A major fall of nitrogen dioxide in China since the outbreak of Covid-19.
Nitrogen dioxide is a nasty-smelling gas. Some nitrogen dioxide is formed naturally in the atmosphere by lightning and some is produced by plants, soil and water. However, only about 1% of the total amount of nitrogen dioxide found in our cities’ air is formed this way.
Nitrogen dioxide is an important air pollutant because it contributes to the formation of photochemical smog, which can have significant impacts on human health. The main effect of breathing in raised levels of nitrogen dioxide is the increased likelihood of respiratory problems. Nitrogen dioxide inflames the lining of the lungs, and it can reduce immunity to lung infections. This can cause problems such as wheezing, coughing, colds, flu and bronchitis.
***
United States intelligence agencies are using “a wide range” of tools, ranging from open-source collection to communications interception and human intelligence, to collect desperately needed data about the spread of the coronavirus, according to sources. As of late last week, some of the most dependable data on the spread of the virus, known as COVID-19, came from military channels of information, according to Yahoo News’ National Security and Investigations Reporter Jenna McLaughlin.
Writing last Friday, McLaughlin cited “two sources familiar with the matter”, who said that the Office of the Director of National Intelligence and the Central Intelligence Agency’s Global Issues Mission Center were collecting and analyzing real-time data on the coronavirus. The spread of the disease was also being monitored by the National Center for Medical Intelligence, which assesses the impact of disease outbreaks on American and foreign military personnel, said McLaughlin. She added that the intelligence generated by these agencies was being channeled to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the Department of Health and Human Services, which lead the White House’s Task Force on COVID-19.
A major concern of the US Intelligence Community is that the Chinese, Iranian and other governments around the world may not be sharing comprehensive data on the spread of the virus and its impact. “No data means spying”, one unnamed source told McLaughlin. According to Reuters’ Mark Hosenball, US intelligence agencies have been using “a wide range of intelligence tools”, including human intelligence and electronic communications interception to track the spread of COVID-19. A major question that US intelligence agencies are trying to answer is whether governments like China’s or Iran’s have effective “continuity operations” plans in place, which relate to preserving the main functions of government during a major national disaster.
According to Hosenball, there is pessimism among US intelligence experts about the ability of developing countries around the world to respond to a massive COVID-19 outbreak. One example is India, whose dense population and rudimentary public-health infrastructure raises serious concerns about the government’s ability to protect the country’s population from a major pandemic. The report adds that there “deep concern” in US government circles about the possibility that Iran may be covering up the details about the spread of COVID-19.
***
The coronavirus is coinciding with “significant decreases” in nitrogen dioxide over China, according to NASA, as authorities there continue to place more people under quarantines and some businesses remain closed amid the outbreak.
Pollution monitoring satellites operated by NASA and the European Space Agency (ESA) detected the decreases over a two-month span, according to a news release. The drops coincided with the outbreak and the Lunar New Year, which was unusually tame because many decided to stay indoors rather than risk becoming infected.
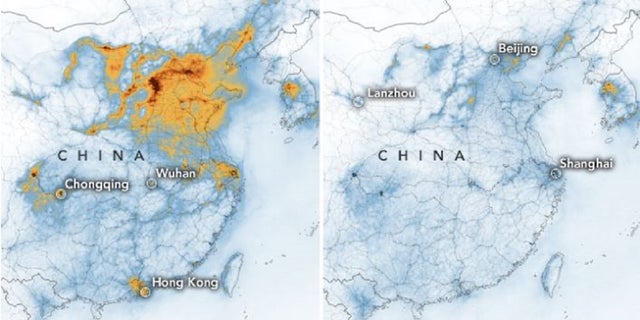
In January, Chinese authorities locked down several cities and shut down all transportation going into and out of the city of Wuhan, the epicenter of the outbreak.
The pollution reduction is shown in two maps released by the space agencies. The first shows large concentrations of nitrogen dioxide levels over Beijing and near Wuhan from Jan. 1 through 20, before mandated quarantines were issued. More here.