Harvesting posts on social media platforms has become necessary to track all kinds of human conditions. There was once a time it was a scandal when Edward Snowden revealed NSA platforms but now it is widely accepted apparently.
When it comes to tracking people movement, medical and humanitarian issues and patterns, the Pentagon is working social media. If there are protests, intermittent battles or hostilities or airstrikes, social media is the go to immediate source.
It is so valuable, the United Nations is now passing out phones and or sim cards to migrants and refugees. Question is who is paying the full connectivity access and to what wireless company?
Pentagon Mapmakers Are Using Social Media to Chart Syrians’ Exodus
Officials admit the National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency’s approach has its limitations
DefenseOne: Streams of Facebook, Instagram, and other social media posts shared by smartphone-toting children and families at border crossings are providing U.S. intelligence analysts with a real-time map of the Syrian exodus. It’s not picture perfect, but it fills in gaps for the nation’s spy cartographers, a top Defense Department official says.
By searching public posts, the National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency fulfills its duty to provide decision-makers with past, present and future insights into locations during a global emergency.
Viewing Defense Department satellite imagery from “space isn’t a great way to sense human activity of that magnitude, but people talking on the ground and people tweeting about lack of food, or pictures about lines at gates at borders is really incredibly useful,” Sue Gordon, the spy map agency’s deputy director, tells Nextgov. “You will have the ability to see what’s going on from an intelligence perspective, but social media will give you that on-the-ground look to help you correlate disparate activities or to get a different view of what is real.”
Photos and vignettes that refugees and relief workers publish depict the kindnesses and bloodshed arising from a civil war that has torn an estimated 14 million people from their homes.
The images are made possible, in part, by governmental organizations. As of August, the Office of the United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees had distributed 33,000 mobile SIM cards to displaced Syrians in Jordan alone.
Geotags on posts — metadata indicating where and when messages were sent — can be searched or plotted on a map.
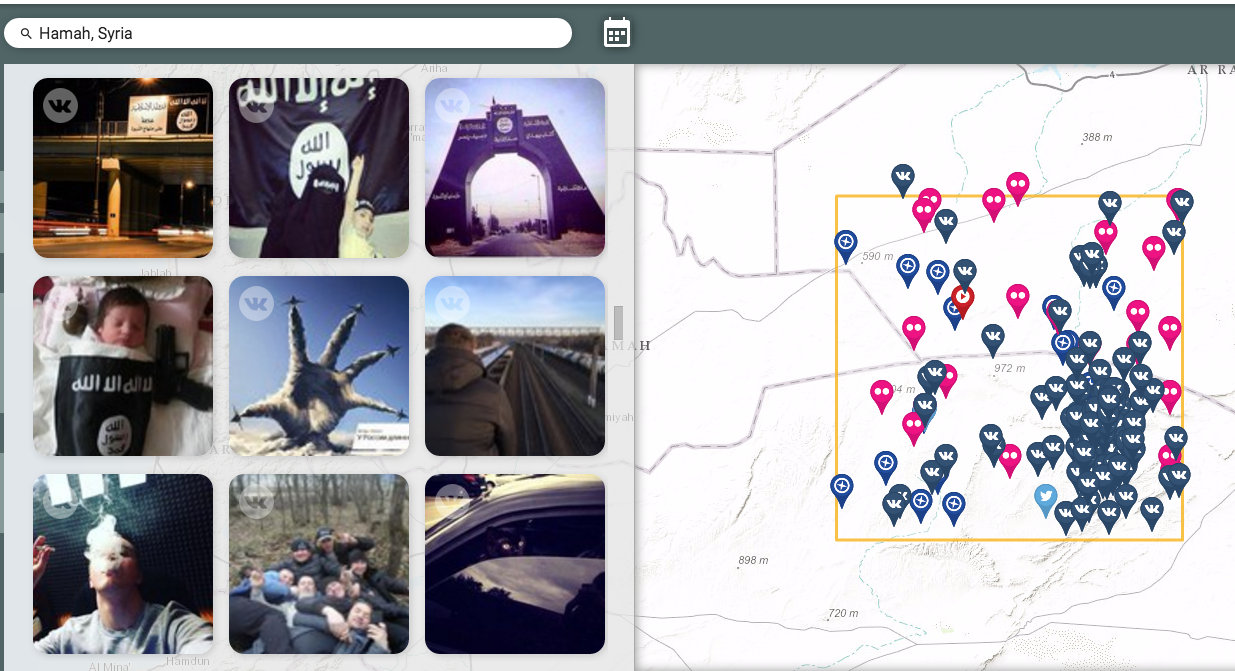
For example, one government vendor that specializes in the marriage of geographic data and social media pins refugee-related items from Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and other social networks on a map of the Middle East and Europe. (Here is a map of posts filtered by the keywords, “Hamah, Syria.”)
