The Biden administration is waiting for good behavior by the Taliban before it officially recognizes the Taliban as the official government in Afghanistan, that is while China already has.
FB: Chinese diplomats relegated Biden climate czar John Kerry to a Zoom conference the same day China joined Taliban leaders in a photo-op to pledge “friendly relations” with the terror group.
Kerry was denied face-to-face interactions with senior Chinese officials such as Foreign Minister Wang Yi and Vice Premier Han Zheng. China instead dispatched a junior-level climate official to meet with the former secretary of state in the city of Tianjin. Kerry’s bungled visit coincided with Beijing’s open-arms embrace of Taliban leadership at an in-person visit in Qatar, affirming China’s interest in furthering “friendly relations” to fill the vacuum in Afghanistan left by America’s withdrawal.
Kerry met separately with Yi and Zheng over Zoom. The Chinese officials reportedly bristled at Kerry’s suggestions to decouple climate change from other issues fraught with tensions between China and the United States, leaving no immediate results from the meetings. One expert told Voice of America the Taliban received a better welcome than Kerry. The Biden climate czar, however, said the meetings proved “very constructive and detailed,” but deferred to Secretary of State Antony Blinken and President Joe Biden to set a timetable for further talks with the Chinese.
The White House did not return a request for comment about their plans for future climate talks with Beijing. The State Department declined to comment.

FB: A Taliban spokesman on Tuesday announced the appointment of a terrorist on the FBI’s most-wanted list to a cabinet-level position in its new government.
Sirajuddin Haqqani, who is a senior leader in the al Qaeda-aligned Haqqani network of terror groups, will serve in the Taliban’s government as minister of the interior. He is wanted by federal authorities for his involvement in a 2008 bombing in Kabul that killed Thor Hesla, a U.S. citizen. The State Department is offering up to $5 million for information leading to Haqqani’s arrest.
Haqqani authored an op-ed in the New York Times in February 2020, which expressed the demands of the Taliban ahead of talks with U.S. officials in Qatar.
The Taliban leader said his organization would work to protect human rights for all Afghans and work toward “mutual respect” with foreign powers. The claims run counter to reports of atrocities the Taliban have committed against Afghans, many of whom assisted the United States during its 20-year war in Afghanistan.
Haqqani’s op-ed ran four months before a now-infamous New York Times editorial by Sen. Tom Cotton (R., Ark.) that argued federal forces should be deployed to quell violence and restore order in America’s cities during the summer’s riots. Whereas some employees said Cotton’s views put black journalists at the newspaper “in danger,” no Times employees said publishing a known terrorist’s words in their opinion pages put any subgroup of U.S. citizens at risk.
United Nations-sanctioned terrorist Mohammad Hasan Akhund will lead the newly installed Taliban government. A 2020 report from the United Nations Security Council said the Taliban’s senior council of 20 members—including Akhund—maintained close ties with al Qaeda during negotiations with the West.
***
JTN: The new interior minister is Sirajuddin Haqqani, who led the Haqqani network, has a $5 million bounty out on him by the FBI for being on their most-wanted list, and is believed to be still holding an American hostage, The Associated Press reported. The American, a civilian contractor named Mark Frerichs, has not been heard from since being abducted by the network in January 2020.
The Haqqani network, which controls much of eastern Afghanistan, has been blamed for coordinating kidnappings, often of Americans, and attacks in Kabul over the last 20 years.
Taliban spokesman Zabihullah Mujahid explained in announcing the cabinet that the appointments were temporary, but did not say how long they would last or what would be the reason for a change, according to the AP. The Taliban has not indicated that they plan on holding elections.
Mullah Hasan Akhund, the interim prime minister, led the Taliban government during the final years of its previous rule. One of his two deputies, Mullah Abdul Ghani Baradar, led talks with the U.S. and signed the deal leading to the withdrawal. The other deputy, Abdul Salam Hanafi, is a long-time Taliban member, the AP reported.
The new defense minister is Mullah Mohammad Yaqoob, who is the son of Taliban founder Mullah Mohammad Omar.
Amir Khan Muttaqi is the foreign minister, and was also a prominent figure from the Taliban’s last rule.
***
FNC: Four out of five Guantanamo detainees whom former President Barack Obama released in exchange for former U.S. Army Sgt. Bowe Bergdahl in 2014 now hold senior positions in the interim government created by the Taliban in Afghanistan.
Thomas Joscelyn, a senior fellow for the Foundation for Defense of Democracies (FDD), noted that Fazl will also return to his role as deputy defense minister. “U.S. officials found that Fazl worked with senior al Qaeda personnel, including Abdel Hadi al Iraqi, one of Osama bin Laden’s chief lieutenants,” Joscelyn wrote in a tweet. “Al Iraqi is still held at Guantanamo.”
Late last month, following the Taliban’s takeover of Afghanistan, the Taliban announced that Mohammad Nabi Omari, another former Guantanamo Bay Naval Base (GTMO) detainee with close ties to al Qaeda, would govern Khost Province.
In 2011, a Washington, D.C., district court judge found that Khairkhwa “was, without question, a senior member of the Taliban both before and after the US-led invasion of Afghanistan in October 2001.”
The court also denied Khairkhwa’s petition for a writ of habeas corpus, concluding that he “has repeatedly admitted that after the terrorist attacks of September 11, 2001, he served as a member of a Taliban envoy that met clandestinely with senior Iranian officials to discuss Iran’s offer to provide the Taliban with weapons and other military support in anticipation of imminent hostilities with US coalition forces.”
Sirajuddin Haqqani, the head of the militant group known as Haqqani Network, now serves as acting interior minister for the Taliban government. The U.S. has put a $10 million bounty on Haqqani’s head. Since 2016, Haqqani has served as one of two deputy leaders of the Taliban.
Nebraska GOP Sen. Ben Sasse released a statement on Tuesday regarding the Taliban’s formation of the government, insisting that the trust President Joe Biden and U.S. officials placed in the Taliban is “pathetic.”
“President Biden still clings to an insane fantasy that the Taliban is kinder and gentler,” Sasse said. “It’s nonsense. Haqqani is the Taliban’s new interior minister for precisely the same reason the FBI’s got a $5 million bounty on his head: he’s a bloodthirsty terrorist. He’s armed, dangerous, and running a country we just abandoned.”

