Anyone remember Brexit? People across the globe are speaking out and the vote in Britain to get out of a union and regain sovereignty is a message. It is not being heard and such is the case at the United Nations General Assembly.
Borderless….policy by global leaders is promoting this, while citizens are demanding otherwise. Have you taken a moment to look at our domestic universities where classes are filled with foreign students? Have you look at how intertwined governments are with each other’s economies? When one government financially aides another to keep it from a tailspin, major strings are attached and ethical behavior and compliance with law is dismissed.
Have you seen this hashtag? #UN4RefugeesMigrants It is the newest in vogue talking point and condition globally. To view how borderless the West is becoming, click here to see the topics of discussions planned at the United Nations.
The newest mission is to control the oceans and John Kerry is leading the way. Who owns those oceans and the sea life?
Related reading: John Kerry expresses hope over ‘life and death issue’ of oceans
The Secretary of State sees the future of the seas as a global threat equal to world conflicts.
So, back to the United Nations and how the above and much more are being covered and delivered. Chilling conditions as noted below:
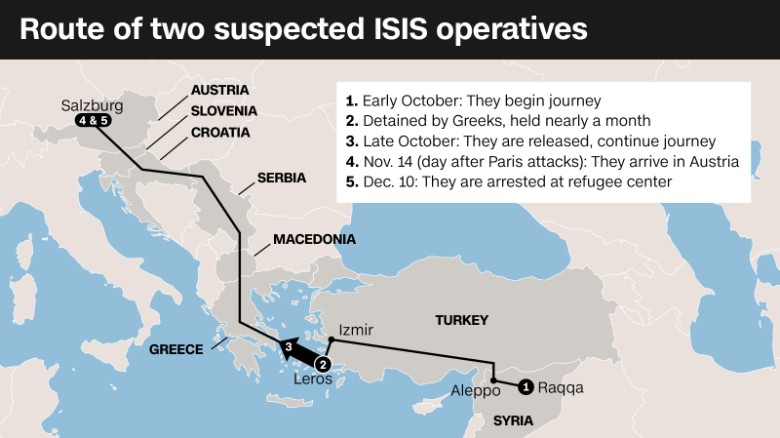
President Obama is hosting the Leaders’ Summit on Refugees, alongside co-hosts Canada, Ethiopia, Germany, Jordan, Mexico and Sweden, which will appeal to governments to pledge significant new commitments on refugees. While the Leaders’ Summit will focus on refugees, not migrants, the General Assembly High-Level Summit will address large movements of both. See the full program here.
Then we have Europe:
The European Union at the United Nations
“Stronger partnerships are the building blocks of our foreign policy. All today’s challenges
transcend borders and national sovereignties. None of us, alone, can carry the weight of the
world on its shoulders.”High Representative/ Vice-President Federica Mogherini at the UN Security Council 6 June 2016
The EU’s commitment to effective multilateralism, with the UN at its core, is a central element of its external action. The Lisbon Treaty provides that “The Union … shall promote multilateral solutions to common problems, in particular in the framework of the United Nations.” (Article 21-1 TEU) and that “The Union …shall work for a high degree of cooperation in all fields of international relations, in order to (…) preserve peace, prevent conflicts and strengthen international security, in accordance with the purposes and principles of the United Nations Charter.” (Art. 21-2)
Multilateralism is also one of the core principles and priorities in the new EU Global Strategy for Foreign and Security Policy. To respond successfully to global crises, threats and challenges, the international community needs an efficient multilateral system, founded on universal rules and values. The United Nations is both: a key EU partner and an indispensable global forum for tackling global challenges, within the overall framework of the 2030 Agenda and its 17 Sustainable Development Goals. The EU thus works closely both with the UN and in the UN.
“Without global norms and the means to enforce them, peace and security, prosperity and democracy – our vital interests – are at risk. Guided by the values on which it is founded, the EU is committed to a global order based on international law, including the principles of the UN Charter. The EU will strive for a strong UN as the bedrock of the multilateral rules-based order, and develop globally coordinated responses with international and regional organisations, states and non-state actors.”
