Now, who is Dr. Robert Epstein? He is a distinguished research psychologist and the former editor in chief of Psychology Today. He has authored 15 books and published 250 articles. He is a committed Democrat and voted for Hillary Clinton in 2016.
So, you MUST watch this video clip from C-Span today before the Senate. More terrifying than even Russia interfering in the American election infrastructure.
Hat tip to Senator Ted Cruz.
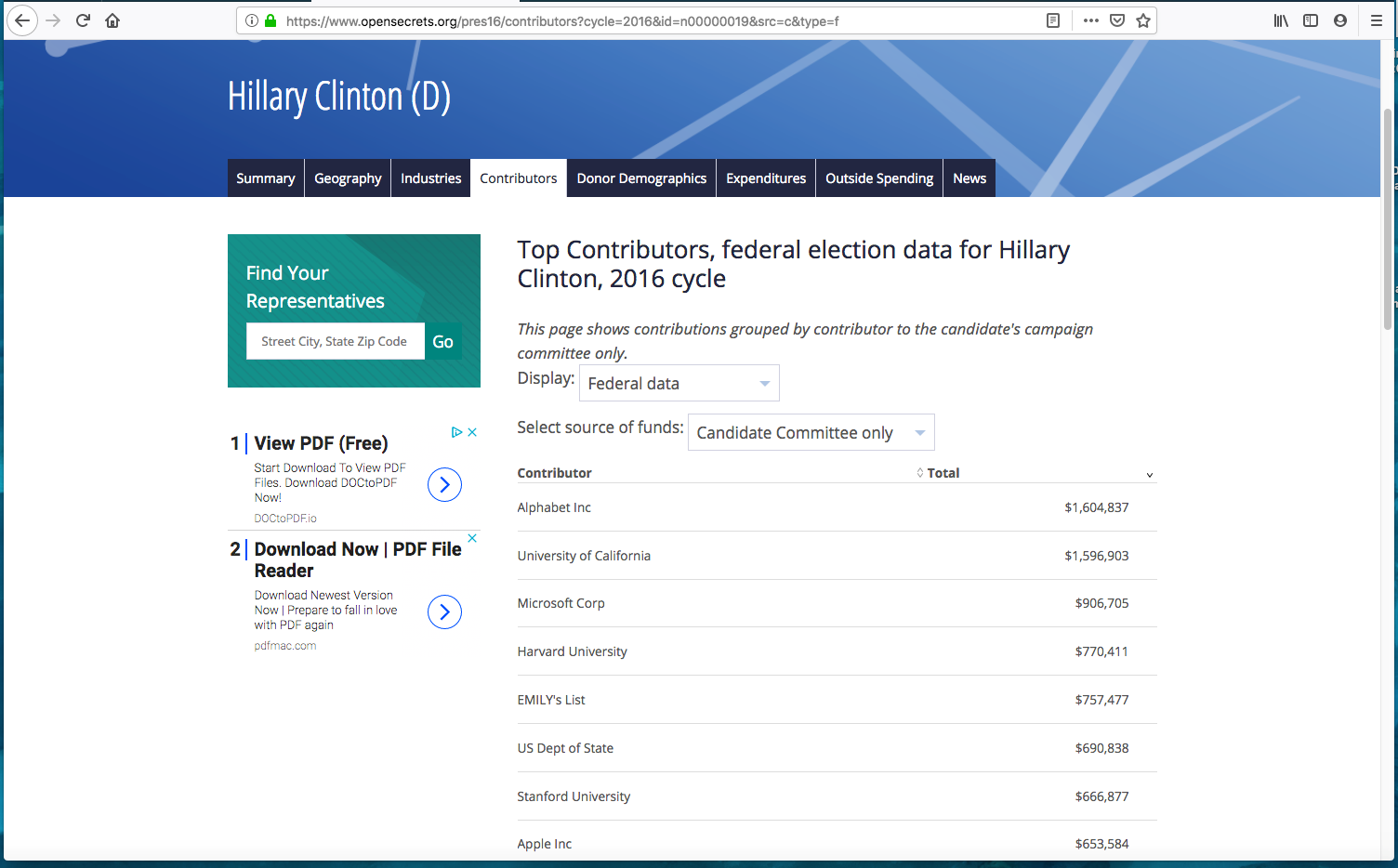
Can you guess who was the top campaign contributor? Yes, Alphabet, the parent company of Google.
Now, he published this piece about Google and it too is a must read.
Recognition is growing worldwide that something big needs to be done about Big Tech, and fast.
More than $8 billion in fines have been levied against Google by the European Union since 2017. Facebook Inc., facing an onslaught of investigations, has dropped in reputation to almost rock bottom among the 100 most visible companies in the U.S. Former employees of Google and Facebook have warned that these companies are “ripping apart the social fabric” and can “hijack the mind.”
