If you missed the press conference held by the House Oversight Committee on the investigation into the Biden crime family, no worries, below is a summary.
Enjoy the preliminary primer for context…
Several months ago, I did a little research and found the following:
- Hudson West LLC is a Delaware company created in 2016 and the registered agent is Corporation Service Company, a common template service for establishing obscure corporations. Hudson West was/is a joint venture operation between Hunter Biden and an un-named Chinese company to sell natural gas to China. Other Chinese officials included in the Hudson West operation include Gong Wendong and Ye Jiamming.
- An interesting audio with admissions from the Hunter laptop speaking of the China spy chief. The founder of CEFC is Ye Jiamming and in 2018, he was named in a corruption case and disappeared. Another head of CEFC was Chi Ping Patrick Ho. In March of 2017, CEFC announced a very large p;artnership throught the Securities and Exchange Commission with the Cowan Group. There was a filing with the Committee for Foreign Investments in the United States however it was withdrawn later in the year possibly due to the Patrick Ho, as in 2019 was sentenced to 3 years in prison for bribery in two countries, Chad and Uganda.
- The FBI issued subpoenas for the Hunter laptop in connection with a money-laundering scheme where the investigative FBI agent Joshua Wilson signed the subpoenas. Case ID is 272D-BA-3065729. (Note 272 is the Bureau’s classification for money-laundering on a transnational basis. BA indicates the case was opened in the Baltimore FBI office.
- Owasco OC and Owasco LLC was yet another company which had associated bank accounts established by Hunter. The name Owasco is for a home in New York where the Biden family used to spend their summers. No paycheck for the intern working at Owasco unless she had sex with Hunter?
Okay…read on…get comfortable, this is long and great investigative work so far.
The financial records also reveal how the Bidens used complicated transactions to hide payments from foreign nationals, including CCP-linked associates, and provide clear indications of influence peddling schemes during then-Vice President Biden’s tenure.
“The Bidens intentionally sought to hide, confuse, and conceal their influence peddling schemes, but bank records don’t lie. The Bidens made millions from foreign nationals providing what seems to be no services other than access and influence. From the thousands of records we’ve obtained so far, we know the Biden family set up over a dozen companies when Joe Biden was vice president. The Bidens engaged in many intentionally complicated financial transactions to hide these payments and avoid scrutiny. In at least one instance, the Bidens’ CCP-linked associates took steps to conceal the source of the payment to the Bidens.
“The Bidens’ foreign entanglements are breathtaking and raise serious questions about why foreign actors targeted the Biden family, what they expected in return, and whether our national security is threatened. We will continue to pursue additional bank records to follow the money trail and inform legislative solutions to prevent this type of corruption. Americans deserve answers, transparency, and accountability,” said Chairman Comer.
- The Complicated Web of Biden Family and Associates’ Companies: Biden family members and business associates created a web of over 20 companies—most were limited liability companies formed after Joe Biden became Vice President.
- The Biden Family Received Millions of Dollars from Foreign Sources: Bank records show the Biden family, their business associates, and their companies received over $10 million from foreign nationals’ and their related companies. The Committee has identified payments to Biden family members from foreign companies while he served as Vice President and after he left public office.
- The Biden Family Used Business Associates’ Companies to Receive Foreign Funds: Despite creating many companies after Vice President Biden took office, the Biden family used business associates’ companies to receive millions of dollars from foreign companies.
- Attempts to Conceal Large Financial Transactions: After foreign companies sent money to business associates’ companies, the Biden family received incremental payments over time to different bank accounts. These complicated financial transactions appear to be meant to conceal the source of the funds and reduce the conspicuousness of the total amounts made into the Biden bank accounts.
- Chinese Nationals Hid the Source of the Money:Chinese nationals and companies with significant ties to Chinese intelligence and the Chinese Communist Party hid the source of the funds paid out to the Bidens by layering domestic limited liability companies. The Biden family and associates’ activities in coordination with Chinese nationals and their corporate entities appear to be an attempt to engage in financial deception. Multiple Biden family members received money from the Chinese after it passed through an associate’s account. Additionally, Hunter Biden received money directly into his company’s account from a Chinese-controlled entity.
- Biden Family and Associates’ Activities in Romania Indicate Influence Peddling Scheme: The Biden family and associates’ activities in Romania bear clear indicia of a scheme to peddle influence from 2015 to 2017. While Vice President Biden lectured Romania on corruption and ethics, the Bidens received over a million dollars from a company controlled by a Romanian individual accused of corruption, Gabriel Popoviciu, through a Biden family associate.
- Bank records from just a few banks and many more to come, scroll the list and payouts.
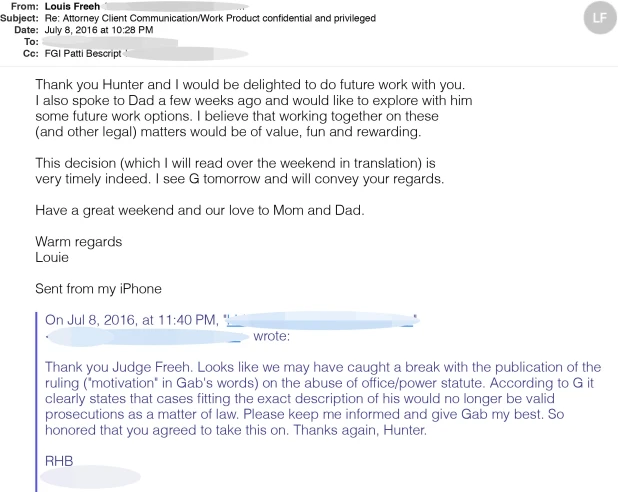
- Then one must question the former FBI Director, Louis Freeh as he donated $100,000 to the Biden family Trust. Was there some other favor attached to that donation? Yup…to be part of business deals.