While much of the global hacking came to a scandal status in 2015-16, the Russian ‘Fancy Bear’ activity goes back to at least 2008. The FBI is an investigative wing and works in collaboration with foreign intelligence and outside cyber experts. For official warnings to be provided to U.S. government agencies, contractors, media or political operations, the FBI will generally make an official visit to affected entities to gather evidence. The NSA, Cyber Command and the DHS all have cyber experts that track and work to make accurate attributions of the hackers.

The Department of Homeland Security is generally the agency to make official warnings. The Associated Press gathered independent cyber experts to perform an independent study and is ready to blame the FBI for not going far enough in warnings.
When it came to the Clinton presidential campaign hack, the FBI made several attempts to officials there and were met with disdain and distrust. The FBI wanted copies of the ‘log-in’ files for evidence and were denied.
In part the AP report states:
“CLOAK-AND-DAGGER”
In the absence of any official warning, some of those contacted by AP brushed off the idea that they were taken in by a foreign power’s intelligence service.
“I don’t open anything I don’t recognize,” said Joseph Barnard, who headed the personnel recovery branch of the Air Force’s Air Combat Command.
That may well be true of Barnard; Secureworks’ data suggests he never clicked the malicious link sent to him in June 2015. But it isn’t true of everyone.
An AP analysis of the data suggests that out of 312 U.S. military and government figures targeted by Fancy Bear, 131 clicked the links sent to them. That could mean that as many as 2 in 5 came perilously close to handing over their passwords.
It’s not clear how many gave up their credentials in the end or what the hackers may have acquired.
Some of those accounts hold emails that go back years, when even many of the retired officials still occupied sensitive posts.
Overwhelmingly, interviewees told AP they kept classified material out of their Gmail inboxes, but intelligence experts said Russian spies could use personal correspondence as a springboard for further hacking, recruitment or even blackmail.
“You start to have information you might be able to leverage against that person,” said Sina Beaghley, a researcher at the RAND Corp. who served on the NSC until 2014.
In the few cases where the FBI did warn targets, they were sometimes left little wiser about what was going on or what to do.
Rob “Butch” Bracknell, a 20-year military veteran who works as a NATO lawyer in Norfolk, Virginia, said an FBI agent visited him about a year ago to examine his emails and warn him that a “foreign actor” was trying to break into his account.
“He was real cloak-and-dagger about it,” Bracknell said. “He came here to my work, wrote in his little notebook and away he went.”
Left to fend for themselves, some targets have been improvising their cybersecurity.
Retired Gen. Roger A. Brady, who was responsible for American nuclear weapons in Europe as part of his past role as commander of the U.S. Air Force there, turned to Apple support this year when he noticed something suspicious on his computer. Hughes, a former DIA head, said he had his hard drive replaced by the “Geek Squad” at a Best Buy in Florida after his machine began behaving strangely. Keller, the former senior spy satellite official, said it was his son who told him his emails had been posted to the web after getting a Google alert in June 2016.
A former U.S. ambassador to Russia, Michael McFaul, who like many others was repeatedly targeted by Fancy Bear but has yet to receive any warning from the FBI, said the lackluster response risked something worse than last year’s parade of leaks.
“Our government needs to be taking greater responsibility to defend its citizens in both the physical and cyber worlds, now, before a cyberattack produces an even more catastrophic outcome than we have already experienced,” McFaul said. Read the full article here.
***
Every organization has a Chief Technology Officer, even small business has a ‘go-to’ person for issues. To be in denial there are any vulnerabilities is reckless and dangerous. To assume systems are adequately protected against cyber intrusions is also derelict in duty.
Fancy Bear is listed as APT 28. APT=Advanced Persistent Threat.
APT28 made at least two attempts to compromise Eastern European government organizations:•In a late 2013 incident, a FireEye devicedeployed at an Eastern European Ministry ofForeign Affairs detected APT28 malware inthe client’s network.•More recently, in August 2014 APT28 used alure (Figure 3) about hostilities surrounding aMalaysia Airlines flight downed in Ukraine ina probable attempt to compromise the Polishgovernment. A SOURFACE sample employedin the same Malaysia Airlines lure wasreferenced by a Polish computer securitycompany in a blog post.The Polish securitycompany indicated that the sample was “sentto the government,” presumably the Polishgovernment, given the company’s locations and visibility.
Other probable APT28 targets that we haveidentified:•Norwegian Army (Forsvaret)•Government of Mexico•Chilean Military•Pakistani Navy•U.S. Defense Contractors•European Embassy in Iraq•Special Operations Forces Exhibition (SOFEX)in Jordan•Defense Attaches in East Asia•Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation
MALWAREEvolves and Maintains Tools for Continued, Long-Term Use•Uses malware with flexible and lasting platforms•Constantly evolves malware samples for continued use•Malware is tailored to specific victims’ environments, and is designed to hamper reverse engineering efforts•Development in a formal code development environmentVarious Data Theft Techniques•Backdoors using HTTP protocol•Backdoors using victim mail server•Local copying to defeat closed/air gapped networksTARGETINGGeorgia and the Caucasus•Ministry of Internal Affairs•Ministry of Defense•Journalist writing on Caucasus issues•Kavkaz CenterEastern European Governments & Militaries•Polish Government•Hungarian Government•Ministry of Foreign Affairs in Eastern Europe•Baltic Host exercisesSecurity-related Organizations•NATO•OSCE•Defense attaches•Defense events and exhibitionsRUSSIAN ATTRIBUTESRussian Language Indicators•Consistent use of Russian language in malware over a period of six years•Lure to journalist writing on Caucasus issues suggests APT28 understands both Russian and EnglishMalware Compile Times Correspond to Work Day in Moscow’s Time Zone•Consistent among APT28 samples with compile times from 2007 to 2014•The compile times align with the standard workday in the UTC + 4 time zone which includes major Russian cities such as Moscow and St. Petersburg

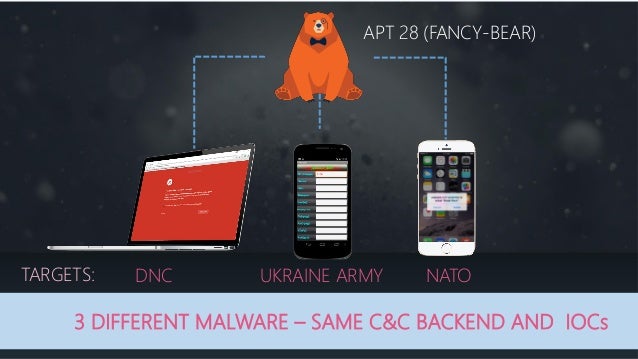

 photo (attribution for photo removed due to malware alert)
photo (attribution for photo removed due to malware alert)





