Now, exactly why would a U.S. delegation visit the Wuhan laboratory in the first place and be granted permission to do so?
Experts in the field of virology have been collaborating on research related to viruses in China for years. This includes government health officials, university research/medical schools as well as scientists and laboratory technicians. Last month, I published an article about the collaboration between various health/virus experts and the P4 laboratory in question located in Wuhan, using Duke NUS Medical School as but one example.
But, there is another reason for U.S. access and that is the U.S, government gave a sizeable grant to the Wuhan laboratory at the center of the pandemic. Yes, a mere $3.7 MILLION. Likely, the most experienced scientist at this facility is Shi Zhengli. She is honest, candid and desperate. She gladly works with organizations outside of China and even asked for more U.S. help with security measures and control of the facility.
The Chinese laboratory at the center of scrutiny over a potential coronavirus leak has been using U.S. government money to carry out research on bats from the caves which scientists believe are the original source of the deadly outbreak.
The Wuhan Institute of Virology undertook coronavirus experiments on mammals captured more than 1,000 miles away in Yunnan which were funded by a $3.7 million grant from the US government.
Sequencing of the COVID-19 genome has traced it back to bats found in Yunnan caves but it was first thought to have transferred to humans at an animal market in Wuhan.
The revelation that the Wuhan Institute was experimenting on bats from the area already known to be the source of COVID-19 – and doing so with American money – has sparked further fears that the lab, and not the market, is the original outbreak source.
Lawmakers and pressure groups were quick to hit out at U.S. funding being provided for the ‘dangerous and cruel animal experiments at the Wuhan Institute’.
US Congressman Matt Gaetz said: ‘I’m disgusted to learn that for years the US government has been funding dangerous and cruel animal experiments at the Wuhan Institute, which may have contributed to the global spread of coronavirus, and research at other labs in China that have virtually no oversight from US authorities.’
On Saturday, Anthony Bellotti, president of the US pressure group White Coat Waste, condemned his government for spending tax dollars in China, adding: ‘Animals infected with viruses or otherwise sickened and abused in Chinese labs reportedly may be sold to wet markets for consumption once experiments are done.’
The $37million Wuhan Institute of Virology, the most advanced laboratory of its type on the Chinese mainland, is based twenty miles from the now infamous wildlife market that was thought to be the location of the original transfer of the virus from animals to humans.
According to documents obtained by The Mail on Sunday, scientists there experimented on bats as part of a project funded by the US National Institutes of Health, which continues to licence the Wuhan laboratory to receive American money for experiments.
The NIH is the primary agency of the United States government responsible for biomedical and public health research.
The Wuhan Institute lists them on their website as a partner as well as several other American academic institutions.
Other U.S. partners include the University of Alabama, the University of North Texas, Harvard University, and the National Wildlife Federation.
As part of the NIH research at the institute, scientists grew a coronavirus in a lab and injected it into three-day-old piglets.
The news that COVID-19 bats were under research there means that a leak from the Wuhan laboratory can no longer be completely ruled out.
According to one unverified claim, scientists at the institute could have become infected after being sprayed with blood containing the virus, and then passed it on to the local community.
A second institute in the city, the Wuhan Centre for Disease Control – which is barely three miles from the market – is also believed to have carried out experiments on animals such as bats to examine the transmission of coronaviruses.
The Wuhan Institute, which keeps more than 1,500 strains of deadly viruses, specializes in the research of ‘the most dangerous pathogens’, in particular the viruses carried by bats.
Chinese officials decided to build the institute after the country was ravaged by an outbreak of SARS in 2002 and 2003.
SARS, another kind of coronavirus, killed 775 people and infected more than 8,000 globally in an epidemic.
Since an outbreak of the novel coronavirus emerged in the city in December, it has been at the center of conspiracy theories which suggest that the bug originated there.
While scientists believe that the virus jumped to humans from wild animals sold as food in a market in Wuhan, conspiracy theorists promote different assumptions.
