One has to apply some critical thinking here. The money clue –> Unbeknownst to Harvard University beginning in 2011, Lieber became a “Strategic Scientist” at Wuhan University of Technology (WUT) in China and was a contractual participant in China’s Thousand Talents Plan from in or about 2012 to 2017. Wuhan is ground-zero for the virus. The United States along with the Center for Disease Control has offered substantial assistance to China providing expertise including microbiology, immunology and virology relating directly to the coronavirus. but China refused. Hummm. The U.S. patent office has approved several patent applications relating to the virus, the most recent in 2008 from what appears to be from a team from Vanderbilt University.
A close friend found another interesting event recently held event from October 2019 that was hosted in New York by Johns Hopkins Center for Health Security, the World Economic Forum and the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation called Event 201. 130 people attended to discuss pandemics. A good takeaway document discussing pandemic communications is found here. Note we are not getting all the real details from China as Beijing controls all media. Further, there will be false posts and articles in various forms in world media, so do your work.
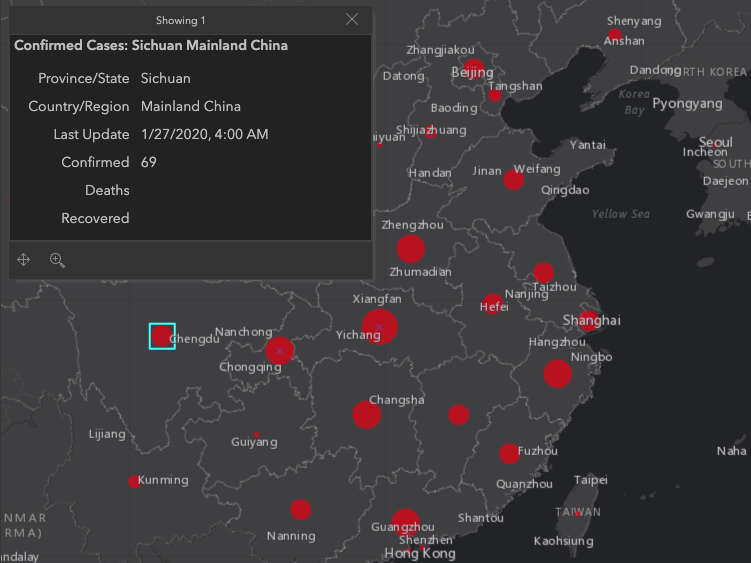 Useful map details and updates found here.
Useful map details and updates found here.
You be the judge.
Department of JusticeOffice of Public Affairs
Tuesday, January 28, 2020Harvard University Professor and Two Chinese Nationals Charged in Three Separate China Related Cases
The Department of Justice announced today that the Chair of Harvard University’s Chemistry and Chemical Biology Department and two Chinese nationals have been charged in connection with aiding the People’s Republic of China.
Dr. Charles Lieber, 60, Chair of the Department of Chemistry and Chemical Biology at Harvard University, was arrested this morning and charged by criminal complaint with one count of making a materially false, fictitious and fraudulent statement. Lieber will appear this afternoon before Magistrate Judge Marianne B. Bowler in federal court in Boston, Massachusetts.
Yanqing Ye, 29, a Chinese national, was charged in an indictment today with one count each of visa fraud, making false statements, acting as an agent of a foreign government and conspiracy. Ye is currently in China.
Zaosong Zheng, 30, a Chinese national, was arrested on Dec. 10, 2019, at Boston’s Logan International Airport and charged by criminal complaint with attempting to smuggle 21 vials of biological research to China. On Jan. 21, 2020, Zheng was indicted on one count of smuggling goods from the United States and one count of making false, fictitious or fraudulent statements. He has been detained since Dec. 30, 2019.
Dr. Charles Lieber
According to court documents, since 2008, Dr. Lieber who has served as the Principal Investigator of the Lieber Research Group at Harvard University, which specialized in the area of nanoscience, has received more than $15,000,000 in grant funding from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) and Department of Defense (DOD). These grants require the disclosure of significant foreign financial conflicts of interest, including financial support from foreign governments or foreign entities. Unbeknownst to Harvard University beginning in 2011, Lieber became a “Strategic Scientist” at Wuhan University of Technology (WUT) in China and was a contractual participant in China’s Thousand Talents Plan from in or about 2012 to 2017. China’s Thousand Talents Plan is one of the most prominent Chinese Talent recruit plans that are designed to attract, recruit, and cultivate high-level scientific talent in furtherance of China’s scientific development, economic prosperity and national security. These talent programs seek to lure Chinese overseas talent and foreign experts to bring their knowledge and experience to China and reward individuals for stealing proprietary information. Under the terms of Lieber’s three-year Thousand Talents contract, WUT paid Lieber $50,000 USD per month, living expenses of up to 1,000,000 Chinese Yuan (approximately $158,000 USD at the time) and awarded him more than $1.5 million to establish a research lab at WUT. In return, Lieber was obligated to work for WUT “not less than nine months a year” by “declaring international cooperation projects, cultivating young teachers and Ph.D. students, organizing international conference[s], applying for patents and publishing articles in the name of” WUT.