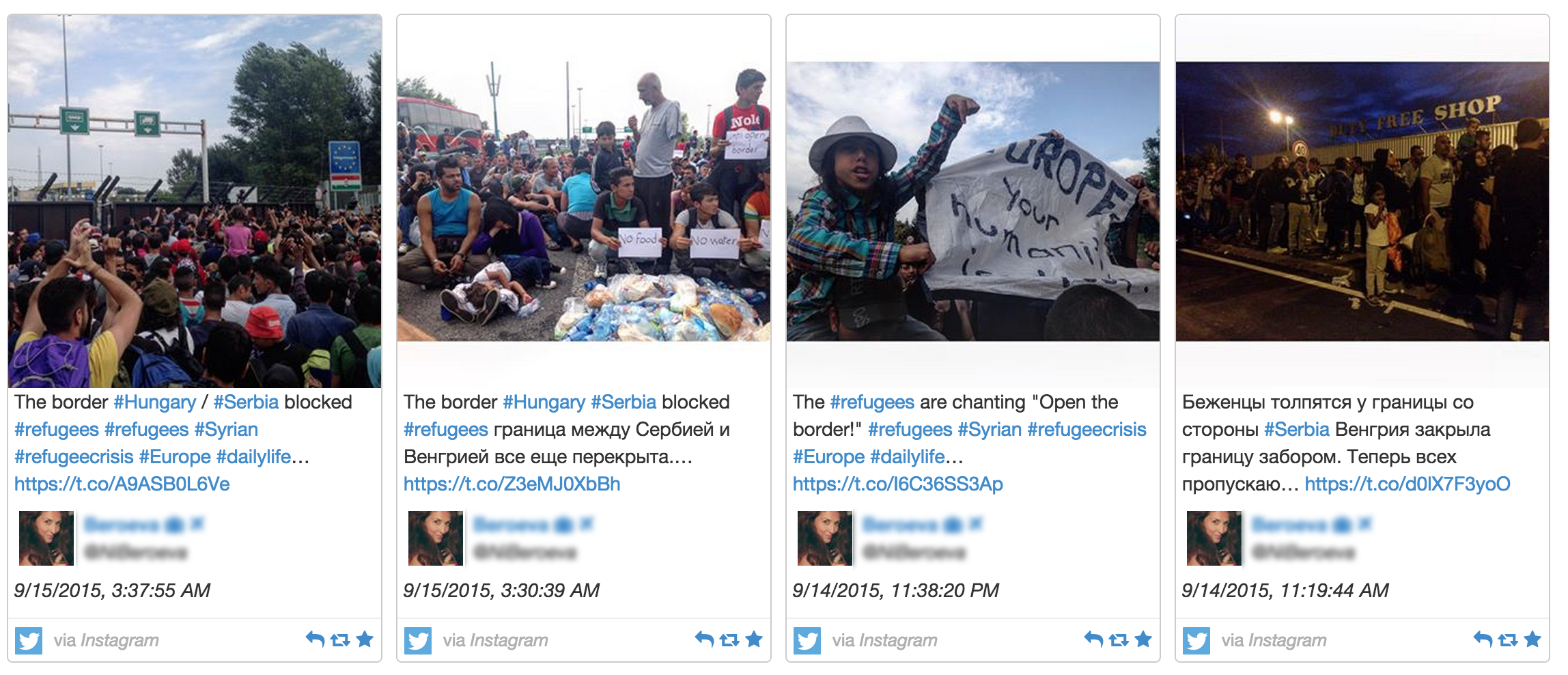
By clicking on a marker, federal analysts can see when and where the messages were sent, as well as their images and words. (Here are a few tweets, containing Instagram links, that depict a blocked Hungary-Serbia border.)
The firm, Canada-based Echosec, uses maps from geospatial software provider Esri. National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency spokeswoman Don Kerr told Nextgov the agency does not currently contract with Echosec but it does use Esri’s technology.
While declining to identify specific federal clients, Echosec marketing executive Kira Kirk said that as the Syrian conflict has escalated, the company’s tools have followed the growing numbers of displaced civilians moving into countries like Turkey, Lebanon, Greece and Hungary.
At the Za’atari Syrian Refugee Camp in Jordan, 86 percent of the young refugees owned mobile handsets and 83 percent owned SIM cards, according to a March 2015 paper presented by Pennsylvania State University scholars Carleen Maitland and Ying Xu for the 43rd Research Conference on Communication, Information and Internet.
Last month, Defense One contributor Gayle Tzemach Lemmon, reporting from the Turkish Border, said: ”Russian air strikes are among the first things you hear when spending any time among Syrians constantly monitoring what is happening to family and friends via What’sApp and Facebook. YouTube videos are played and the carnage people are witnessing is discussed.”
Unlike law enforcement authorities or covert operatives, NGA personnel do not engage social media users they follow online.
“We’re not out there interacting with it and trying to influence it,” said Gordon, during an interview at Esri’s FedGIS conference in Washington. Rather, analysts subscribe to various feeds, open accounts and watch YouTube videos,
This passive approach to social media monitoring has its limitations, including spin.
Intelligence analysts can get the wrong impression from trolls, propagandists or other users with selective memories, just as Facebook stalkers sometimes feel down when bombarded with pictures of parties and achievements on their friends’ timelines.
“They get depressed because they see all these people having this great life, but I think it makes the point that all this stuff that is produced by humans comes with a perspective and you may perceive it to be true but you still have to think about what it is” indicating, Gordon said. “And then you have other truths that can help out.”
To her point, Jill Walker Rettberg, a University of Bergen digital culture professor, said of a Vocativ Instagram narrative showing one Syrian man’s journey to Germany, ”The absence of women and children is striking.”
Still, localized data points can make life a little easier for an agency dealing with information overload.
“It has a real lovely temporal quality to it because it’s always being captured by somebody who cares about that event and that event in time,” Gordon said. ”The Syrian migration is just a really great example, or any humanitarian crisis or migratory crisis, because we have overhead assets but the real intelligence is on the ground.”