And you can bet that the Obama White House and the John Kerry State Department knew all of this when they concocted the JCPOA, the nuclear deal, which by way almost now seems like America reimbursed Iran for the financial support of al Qaeda. (that was $1.7 billion in all cash in addition to $400 million)
Anyway…this is some great news if you want to know more about Usama bin Ladin and the al Qaeda network which still exists today.
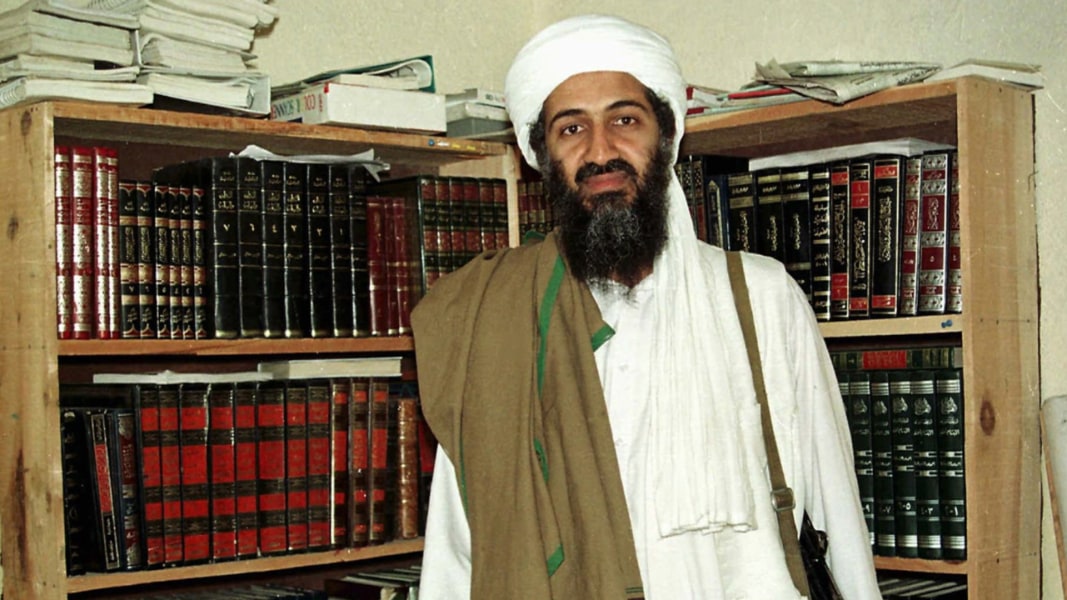
TLWJ: The CIA is releasing hundreds of thousands of documents, images, and computer files recovered during the May 2011 raid on Osama bin Laden’s compound in Abbottabad, Pakistan. The newly-available material provides invaluable insights into the terrorist organization that struck America on September 11, 2001.
FDD’s Long War Journal has advocated for the release of bin Laden’s secret cache since 2011, arguing that such transparency would help to better inform the American people, experts and policymakers. Today’s release goes a long way toward satisfying that goal. We applaud the CIA and Director Mike Pompeo for making this material available to the public.
While the world has changed dramatically since the al Qaeda founder’s death more than six years ago, many of the files are still relevant today. Indeed, the CIA has withheld an unspecified number of documents for reasons related to protecting national security. We don’t doubt that some documents are still sensitive, but we hope that everything can be eventually released.
The CIA provided FDD’s Long War Journal with an advance copy of many of the files. It will take years for experts and researchers to comb through this treasure trove of information. However, we offer some preliminary observations below.
Al Qaeda has survived more than sixteen years of war. The group has failed to execute another 9/11-style attack inside the US, despite bin Laden’s continued desire to bring mass terror to America’s shores. Numerous plots have been thwarted by counterterrorism and intelligence professionals. And bin Laden’s organization has suffered setbacks, including the loss of key leaders.