 Taliban arrives in Pakistan to discuss more cooperation and the way forwarad.
Taliban arrives in Pakistan to discuss more cooperation and the way forwarad.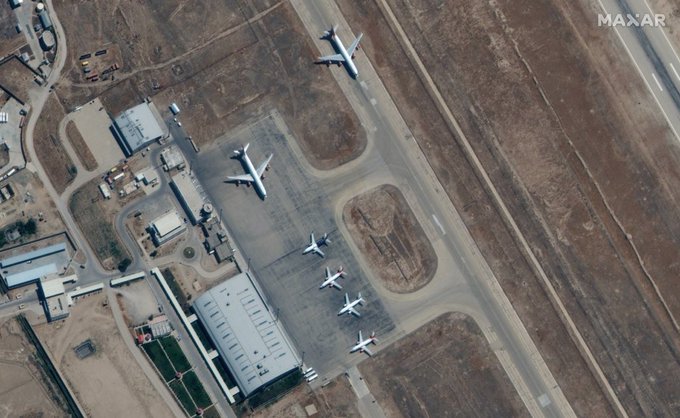
![Passengers disembark as they arrive from Kandahar, at Hamid Karzai International Airport in Kabul. [Wali Sabawoon/AP Photo]](https://www.aljazeera.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/09/AP21248376529092.jpg?resize=1170%2C780)



 Voice of America is taxpayer funded. And Radio Free Europe is United States government-funded organization that broadcasts and reports news, information, and analysis to countries in Eastern Europe, Central Asia, Caucasus, and the Middle East.
Voice of America is taxpayer funded. And Radio Free Europe is United States government-funded organization that broadcasts and reports news, information, and analysis to countries in Eastern Europe, Central Asia, Caucasus, and the Middle East.