Some of them claim that the virus, formally known as SARS-CoV-2, could be a biological warfare weapon engineered there. Others suspect that it escaped from the lab.
China has repeatedly denied the allegations.
Shi Zhengli, a deputy director of the institute, told the press in February that she ‘guaranteed with her own life’ that the outbreak was not related to the lab.
She admits that when summoned back from a conference to investigate the new disease, she wondered at first if a coronavirus could have escaped from her unit.
She has warned about the danger of epidemics from bat-borne viruses.
But she says she did not expect such an outbreak in Wuhan, in the center of China, since her studies suggested subtropical areas in the south had the highest risk of such ‘zoonotic’ transmission to humans.
Shi told the respected science journal Scientific American last month of her relief when, having checked back through disposal records, none of the genome sequences matched their virus samples.
‘That really took a load off my mind. I had not slept a wink for days,’ she said.
Many international experts have also dismissed such theories.
Dr Keusch, Professor of Medicine and International Health at Boston University’s Schools of Medicine and Public Health, stressed that no release of viruses from a high-level lab, such as the one in Wuhan, ‘has ever happened’.
He defended his peers in the Chinese city as he said: ‘The Wuhan lab is designed to the highest standards with redundant safety systems and the highest level of training.
‘Many of its research faculty trained at a similar laboratory in Galveston, Texas. So we know the Wuhan team is as qualified as the Texas group…
‘This means the assertion of a leak, rather than being highly likely, instead is highly unlikely.’
Last week, further doubt was cast on the animal market theory, however, after Cao Bin, a doctor at the Wuhan Jinyintan Hospital, highlighted research showing that 13 of the first 41 patients diagnosed with the infection had not had any contact with the market.
‘It seems clear that the seafood market is not the only origin of the virus,’ he said.
American biosecurity expert Professor Richard Ebright, of Rutgers University’s Waksman Institute of Microbiology, New Jersey, said that while the evidence suggests COVID-19 was not created in one of the Wuhan laboratories, it could easily have escaped from there while it was being analyzed.
Prof Ebright said he has seen evidence that scientists at the Centre for Disease Control and the Institute of Virology studied the viruses with only ‘level 2’ security – rather than the recommended level 4 – which ‘provides only minimal protections against infection of lab workers’.
He added: ‘Virus collection, culture, isolation, or animal infection would pose a substantial risk of infection of a lab worker, and from the lab worker then the public.’
He concluded that the evidence left ‘a basis to rule out [that coronavirus is] a lab construct, but no basis to rule out a lab accident’.
Results of the U.S-funded research at the Wuhan Institute were published in November 2017 under the heading: ‘Discovery of a rich gene pool of bat SARS-related coronaviruses provides new insights into the origin of SARS coronavirus.’
The exercise was summarized as: ‘Bats in a cave in Yunnan, China were captured and sampled for coronaviruses used for lab experiments.
‘All sampling procedures were performed by veterinarians with approval from the Animal Ethics Committee of the Wuhan Institute of Virology.
‘Bat samplings were conducted ten times from April 2011 to October 2015 at different seasons in their natural habitat at a single location (cave) in Kunming, Yunnan Province, China. Bats were trapped and faecal swab samples were collected.’
Another study, published in April 2018, was titled ‘fatal swine acute diarrhoea syndrome caused by an HKU2-related coronavirus of bat origin’ and described the research as such: ‘Following a 2016 bat-related coronavirus outbreak on Chinese pig farms, bats were captured in a cave and samples were taken.
Experimenters grew the virus in a lab and injected it into three-day-old piglets.
Intestinal samples from sick piglets were ground up and fed to other piglets as well.
The coronavirus pandemic has killed more than 108,000 people and infected over 1.7 million worldwide.’
On Saturday, the American outbreak became the deadliest in the world over 2,000 deaths in a day.