But al Qaeda has adapted and in some ways grown, spreading its insurgency footprint in countries where it had little to no capacity for operations in 2001. The newly-released files help to explain how al Qaeda groomed supporters everywhere from West Africa to South Asia.
With that perspective in mind, here is some of what we’ve already learned from the files posted online today.
The world can see Hamza bin Laden’s face, as a young man, for the first time.
Since 2015, al Qaeda has released a string of audio messages from Osama bin Laden’s son, Hamza. Al Qaeda is clearly attempting to capitalize on the bin Laden brand name and build Hamza’s profile in jihadi circles. Yet, the organization has refused to release current images of Hamza, likely fearing that this would increase the threats to his safety. On the most recent anniversary of the Sept. 11 attacks, for example, al Qaeda produced an image of the World Trade Center with a stock photo of Hamza as a young boy superimposed on one of the towers.
Two newly-released videos show scenes from Hamza’s wedding, publicly revealing his face as a young adult for the first time. The images are not current, but they are much more recent than the photo al Qaeda is willing to distribute. That same video footage shows other senior al Qaeda figures, including Mohammed Islambouli, the brother of Anwar Sadat’s assassin. Islambouli lived in Iran for much of the post-9/11 period and, in more recent times, has been in Turkey.
The public can finally examine Osama bin Laden’s personal journal.
One of the newly-available files is a handwritten, 228-page journal kept by Osama bin Laden himself. The notebook contains the al Qaeda master’s private reflections on the world and al Qaeda’s place in it. Some of the pages contain bin Laden’s thoughts on the 2011 Arab uprisings, which bin Laden wanted his men to capitalize on. While al Qaeda did not predict the revolutions that swept through North Africa and the Middle East, it moved quickly to set up operations in countries such as Libya.
Bin Laden was in charge of al Qaeda’s global network.
The Abbottabad repository confirms that bin Laden was anything but retired when US forces knocked down his door. He was not a mere figurehead. During the final months of his life, Osama bin Laden was communicating with subordinates around the globe. Recovered memos discuss the various committees and lieutenants who helped bin Laden manage his sprawling empire of terror.
In fact, al Qaeda’s network was a great deal more cohesive than was widely suspected in May 2011. Groups such as Al Qaeda in the Arabian Peninsula (AQAP), Al Qaeda in the Islamic Maghreb (AQIM), and Shabaab (in Somalia) regularly sought and received the al Qaeda master’s direction. Other organizations, such as the Pakistani Taliban, are featured throughout the documents as well. And al Qaeda continued to maintain a significant footprint inside Afghanistan, relocating personnel to the country in 2010 and fighting alongside the Taliban.
Bin Laden wasn’t always pleased with the course his subordinates pursued and his men debated a variety of matters internally. The al Qaeda master sometimes instructed his followers to hide their allegiance to him, calculating that it would cause additional problems if their fealty was acknowledged. The al Qaeda founder also viewed the world through a conspiratorial lens, often misjudging his main adversary: America.
However, bin Laden kept up with current events and studied America’s approach to the wars in Afghanistan and Iraq. One of his minions even translated sections of Bob Woodward’s 2010 book, Obama’s Wars, so that he could understand the Obama administration’s strategy for those conflicts.