– EU Global Strategy for Foreign and Security Policy –
Working closely with the UN Secretariat and the various UN Agencies, Funds and Programmes, the EU has established a strong relationship with the UN. Cooperation takes place across a broad range of areas: development, human rights, climate change, peace building, crisis management, disarmament and non-proliferation, humanitarian assistance, fighting corruption and crime, addressing global health concerns, managing migratory flows and labour issues.
The UN General Assembly is the main deliberative, policymaking and representative organ of the UN. The added value of the EU is to coordinate among its 28 Member States to present a unified position.
In 2011, the UN General Assembly adopted Resolution A/65/276 upgrading the observer status allow the EU to present common positions, make interventions, present proposals and participate in the general debate each September. As an observer with enhanced status, enabling EU representatives to speak on behalf of the EU and its member states in the UN. Since then it is also the President of the European Council who delivers the EU statement in the General debate, and no longer the rotating Presidency, bringing EU representation in New York in line with Lisbon Treaty provisions. The EU has obtained a special “full participant” status in a number of important UN conferences.
The Council of the European Union adopted the EU priorities at the United Nations at the 71st United Nations General Assembly on 18 July 2016. The coming year will be focused on consolidation and implementation of the agreements reached in the past year. These include the 2030 agenda for sustainable development, the Addis Ababa action agenda of the third international conference on financing for development and the Paris climate agreement.
The EU coordinates its voting within the General Assembly’s six main committees and other bodies and agencies such as the Economic and Social Council. To this end, more than 1300 internal EU coordination meetings are held at the UN in New York alone to develop a common EU stance and speak with one voice. Article 34 of the EU Treaty also stipulates that EU members on the Security Council must act in concert and foster the interests of the EU. In 2015, the EU delivered more than 220 statements at the UN in New York, including 31 at the Security Council.
Global Security Provider
The EU has a wide range of tools available to prevent and solve crises in close cooperation with international and regional partners. For this reason, the High Representative provides regular updates to theSecurity Council and the EU is often invited to address issues of common concern, such as the fight against terrorism. Regular UN Security Council meetings on UN-EU cooperation in maintaining international peace and security are testimony to the importance both place on it.
“In our conflictual world, where power is scattered and diffuse, global peace and security only stands a chance if our nations and our regions are united. Our European Union will always come back to the United Nations, to the core of the international multilateral system, to the stubborn idea of a cooperative world order.”
HRVP briefing to UNSC 6 June 2016
The Security Council endorsed the relationship with the EU in 2014 when it adopted a presidential statement on cooperation between the EU and the UN.
Major contributor
Collectively, the EU and its Member States are the single largest financial contributor to the UN system. The sum of the contributions of the 28 EU Member States amounts to 30.38% of the UN regular budget and 33.17% of the UN peacekeeping budgets. In addition, the EU and its Member States also provide about one-half of all the voluntary contributions to UN funds and programmes. The European Commission alone contributed more than $1.5 billion to support UN external assistance programmes and projects in 2014. The European Union and its Member States retained their place as the world’s largest aid donor in 2014, according to OECD figures. In 2014, EuropeAid’s financial contributions to the UN exceeded €983 million, with the most funding going to UNDP (40%), UNICEF (18%), FAO (12%), UNRWA (10%), and WFP (8%). In 2015, ECHO (European Commission Humanitarian Aid and Civil Protection) provided €514 million (an increase from €452 in 2014) to UN agencies, funds and programmes, including €207 million to WFP, €127 million to UNHCR and €108 million to UNICEF.
UN Reform and Increased Efficiency
Effective multilateralism requires an effective United Nations at its core. The EU supports the reform of the UN system, including its bodies and organs, to ensure it is fit to address the complex, multi-sectoral challenges we face today. This should include comprehensive reform of the UN Security Council as well as revitalisation of the work of the General Assembly. The EU supports the notion that the United Nations must be ‘fit for purpose’ as well as increasingly effective and efficient, including to support successful implementation of the 2030 Agenda.