The national deaths toll is 20,087 and there are 522,643 confirmed cases as of Saturday evening.
China muzzled its Bat Woman: Beijing authorities hushed up the findings of a scientist who unlocked the genetic make-up of the coronavirus within days of the outbreak – which is vital for tests and vaccines
A Chinese scientist who is the one of the world’s leading experts on coronaviruses was ‘muzzled’ after unraveling the genetic composition of the new disease, which is crucial for developing diagnostic tests and vaccines.
The revelation will fuel fresh concerns over China‘s cover-up of the pandemic after it erupted in the city of Wuhan. Critics argue that Communist Party chiefs frustrated efforts to contain the outbreak before it exploded around the world.
At the centre of the new claims is Shi Zhengli, known as China’s ‘Bat Woman’ after years spent on difficult virus-hunting expeditions in dank caves that have led to a series of important scientific discoveries.
The virologist was called back to her highsecurity laboratory in Wuhan at the end of last year after a mysterious new respiratory condition in the city was identified as a novel coronavirus – and within three days she completed its gene sequencing.
Her team’s work, and several other breakthroughs in subsequent days, indicated the virus was linked to horseshoe bats found more than 1,000 miles away in Yunnan, a region of southern China.
Their findings showed it was similar to SARS, a respiratory disease that sparked an epidemic in 33 countries after emerging from China in 2002.
Gao Yu, a Chinese journalist freed last week after 76 days of lockdown in Wuhan, said he spoke to Shi during his incarceration and revealed: ‘We learned later her institute finished gene-sequencing and related tests as early as January 2 but was muzzled.’
The Mail on Sunday has learned that on that same day, Yanyi Wang, director of the Wuhan Institute of Virology, sent an email to staff and key officials ordering them not to disclose information on the disease.
She warned, according to a leak on social media confirmed by activists and Hong Kong media, that ‘inappropriate and inaccurate information’was causing ‘general panic’ – thought to refer to eight whistle-blowing doctors whose warnings to local citizens had led to their arrest.
Wang said the National Health Commission ‘unequivocally requires that any tests, clinical data, test results, conclusions related to the epidemic shall not be posted on social media platforms, nor shall [it] be disclosed to any media outlets including government official media, nor shall [it] be disclosed to partner institutions.’
Eight days later, a team led by a professor in Shanghai who received samples from an infected patient, published a genome sequence on an open access platform.
His laboratory was closed for ‘rectification’ two days later.
At the time, the public was being told that no new cases had been reported in Wuhan for more than a week and there was no clear evidence of human transmission, although dozens of health workers were starting to fall ill with the disease.
In an online lecture last month, Shi Zhengli said her team found on January 14 that the new virus could infect people – six days before this fact was revealed by China.
On the same day, the World Health Organisation issued a tweet backing China’s denials of human transmissions.
Shi’s team released its data identifying the disease on January 23 on a scientific portal before publication the next month by the journal Nature.
It said the genomic sequence was 96 per cent identical to another virus they found in horseshoe bats in Yunnan.
Shi is a specialist in emerging diseases and has earned global acclaim for work investigating links between bats and coronaviruses, aided by expeditions to collect samples and swabs in the fetid cave networks of southern China.
She was a key part of the team that traced SARS to horseshoe bats through civets, a cat-like creature often eaten in China.
