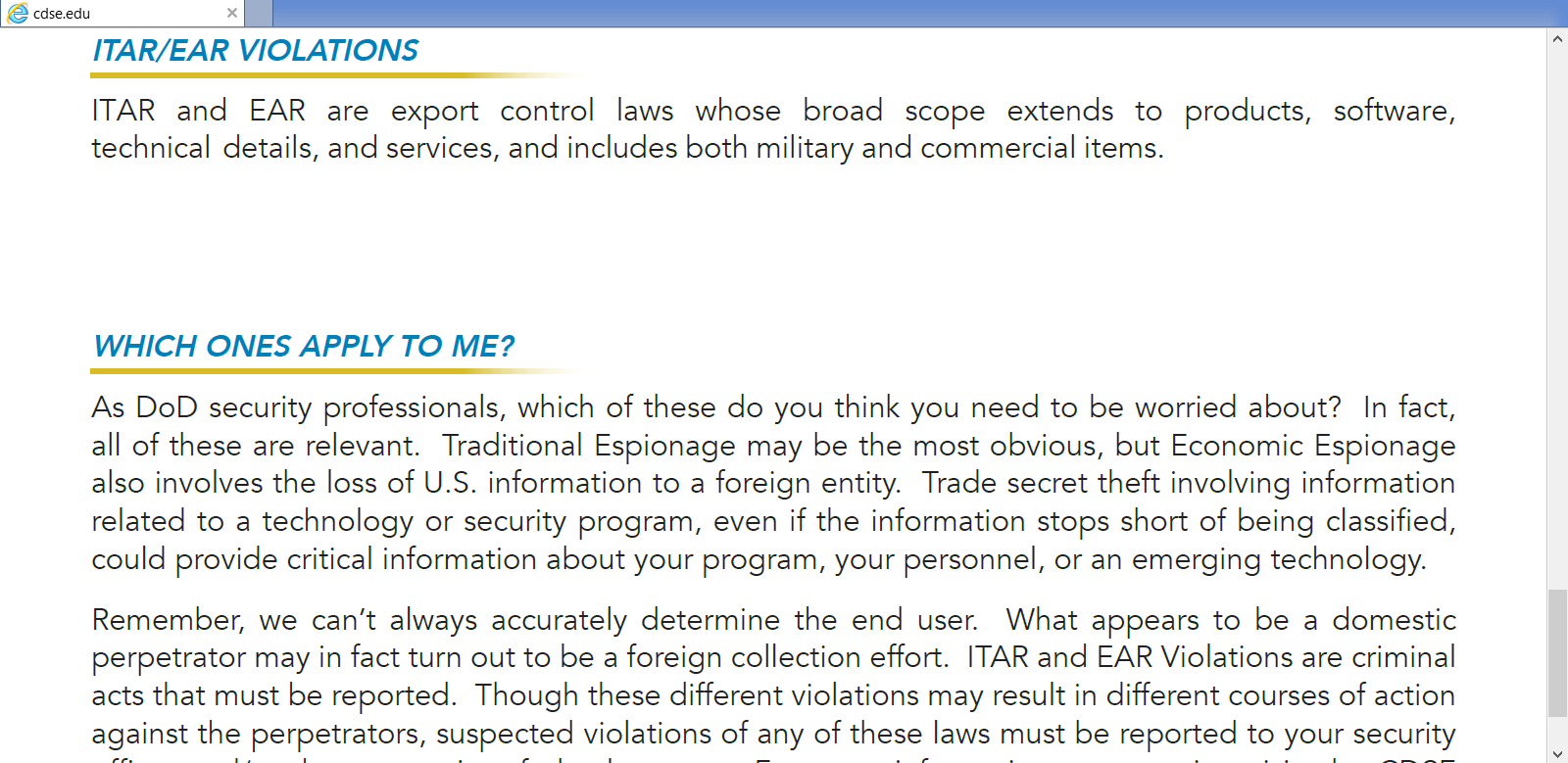
Pastor Andrew Brunson faces life in prison in Turkey for fraudulent charges of supporting a terror organization and political espionage. Brunson has lived in Turkey for 23 years. He even filed an application to renew his visa application in October of 2016. More details here.
Meanwhile, as the Turkish currency tanked due to sanctions and trade issues, the lira value held for about a week until investors got in the game due to interest and enticements by the Turkish Finance Minister and President Erdogan.
So, what is the reason for detaining and the charges on the Pastor? Seems, Erdogan is using the Pastor as a tool for two reasons. One includes an anti-Erdogan activist that has lived in the United States 1999. He was/is a preacher himself and has an estimate 5 million followers. Erdogan included Gulen as one of the reasons for the attempted/alleged coup.
But the other reason is Iran. Seems Eli Lake an investigative journalist understands it better than all the rest. Why? During the Obama administration, nothing else mattered but to get an Iran nuclear deal. Those rogue governments, foreign leaders and financial institutions helping Iran evade sanctions were purposely ignored and overlooked by the Obama White House.
It was last week that the Erdogan government made an offer to the United States to release Pastor Brunson if the United States would drop charges and the investigation of the Halkbank.
President Trump gave Turkey an answer….NO.
The Trump administration rebuffed Turkey’s offer to release detained American pastor Andrew Brunson if the U.S. halts the investigation into Turkish bank Halkbank, The Wall Street Journal reported Sunday.
The Turkish government agreed to drop terrorism charges against the pastor in exchange of the U.S. government dropping fines totaling billions of dollars against the bank. A senior White House official said the offer was rejected.
Turkey has taken advantage of the United States for many years. They are now holding our wonderful Christian Pastor, who I must now ask to represent our Country as a great patriot hostage. We will pay nothing for the release of an innocent man, but we are cutting back on Turkey!
— Donald J. Trump (@realDonaldTrump) August 16, 2018
So, there is this bank and the gold. Happened earlier this year, stemming from a 2012-2013 case:
Mehmet Hakan Atilla, an executive at Turkey’s majority state-owned Halkbank (HALKB.IS), was convicted on five of six counts he faced, including bank fraud and conspiracy to violate U.S. sanctions law, in Manhattan federal court.
Atilla was also found not guilty on a money laundering charge.
Prosecutors had accused Atilla of conspiring with gold trader Reza Zarrab and others to help Iran escape sanctions using fraudulent gold and food transactions. Zarrab pleaded guilty and testified for the prosecutors.
In several days on the witness stand, Zarrab had described a sprawling scheme that he said included bribes to Turkish government officials and was carried out with the blessing of current President Tayyip Erdogan.
Halkbank had no immediate comment. Attempts to reach Erdogan’s spokesman for comment on the allegations at the trial have been unsuccessful. Erdogan has publicly dismissed the case as a politically motivated attack on his government.
U.S. prosecutors have criminally charged nine people, though only Zarrab, 34, and Atilla, 47, have been arrested by U.S. authorities.
BANKERS’ CHOICE
“Foreign banks and bankers have a choice: you can choose willfully to help Iran and other sanctioned nations evade U.S. law, or you can choose to be part of the international banking community transacting in U.S. dollars,” Joon Kim, the acting U.S. Attorney in Manhattan, said in a statement after the verdict was read. “But you can’t do both.”
In December of 2017, the Turkish Justice Minister Abdulhamit Gul demanded in a letter to U.S. Attorney General Jeff Sessions that Korkmaz be returned to Turkey, calling him “a fugitive, a terror suspect facing serious allegations.”
The Turkish government has said that followers of the U.S.-based cleric Fethullah Gulen were behind both the Turkish investigation and the U.S. case, as well as the 2016 failed coup in Turkey. Gulen has denied the accusations. More here.