Adding substance to the concerns, documents and videos have been leaking from Big Tech companies, supporting fears—most often expressed by conservatives—about political manipulations and even aspirations to engineer human values.
Fixes on the table include forcing the tech titans to divest themselves of some of the companies they’ve bought (more than 250 by Google and Facebook alone) and guaranteeing that user data are transportable.
But these and a dozen other proposals never get to the heart of the problem, and that is that Google’s search engine and Facebook’s social network platform have value only if they are intact. Breaking up Google’s search engine would give us a smattering of search engines that yield inferior results (the larger the search engine, the wider the range of results it can give you), and breaking up Facebook’s platform would be like building an immensely long Berlin Wall that would splinter millions of relationships.
With those basic platforms intact, the three biggest threats that Google and Facebook pose to societies worldwide are barely affected by almost any intervention: the aggressive surveillance, the suppression of content, and the subtle manipulation of the thinking and behavior of more than 2.5 billion people.
Different tech companies pose different kinds of threats. I’m focused here on Google, which I’ve been studying for more than six years through both experimental research and monitoring projects. (Google is well aware of my work and not entirely happy with me. The company did not respond to requests for comment.) Google is especially worrisome because it has maintained an unopposed monopoly on search worldwide for nearly a decade. It controls 92 percent of search, with the next largest competitor, Microsoft’s Bing, drawing only 2.5%.
Fortunately, there is a simple way to end the company’s monopoly without breaking up its search engine, and that is to turn its “index”—the mammoth and ever-growing database it maintains of internet content—into a kind of public commons.
There is precedent for this both in law and in Google’s business practices. When private ownership of essential resources and services—water, electricity, telecommunications, and so on—no longer serves the public interest, governments often step in to control them. One particular government intervention is especially relevant to the Big Tech dilemma: the 1956 consent decree in the U.S. in which AT&T agreed to share all its patents with other companies free of charge. As tech investor Roger McNamee and others have pointed out, that sharing reverberated around the world, leading to a significant increase in technological competition and innovation.
Doesn’t Google already share its index with everyone in the world? Yes, but only for single searches. I’m talking about requiring Google to share its entire index with outside entities—businesses, nonprofit organizations, even individuals—through what programmers call an application programming interface, or API.
Google already allows this kind of sharing with a chosen few, most notably a small but ingenious company called Startpage, which is based in the Netherlands. In 2009, Google granted Startpage access to its index in return for fees generated by ads placed near Startpage search results.
With access to Google’s index—the most extensive in the world, by far—Startpage gives you great search results, but with a difference. Google tracks your searches and also monitors you in other ways, so it gives you personalized results. Startpage doesn’t track you—it respects and guarantees your privacy—so it gives you generic results. Some people like customized results; others treasure their privacy. (You might have heard of another privacy-oriented alternative to Google.com called DuckDuckGo, which aggregates information obtained from 400 other non-Google sources, including its own modest crawler.)
If entities worldwide were given unlimited access to Google’s index, dozens of Startpage variants would turn up within months; within a year or two, thousands of new search platforms might emerge, each with different strengths and weaknesses. Many would target niche audiences—some small, perhaps, like high-end shoppers, and some huge, like all the world’s women, and most of these platforms would do a better job of serving their constituencies than Google ever could.
These aren’t just alternatives to Google, they are competitors—thousands of search platforms, each with its special focus and emphasis, each drawing on different subsets of information from Google’s ever-expanding index, and each using different rules to decide how to organize the search results they display. Different platforms would likely have different business models, too, and business models that have never been tried before would quickly be tested.
This system replicates the competitive ecology we now have of both traditional and online media sources—newspapers, magazines, television channels, and so on—each drawing on roughly the same body of knowledge, serving niche audiences, and prioritizing information as it sees fit.
But what about those nasty filter bubbles that trap people in narrow worlds of information? Making Google’s index public doesn’t solve that problem, but it shrinks it to nonthreatening proportions. At the moment, it’s entirely up to Google to determine which bubble you’re in, which search suggestions you receive, and which search results appear at the top of the list; that’s the stuff of worldwide mind control. But with thousands of search platforms vying for your attention, the power is back in your hands. You pick your platform or platforms and shift to others when they draw your attention, as they will all be trying to do continuously.
If that happens, what becomes of Google? At first, not much. It should be allowed, I believe, to retain ownership and control of its index. That will assure it continues to do a great job maintaining and updating it. And even with competition looming, change will take time. Serious competitors will need months to gather resources and generate traffic. Eventually, though, Google will likely become a smaller, leaner, more diversified company, especially if some of the other proposals out there for taming Big Tech are eventually implemented. If, over time, Google wants to continue to spy on people through its search engine, it will have to work like hell to keep them. It will no longer be able to rest on its laurels, as it has for most of the past 20 years; it’s going to have to hustle, and we will all benefit from its energy.
