Apparently, they do work and have some significant value, in Europe that is. With the constant flow of migrants, several major problems have literally cracked the security of countries. Further, there are no signs that migrants flowing into Europe will wane or stop at all, so the true costs in 2016 or beyond. The immigration flood in Europe is a clarion call to the United States as the issues are virtually the same. Not only is the United States taking in Middle Eastern refugees, but we have been taking in Cubans, Mexicans, as well as Central and South Americans. For America is goes much further that a trifecta and costs and security.
Anti-migrant force builds in Europe, hurting Merkel’s quest
WARSAW, Poland (AP) — So where should the next impenetrable razor-wire border fence in Europe be built?
Hungary’s right-wing Prime Minister Viktor Orban thinks he knows the best place – on Macedonia’s and Bulgaria’s borders with Greece – smack along the main immigration route from the Middle East to Western Europe. He says it’s necessary because “Greece can’t defend Europe from the south” against the large numbers of Muslim refugees pouring in, mainly from Syria and Iraq.
The plan is especially controversial because it effectively means eliminating Greece from the Schengen zone, Europe’s 26-nation passport-free travel region that is considered one of the European Union’s most cherished achievements.
Orban’s plan will feature prominently Monday at a meeting in Prague of leaders from four nations in an informal gathering known as the Visegrad group: Hungary, Poland, the Czech Republic and Slovakia. The Visegrad group, formed 25 years ago to further the nations’ European integration, is marking that anniversary Monday. Still, it has only recently found a common purpose in its unified opposition to accepting any significant number of migrants.
This determination has emboldened the group, one of the new mini-blocs emerging lately in Europe due to the continent’s chaotic, inadequate response to its largest migration crisis since World War II. The Visegrad group is also becoming a force that threatens the plans of German Chancellor Angela Merkel, who wants to resettle newcomers across the continent while also slowing down the influx.
“The plan to build a new “European defense line” along the border of Bulgaria and Macedonia with Greece is a major foreign policy initiative for the Visegrad Four and an attempt to re-establish itself as a notable political force within the EU,” said Vit Dostal, an analyst with the Association for International Affairs, a Prague based think tank.
At Monday’s meeting, leaders from the four nations will be joined by Macedonian President Gjorge Ivanov and Bulgarian Prime Minister Boiko Borisov so they can push for the reinforcements along Greece’s northern border. Macedonia began putting up a first fence in November, and is now constructing a second, parallel, fence.
“If it were up only to us Central Europeans, that region would have been closed off long ago,” Orban said at a press conference recently with Poland’s prime minister. “Not for the first time in history we see that Europe is defenseless from the south … that is where we must ensure the safety of the continent.”
Poland has indicated a willingness to send dozens of police to Macedonia to secure the border, something to be decided at Monday’s meeting.
“If the EU is not active, the Visegrad Four have to be,” Slovak Prime Minister Robert Fico said recently. “We have to find effective ways of protecting the border.”
The leaders will try to hash out a unified position ahead of an important EU meeting Thursday and Friday in Brussels that will take up both migration and Britain’s efforts to renegotiate a looser union with the EU. The Visegrad countries have also recently united against British attempts to limit the welfare rights of European workers, something that would affect the hundreds of thousands of their citizens who now live and work in Britain.
The anti-migrant message resonates with the ex-communist EU member states, countries that have benefited greatly from EU subsidies and freedom of movement for their own citizens but which now balk at requests to accept even small numbers of refugees. The Visegrad nations maintain it is impossible to integrate Muslims into their societies, often describing them as security threats. So far the Poles, Czechs and Slovaks have only accepted small numbers, primarily Christians from Syria.
Many officials in the West are frustrated with what they see as xenophobia and hypocrisy, given that huge numbers of Poles, Hungarians and other Eastern Europeans have received refuge and economic opportunity in the West for decades.
Indeed there are plenty of signs that the countries are squandering a lot of the good will that they once enjoyed in the West for their sacrifices in throwing off communism and establishing democracies.
Orban’s ambitions for Europe got a big boost with the rise to power last year in Poland of the right-wing Law and Justice party, which is deeply anti-migrant and sees greater regional cooperation as one of its foreign policy priorities. Polish Prime Minister Beata Szydlo’s government says it wants to do more to help Syrian refugees at camps in Turkey and elsewhere while blocking their entry into Europe.