Hat tip –> By Frances Mulraney and Glenn Owen For The Mail On Sunday
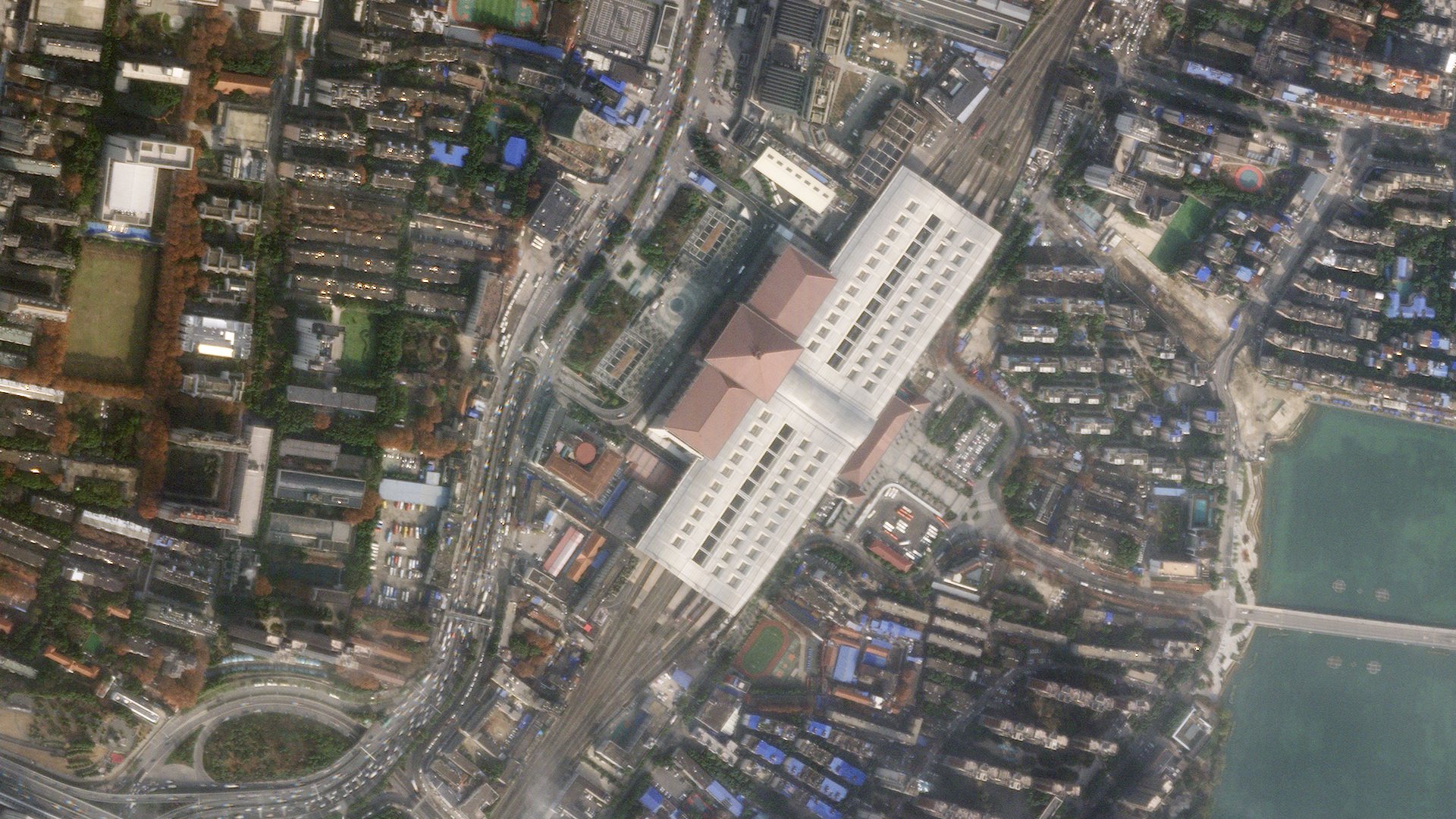
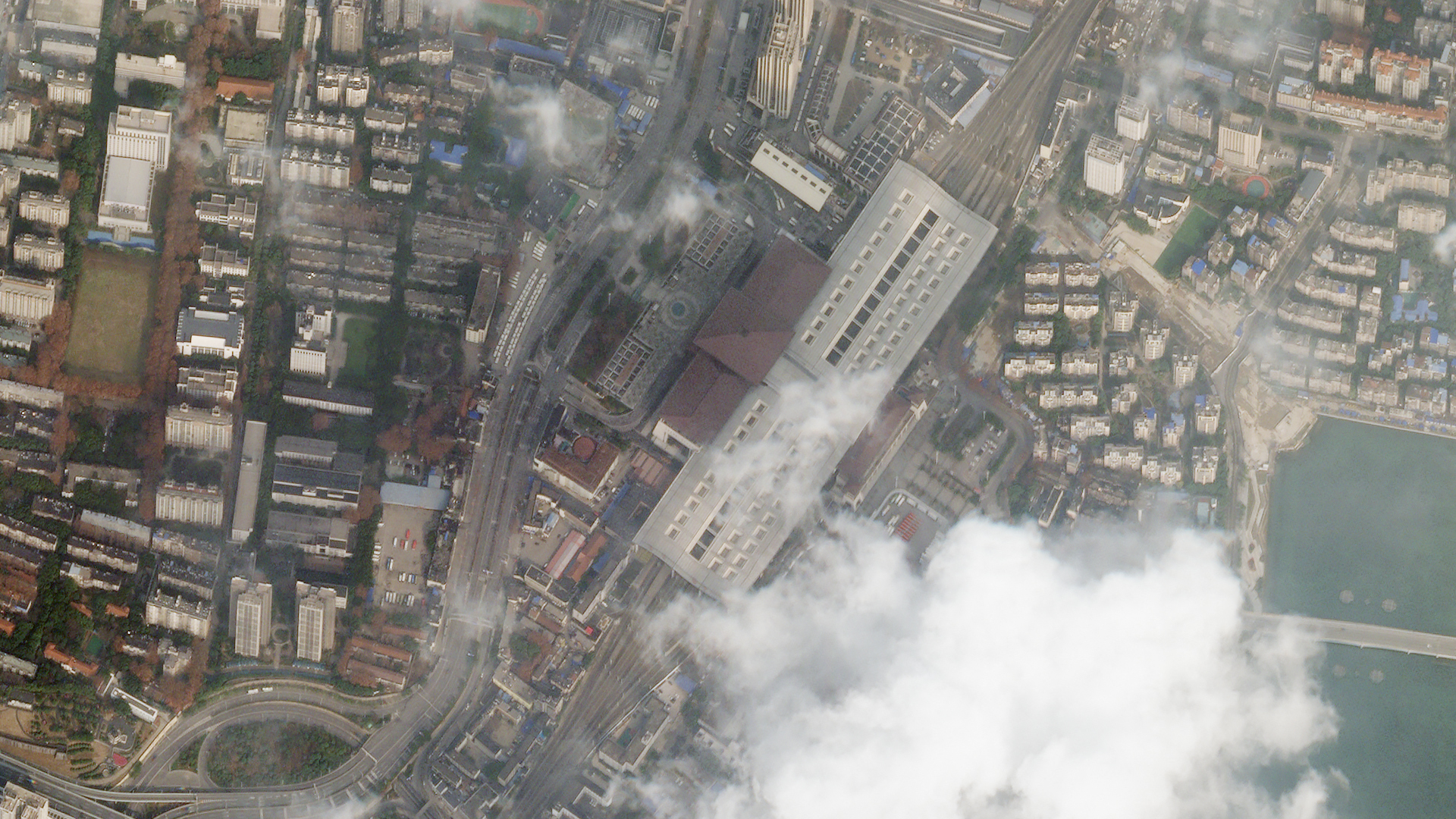



 Photo Credits: Top photo Before The Wuhan Train Station surrounded by an enormous amount of traffic on the roads. Bottom photo After Traffic around the station evaporated following the quarantine. Trains have not been running since its implementation on January 22. PLANET LABS
Photo Credits: Top photo Before The Wuhan Train Station surrounded by an enormous amount of traffic on the roads. Bottom photo After Traffic around the station evaporated following the quarantine. Trains have not been running since its implementation on January 22. PLANET LABS

