AUSTIN – The Department of Information Resources (DIR) is leading the response to a coordinated ransomware attack that has impacted at least twenty local government entities across Texas
AUSTIN – The Department of Information Resources (DIR) is leading the response to a coordinated ransomware attack that has impacted at least twenty local government entities across Texas.
Users are then extorted for cash in order to regain access to their systems, and they are nearly always asked to pay in Bitcoin, a blockchain currency that is virtually untraceable, allowing hackers to pull off these complex operations from a single room halfway around the world.
It is unknown how much the hackers were demanding from Texas officials, which systems are currently offline and whether the impacted cities are expected to pay the ransom.
***  photo
photo
The attack took place on Friday morning, August 16, US time, when several smaller local Texas governments reported problems with accessing their data to the Texas Department of Information Resources (DIR).
DIR officials did not publish a list of impacted local governments. On Friday, the agency couldn’t provide an exact number of impacted entities, but a day later, DIR said the number is 23.
“It appears all entities that were actually or potentially impacted have been identified and notified,” DIR said. “Responders are actively working with these entities to bring their systems back online.”
The organization has been coordinating recovery efforts together with more than ten other Texas and US government agencies, such as the Texas Division of Emergency Management, the FBI, the DHS, the Texas Department of Public Safety, and others.
“At this time, the evidence gathered indicates the attacks came from one single threat actor,” DIR officials said on Saturday.
.JSE ransomware
ZDNet has learned from a local source that the ransomware that infected the networks of the 23 local Texas governments encrypts files and then adds the .JSE extension at the end.
This ransomware strain does not have its own name, being generally called the .jse ransomware –although some antivirus vendors detect it as Nemucod, under the name of the trojan that drops it on infected hosts.
First signs of this .jse ransomware have been spotted as early as August 2018, but activity has continued and has been reported as recently as this month. The ransomware is a strange one as it does not leave a ransom note behind, confusing victims who most of the time don’t know what happened.
In recent months, US cities have been a prime target for ransomware gangs, with infections reported all over the US.
In July, the governor of Louisiana declared a state emergency after a similar coordinated ransomware attack hit several school districts.




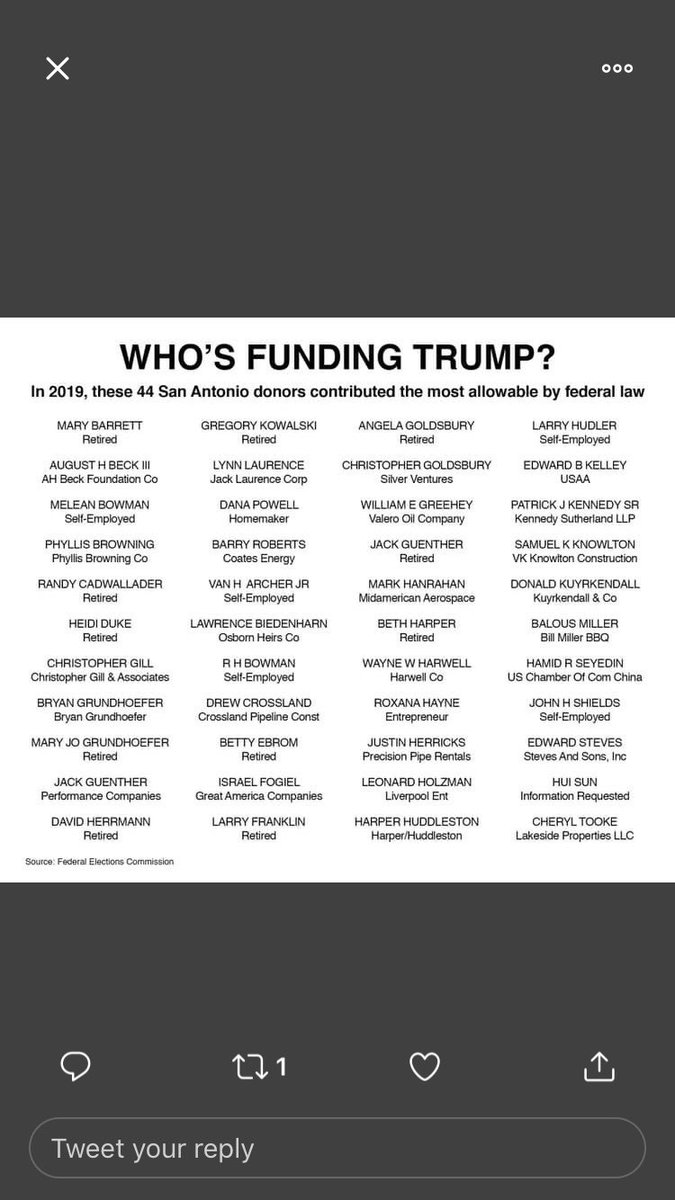 It does not seem to matter that campaign contributions are free speech and fully protected by the 1st Amendment. Will media even go there in reporting this? Nah. Will the House Ethics Committee get involved? Nah. The mayor? Law enforcement? Nah.
It does not seem to matter that campaign contributions are free speech and fully protected by the 1st Amendment. Will media even go there in reporting this? Nah. Will the House Ethics Committee get involved? Nah. The mayor? Law enforcement? Nah.