Although Orban is alienating Greek authorities, who are staggering under the sheer numbers of asylum-seekers crossing the sea from Turkey in smugglers’ boars, he insists he must act as a counterweight to Western leaders, whom he accuses of creating the crisis with their welcoming attitude to refugees.
“The very serious phenomenon endangering the security of everyday life which we call migration did not break into Western Europe violently,” he said. “The doors were opened. And what is more, in certain periods, they deliberately invited and even transported these people into Western Europe without control, filtering or security screening.”
Dariusz Kalan, an analyst at the Polish Institute of International Affairs, said he doesn’t believe that the Visegrad group on its own can destroy European unity but says Orban’s vision is winning adherents across the continent in far-right movements and even among mainstream political parties.
“It’s hard to ignore Orban,” Kalan said. “People in Western Europe are starting to adopt the language of Orban. None are equally tough and yet the language is still quite similar.”

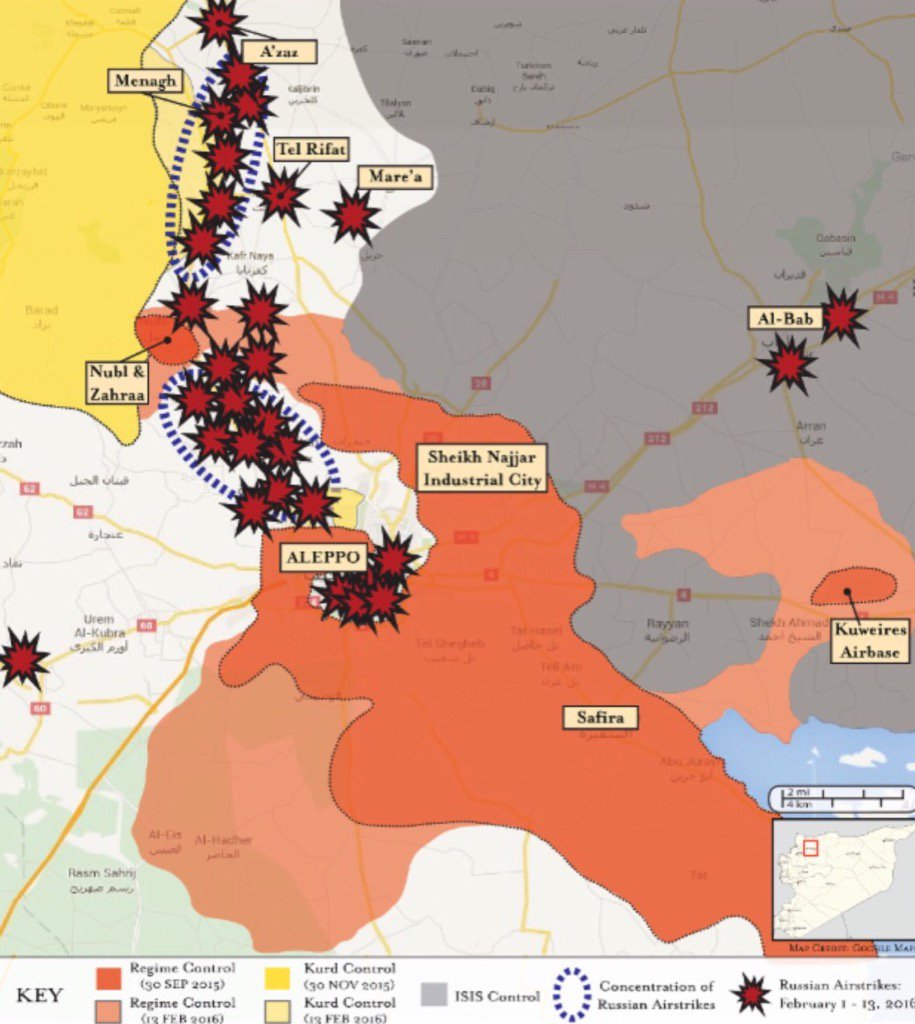 Russian airstrikes in areas around Aleppo.
Russian airstrikes in areas around Aleppo.
