By now we all know the fact that Amazon Web Services canceled Parler and Parler remains dark until the judge decides on the case. We are also learning that other tech companies are cancelling people en masse for violations of terms of service which is selectively applied. Not only are large corporations like Citibank, Blue Cross, Marriott and JP Morgan in the cancel mix but there are others including well known universities like Harvard. How about American Express, Dow, AT&T, Comcast, Disney, 3M, Bank of America, GoDaddy, Hilton, Microsoft, Target, UPS, Tyson and Ford? This is because of few Republicans think independently and ask hard questions. Frankly this is called dissent and oddly enough, even those jurists on the Supreme Court write dissenting opinions. Yeesh.
This is another dimension to cyber war.
Exactly what dissent is not welcomed in the public square? As the cancel-culture manifests, there is no end just yet.
So, now we add Mail Chimp and Loews Hotels to the mix. Loews Hotels just canceled Senator Hawley’s (R-MO) fundraising event in Orlando. As for Mail Chimp, they canceled Virginia Citizens Defense League and changed their terms of service.
Mailchimp, a US based marketing automation service, has updated its Terms of Use regarding types of content that are prohibited for distribution on the platform. In particular, the service now “does not allow the distribution of content that is, in our sole discretion, materially false, inaccurate, or misleading, in a way that could deceive or confuse others about important events, topics, or circumstances.”
You have to wonder what BigTech is really fact-checking and just what some members of Congress really know for fact. The election scandal is not so much about Dominion as it really could be about SmartMatic. So, let’s examine a few things shall we?
Latest SMARTMATIC INTERNATIONAL CORPORATION Patents:
- Enhanced technology of touch-sensitive input peripherals for voter data entry in electronic voting systems
- MEANS TO CREATE A PHYSICAL AUDIT TRAIL VERIFIABLE BY REMOTE VOTERS IN ELECTRONIC ELECTIONS
- Systems, methods, and programs for voter information initialization and consolidation
- ENHANCED TECHNOLOGY OF TOUCH-SENSITIVE INPUT PERIPHERALS FOR VOTER DATA ENTRY IN ELECTRONIC VOTING SYSTEMS
- Paradigm for hybrid network communications protocol morphing
In 2013, there was an interesting lawsuit. In part:
There are two sets of defendants. The first set includes: Dominion Voting Systems International Corporation, a Barbados corporation; Dominion Voting Systems, Inc., a Delaware corporation; and Dominion Voting Systems Corporation, a Canadian corporation(collectively, ―Dominion‖or ―Defendants‖). The remaining defendant, Iron Mountain Intellectual Property Management, Inc.,a Delaware corporation,did not brief the motion before me. In their Answer, Verified Counterclaim, and Third-Party Complaint, Defendants asserted claims against a third-party defendant,Smartmatic TIM Corporation, a Philippines corporation.B.Facts In October 2009, Dominion granted Smartmatic a worldwide (except for the United States and Canada) nonexclusive license to certain precinct count optical scan(―PCOS‖) voting systems that Dominion had developed (the ―License Agreement‖or the ―Agreement‖). The License Agreement granted Smartmatic rights to certain patents and patent applications that Dominion owned or controlled (the ―Licensed Patent Rights‖) and to ―all know-how, trade secrets, methodologies and other technical information owned or possessed by Dominion‖ (the ―Licensed Technology‖).1The License Agreement contains a non-competition provision.
