonds at home.
States that have encouraged diversion of lower-level offenders to prison alternatives include Mississippi, California, and Illinois.
Age matters – Research has long shown that age is one of the most significant predictors of criminality, with criminal or delinquent activity peaking in late adolescence and decreasing significantly with time. As a result, imprisonment of offenders into their 50s, 60s and 70s provides diminishing and often negligible public safety returns. Implementing smart, targeted geriatric release programs can ensure heinous offenders remain behind bars while cutting down on costs and maintaining public safety.
States that have implemented geriatric or compassionate release programs include Alabama, Colorado, and Montana.