My kids think Google was the world’s first search engine, but it was actually the 21st. I can remember when search was highly competitive—when Yahoo! was the big kid on the block and engines such as Ask Jeeves and Lycos were hot commodities. Founded in 1998 amid a crowded field of competitors, Google didn’t begin to dominate search until 2003, by which time it still handled only about a third of searches in the U.S. Search can be competitive again—this time with a massive, authoritative, rapidly expanding index available to all parties.
The alternative is frightening. If Google retains its monopoly on search, or even if a government steps in and makes Google a public utility, the obscene power to decide what information humanity can see and how that information should be ordered will remain in the hands of a single authority. Democracy will be an illusion, human autonomy will be compromised, and competition in search—with all the innovation that implies—might never emerge. With internet penetration increasing rapidly worldwide, do we really want a single player, no matter how benign it appears to be, to control the gateway to all information?
For the system I propose to work fairly and efficiently, we’ll need rules. Here are some obvious ones to think about:
Access. There might have to be limits on who can access the API. We might not want every high school hacker to be able to build his or her own search platform. On the other hand, imagine thousands of Mark Zuckerbergs battling each other to find better ways of organizing the world’s information.
Speed. Google must not be allowed to throttle access to its index, especially in ways that give it a performance advantage or that favor one search platform over another.
Content. To prevent Google from engineering humanity by being selective about what content it adds to its index, all parties with API access must be able to add content.
Visibility. For people using Google to seek information about other search platforms, Google must be forbidden from driving people to itself or its affiliated platforms.
Removal. Google must be prohibited from removing content from its index. The only exception will be when a web page no longer exists. An accurate, up-to-date record of such deletions must be accessible through the API.
Logging. Google must log all visits to its index, and that log must be accessible through the API.
Fees. Low-volume external platforms (think: high school hackers) should be able to access the index free of charge. High-volume users (think: Microsoft Corp.’s Bing) should pay Google nominal fees set by regulators. That gives Google another incentive for maintaining a superior index.
Can we really justify bludgeoning one of the world’s biggest and most successful companies? When governments have regulated, dismembered, or, in some cases, taken ownership of private water or electricity companies, they have done so to serve the public interest, even when the company in question has developed new technologies or resources at great expense. The rationale is straightforward: You may have built the pipelines, but water is a “common” resource that belongs to everyone, as David Bollier reminded us in his seminal book, Silent Theft: The Private Plunder of Our Common Wealth.
In Google’s case, it would be absurd for the company to claim ownership rights over the contents of its index for the simple reason that it copied virtually all those contents. Google scraped the content by roaming the internet, examining webpages, and copying both the address of a page and language used on that page. None of those websites or any external authority ever gave Google permission to do this copying.
Did any external authority give Google permission to demote a website in its search results or to remove a website from its index? No, which is why both individuals and even top business leaders are sometimes traumatized when Google demotes or delists a website.
But when Google’s index becomes public, people won’t care as much about its machinations. If conservatives think Google is messing with them, they’ll soon switch to other search platforms, where they’ll still get potentially excellent results. Given the possibility of a mass migration, Google will likely stop playing God, treating users and constituencies with new respect and humility.
Who will implement this plan? In the U.S., Congress, the Federal Trade Commission, and the Department of Justice all have the power to make this happen. Because Google is a global company with, at this writing, 16 data centers—eight in the U.S., one in Chile, five in the EU, one in Taiwan, and one in Singapore—countries outside the U.S. could also declare its index to be a public commons. The EU is a prime candidate for taking such action.
But there is another possibility—namely, that Google itself will step up. This isn’t as crazy as you might think. Likely prompted by the EU antitrust investigations, the company has quietly gone through two corporate reorganizations since 2015, and experts I’ve talked to in both the U.S. and the U.K. say the main effect of these reorganizations has been to distance Google’s major shareholders from any calamities that might befall the Google search engine. The company’s lawyers have also undoubtedly been taking a close look at the turbulent years during which Microsoft unsuccessfully fought U.S. antitrust investigators.
Google’s leaders have been preparing for an uncertain future in which the search engine might be made a public utility, fined into bankruptcy, frozen by court orders, or even seized by governments. It might be able to avoid ugly scenarios simply by posting the specs for its new public API and inviting people and companies around the world to compete with its search platform. Google could do this tomorrow—and generate glowing headlines worldwide. Google’s data analysts know how to run numbers better than anyone. If the models predict that the company will make more money, minimize risk, and optimize its brand in coming years by making its index public, Google will make this happen long before the roof caves in.





 p
p