As for the Venezuelan connection, per the SmartMatic website published in 2018: (After Maduro remained in power)
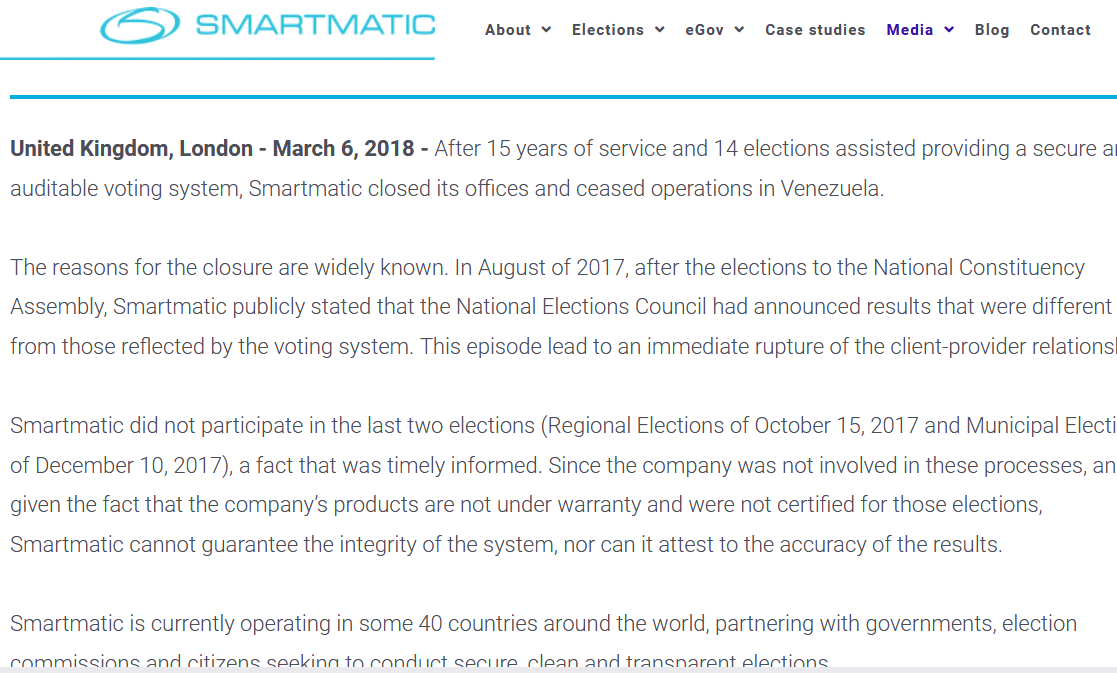
Smartmatic announces cease of operations in Venezuela
United Kingdom, London – March 6, 2018 – After 15 years of service and 14 elections assisted providing a secure and auditable voting system, Smartmatic closed its offices and ceased operations in Venezuela.
The reasons for the closure are widely known. In August of 2017, after the elections to the National Constituency Assembly, Smartmatic publicly stated that the National Elections Council had announced results that were different from those reflected by the voting system. This episode lead to an immediate rupture of the client-provider relationship.
Smartmatic did not participate in the last two elections (Regional Elections of October 15, 2017 and Municipal Elections of December 10, 2017), a fact that was timely informed. Since the company was not involved in these processes, and given the fact that the company’s products are not under warranty and were not certified for those elections, Smartmatic cannot guarantee the integrity of the system, nor can it attest to the accuracy of the results.
Smartmatic is currently operating in some 40 countries around the world, partnering with governments, election commissions and citizens seeking to conduct secure, clean and transparent elections.
Stands to reason that not only should American citizens question known facts but find the unknown facts and the same holds true for members of Congress on both sides of the aisle. So digging deeper, doing an examination of the Congressional record is worthy of time. If those in the Senate are questioning elections and they have more intelligence reports than we outside the Beltway do, perhaps #BigTech should judge slowly and do their own work as well as #BigCorporations before all this cancelling continues. But read on.
On the Senate side, as recently as October, 19, 2020, 7 Senators challenged the election results in Venezuela, 3 were Republicans and 4 were Democrats. Note this was after the Maduro stolen election. There was a Senate Resolution #749. In part:
Whereas the regime of Nicolas Maduro is undertaking efforts
to hold fraudulent legislative elections for Venezuela’s
National Assembly in December 2020 that will not comply with
international standards for free, fair, and transparent
electoral processes;
Whereas the Maduro regime is seeking to use fraudulent
legislative elections to undermine Venezuela’s sitting
democratically elected National Assembly;
Whereas, as codified under section 112 of the VERDAD Act of
2019 (22 U.S.C. 9702), it is the policy of the United States
to recognize the democratically elected National Assembly of
Venezuela, elected in December 2015 and sworn in on January
2016, as the only legitimate national legislative body in
Venezuela;
Whereas the United States Government and members of the
international community have rightly denounced the Maduro
regime’s efforts to hold fraudulent legislative elections in
December 2020;
Whereas, on October 13, 2020, members of the Lima Group–
including Bolivia, Brazil, Canada, Chile, Colombia, Costa
Rica, Guatemala, Haiti, Honduras, Panama, Paraguay, Peru, and
Venezuela–issued a joint declaration on the Maduro regime’s
efforts to hold legislative elections in December 2020 that
expressed “firm rejection of the continuing of the
illegitimate regime of Nicolas Maduro in holding
parliamentary elections without the minimum democratic
guarantees and without the participation of all political
forces”;
Whereas, on September 17, 2020, the International Contact
Group on Venezuela–whose members include Argentina, Costa
Rica, Ecuador, the European Union, France, Germany, Italy,
the Netherlands, Panama, Portugal, Spain, Sweden, the United
Kingdom, and Uruguay–issued a joint declaration on the
Maduro regime’s efforts to hold legislative elections in
December 2020 that stated that “conditions are not met, at
the moment, for a transparent, inclusive, free and fair
electoral process”;
We report you decide…thousands of moving parts here.