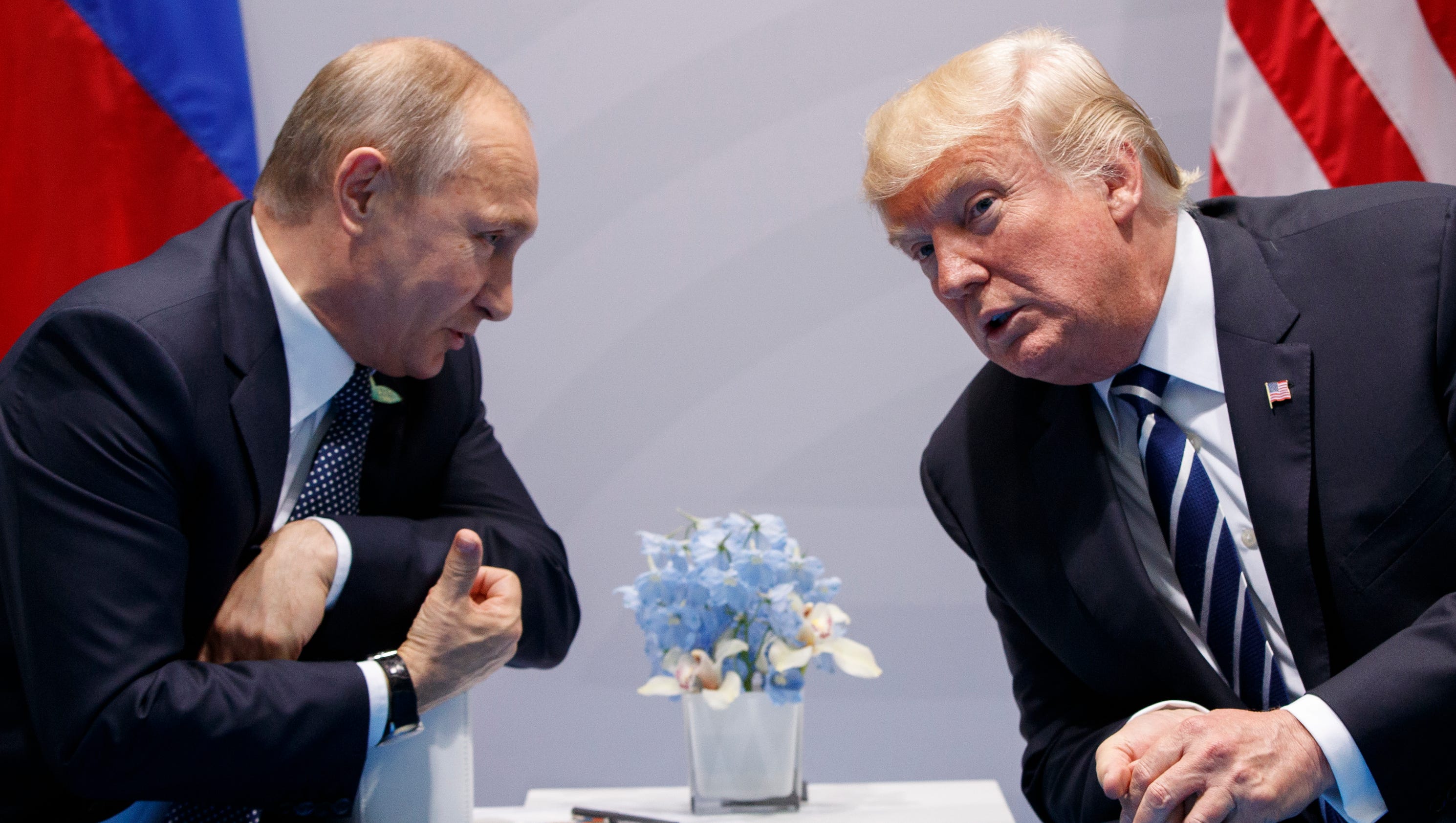
The files provide new details concerning al Qaeda’s relationship with Iran.
One never-before-seen 19-page document contains a senior jihadist’s assessment of the group’s relationship with Iran. The author explains that Iran offered some “Saudi brothers” in al Qaeda “everything they needed,” including “money, arms” and “training in Hezbollah camps in Lebanon, in exchange for striking American interests in Saudi Arabia and the Gulf.” Iranian intelligence facilitated the travel of some operatives with visas, while sheltering others. Abu Hafs al-Mauritani, an influential ideologue prior to 9/11, helped negotiate a safe haven for his jihadi comrades inside Iran. But the author of the file, who is clearly well-connected, indicates that al Qaeda’s men violated the terms of the agreement and Iran eventually cracked down on the Sunni jihadists’ network, detaining some personnel. Still, the author explains that al Qaeda is not at war with Iran and some of their “interests intersect,” especially when it comes to being an “enemy of America.”