The complaint alleges that in 2018 and 2019, Lieber lied about his involvement in the Thousand Talents Plan and affiliation with WUT. On or about, April 24, 2018, during an interview with investigators, Lieber stated that he was never asked to participate in the Thousand Talents Program, but he “wasn’t sure” how China categorized him. In November 2018, NIH inquired of Harvard whether Lieber had failed to disclose his then-suspected relationship with WUT and China’s Thousand Talents Plan. Lieber caused Harvard to falsely tell NIH that Lieber “had no formal association with WUT” after 2012, that “WUT continued to falsely exaggerate” his involvement with WUT in subsequent years, and that Lieber “is not and has never been a participant in” China’s Thousand Talents Plan.
Yanqing Ye
According to the indictment, Ye is a Lieutenant of the People’s Liberation Army (PLA), the armed forces of the People’s Republic of China and member of the Chinese Communist Party (CCP). On her J-1 visa application, Ye falsely identified herself as a “student” and lied about her ongoing military service at the National University of Defense Technology (NUDT), a top military academy directed by the CCP. It is further alleged that while studying at Boston University’s (BU) Department of Physics, Chemistry and Biomedical Engineering from October 2017 to April 2019, Ye continued to work as a PLA Lieutenant completing numerous assignments from PLA officers such as conducting research, assessing U.S. military websites and sending U.S. documents and information to China.
According to court documents, on April 20, 2019, federal officers interviewed Ye at Boston’s Logan International Airport. During the interview, it is alleged that Ye falsely claimed that she had minimal contact with two NUDT professors who were high-ranking PLA officers. However, a search of Ye’s electronic devices demonstrated that at the direction of one NUDT professor, who was a PLA Colonel, Ye had accessed U.S. military websites, researched U.S. military projects and compiled information for the PLA on two U.S. scientists with expertise in robotics and computer science. Furthermore, a review of a WeChat conversation revealed that Ye and the other PLA official from NUDT were collaborating on a research paper about a risk assessment model designed to decipher data for military applications. During the interview, Ye admitted that she held the rank of Lieutenant in the PLA and admitted she was a member of the CCP.
Zaosong Zheng
In August 2018, Zheng entered the United States on a J-1 visa and conducted cancer-cell research at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center in Boston from Sept. 4, 2018, to Dec. 9, 2019. It is alleged that on Dec. 9, 2019, Zheng stole 21 vials of biological research and attempted to smuggle them out of the United States aboard a flight destined for China. Federal officers at Logan Airport discovered the vials hidden in a sock inside one of Zheng’s bags, and not properly packaged. It is alleged that initially, Zheng lied to officers about the contents of his luggage, but later admitted he had stolen the vials from a lab at Beth Israel. Zheng stated that he intended to bring the vials to China to use them to conduct research in his own laboratory and publish the results under his own name.
The charge of making false, fictitious and fraudulent statements provides for a sentence of up to five years in prison, three years of supervised release and a fine of $250,000. The charge of visa fraud provides for a sentence of up to 10 years in prison, three years of supervised release and a fine of $250,000. The charge of acting as an agent of a foreign government provides for a sentence of up to 10 years in prison, three years of supervised release and a fine of $250,000. The charge of conspiracy provides for a sentence of up to five years in prison, three years of supervised release and a fine of $250,000. The charge of smuggling goods from the United States provides for a sentence of up to 10 years in prison, three years of supervised release and a fine of $250,000. Sentences are imposed by a federal district court judge based upon the U.S. Sentencing Guidelines and other statutory factors.
Assistant Attorney General for National Security John C. Demers, United States Attorney Andrew E. Lelling; Special Agent in Charge of the FBI Boston Field Division Joseph R. Bonavolonta; Michael Denning, Director of Field Operations, U.S. Customs and Border Protection, Boston Field Office; Leigh-Alistair Barzey, Special Agent in Charge of the Defense Criminal Investigative Service, Northeast Field Office; Philip Coyne, Special Agent in Charge of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Office of Inspector General; and William Higgins, Special Agent in Charge of the U.S. Department of Commerce, Office of Export Enforcement, Boston Field Office made the announcement. Assistant U.S. Attorneys B. Stephanie Siegmann, Jason Casey and Benjamin Tolkoff of Lelling’s National Security Unit are prosecuting these cases with the assistance of trial attorneys William Mackie and David Aaron at the National Security Division’s Counterintelligence and Export Control Section.
The details contained in the charging documents are allegations. The defendants are presumed innocent unless and until proven guilty beyond a reasonable doubt in a court of law.
These case are part of the Department of Justice’s China Initiative, which reflects the strategic priority of countering Chinese national security threats and reinforces the President’s overall national security strategy. In addition to identifying and prosecuting those engaged in trade secret theft, hacking and economic espionage, the initiative will increase efforts to protect our critical infrastructure against external threats including foreign direct investment, supply chain threats and the foreign agents seeking to influence the American public and policymakers without proper registration.