Bin Laden’s files show the two sides have had heated disagreements. There has been hostility between the two. Al Qaeda even penned a letter to Ayatollah Khamenei demanding the release of family members held in Iranian custody. Other files show that al Qaeda kidnapped an Iranian diplomat to exchange for its men and women. Bin Laden himself considered plans to counter Iran’s influence throughout the Middle East, which he viewed as pernicious.
However, bin Laden urged caution when it came to threatening Iran. In a previously released letter, bin Laden described Iran as al Qaeda’s “main artery for funds, personnel, and communication.” And despite their differences, Iran continued to provide crucial support for al Qaeda’s operations.
In a series of designations and other official statements issued since July 2011, the US Treasury and State Departments have repeatedly targeted al Qaeda’s “core facilitation pipeline” inside Iran. Sources familiar with the intelligence used to justify those designations say they are based, in part, on the Abbottabad files. It is likely that still more revelations concerning al Qaeda’s relationship with Iran remain to be found in the cache made available today.
The files are vital for understanding the history of the Iraqi insurgency and al Qaeda’s role in it.
Since bin Laden’s death, Abu Bakr al Baghdadi’s Islamic State (ISIS) rose to prominence, becoming an international menace in its own right and al Qaeda’s main jihadi competitor. FDD’s Long War Journal has reviewed dozens of audio files and other documents pertaining to the Iraqi insurgency. This valuable, primary source material provides new details on the history of al Qaeda’s efforts in the Iraq, ranging from Abu Musab al Zarqawi’s earliest days inside the country before the war, to the creation of the Islamic State of Iraq (ISI) and Baghdadi’s appointment as its chief.
One newly-available audio file contains a biography for Zarqawi, placing him in Baghdad before the American-led invasion and tracing his travels to Iran, Syria and elsewhere. Other audio files summarize al Qaeda’s opinions of various Saudi sheikhs, some of whom supported the jihadis’ efforts in Iraq.
An assessment of bin Laden’s support network in Pakistan will require careful analysis.
Many people will be interested in what the files have to say about bin Laden’s network inside Pakistan. He was, of course, hunted down in Abbottabad, near a Pakistani military academy. It is likely that the files contain new details concerning the personalities in Pakistan who supported al Qaeda in one way or another, including jihadists sponsored by the state. Parts of the Pakistani military and intelligence establishment have opposed al Qaeda and helped capture senior operatives. Al Qaeda has also helped direct an insurgency against Pakistani forces in the northern part of the country. Some of the files decry Pakistan’s supposed betrayal of the mujahideen after 9/11.
But Pakistan is a complex country, with multiple competing factions, and it is widely suspected that some in the military and intelligence apparatus were complicit in bin Laden’s operations. There may never be a “smoking gun,” but a meticulous review of the documents will likely shed light on previously unknown aspects of bin Laden’s Pakistani-based network. Specifically, any “former” military and intelligence figures named in the files should be closely examined, as should jihadi personalities who have cozy relations with the state. For instance, the New York Times first reported that American officials found contacts between bin Laden’s most trusted courier and Harakat ul Mujahedin (HUM). The contacts were discovered on the courier’s cellphone, which was seized during the Abbottabad raid. FDD’s Long War Journal does not know if this information is included in today’s release, but similar data can be used to build a composite picture of bin Laden’s Pakistani supporters.
The US service members who raided bin Laden’s compound risked their lives to bring the terror master to justice and did an incredible service by seizing the files released today. They did not have the time to recover everything. Pakistani authorities reportedly scooped up the intelligence left behind. We do not know if any of those files were shared with American officials, or if some of them are included in today’s release. But we hope that material will come to light as well.
Today’s release creates a unique opportunity for experts, researchers and journalists to garner a better understanding of al Qaeda.