Most un-noticed in Barack Obama’s responses to questions of his elation at the Iran nuclear agreement was his declared shift on the mission with regard to Syria, turning to Iran to be part of the full strategy talks.
Iran gained additional power and authority by the P5+1
In part from the WSJ: In this quest beyond its Shiite roots, revolutionary Iran has always tried to build bonds with Sunni political Islam, especially the Muslim Brotherhood and its offshoots.
Mr. Khamenei, for one, has personally translated into Persian the writings of the Brotherhood’s seminal ideologue, Sayyid Qutb. Hamas, the Palestinian offshoot of the Egyptian Muslim Brotherhood, was a client of Iran’s since the 1990s, as was overwhelmingly Sunni Sudan.
[12:39:25 PM] tennisaddict: All these alliances, however, began to crumble in the wake of the Arab Spring. Hamas’s relationship with Iran was made unsustainable by Iran’s involvement against Sunni rebels—many of them belonging to the Syrian branch of the Muslim Brotherhood—in the Syrian war. Even Sudan, the one-time conduit for Iranian weapons to Hamas and a major recipient of Iranian military aid, switched sides and backed Saudi Arabia in this year’s war against pro-Iranian Houthi rebels in Yemen.
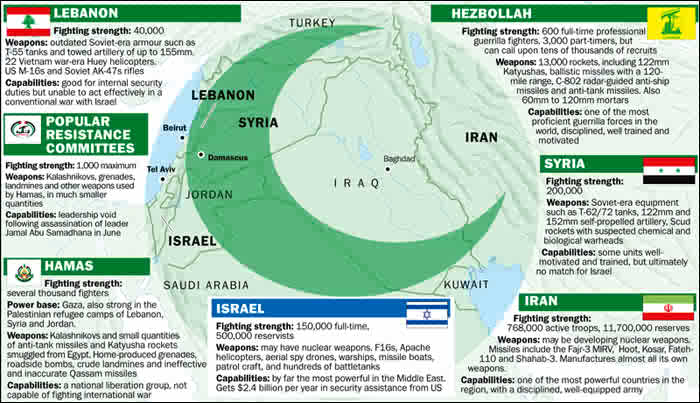
Saudi Arabia stands with Israel and the Iran Threat Obsession
From NYT’s:
For decades, Saudi Arabia has poured billions of its oil dollars into sympathetic Islamic organizations around the world, quietly practicing checkbook diplomacy to advance its agenda.
But a trove of thousands of Saudi documents recently released by WikiLeaks reveals in surprising detail how the government’s goal in recent years was not just to spread its strict version of Sunni Islam — though that was a priority — but also to undermine its primary adversary: Shiite Iran.
The documents from Saudi Arabia’s Foreign Ministry illustrate a near obsession with Iran, with diplomats in Africa, Asia and Europe monitoring Iranian activities in minute detail and top government agencies plotting moves to limit the spread of Shiite Islam.
The scope of this global oil-funded operation helps explain the kingdom’s alarm at the deal reached on Tuesday between world powers and Iran over its nuclear program. Saudi leaders worry that relief from sanctions will give Iran more money to strengthen its militant proxies. But the documents reveal a depth of competition that is far more comprehensive, with deep roots in the religious ideologies that underpin the two nations.

The documents indicate an extensive apparatus inside the Saudi government dedicated to missionary activity that brings in officials from the Foreign, Interior and Islamic Affairs Ministries; the intelligence service and the office of the king.
Recent initiatives have included putting foreign preachers on the Saudi payroll; building mosques, schools and study centers; and undermining foreign officials and news media deemed threatening to the kingdom’s agenda.
At times, the king got involved, ordering an Iranian television station off the air or granting $1 million to an Islamic association in India.
“We are talking about thousands and thousands of activist organizations and preachers who are in the Saudi sphere of influence because they are directly or indirectly funded by them,” said Usama Hasan, a senior researcher in Islamic studies at the Quilliam Foundation in London. “It has been a huge factor, and the Saudi influence is undeniable.”
While the documents do not show any Saudi support for militant activity, critics argue that the kingdom’s campaign against Shiites — and its promotion of a strict form of Islam — has eroded pluralism in the Muslim world and added to the tensions fueling conflicts in Iraq, Syria, Yemen and elsewhere.
The Saudi government has made no secret of its international religious mission, nor of its enmity toward Iran. But it has found the leaks deeply embarrassing and has told its citizens that spreading them is a crime.
While it has acknowledged a link between the documents and an electronic attack on the Foreign Ministry, it has said that some of the documents are fabricated. But many of them contain correct names and telephone numbers, and a number of individuals and associations named in them verified their contents when reached by reporters from The New York Times.
The Foreign Ministry relayed funding requests to officials in Riyadh; the Interior Ministry and the intelligence agency sometimes vetted potential recipients; the Saudi-supported Muslim World League helped coordinate strategy; and Saudi diplomats across the globe oversaw projects. Together, these officials identified sympathetic Muslim leaders and associations abroad; distributed funds and religious literature produced in Saudi Arabia; trained preachers; and gave them salaries to work in their own countries.
One example of this is Sheikh Suhaib Hasan, an Indian Islamic scholar who was educated in Saudi Arabia and worked for the kingdom for four decades in Kenya and in Britain, where he helped found the Islamic Sharia Council, according to a cable from the Saudi Embassy in London whose contents were verified by his son, Mr. Hassan of the Quilliam Foundation.
Clear in many of the cables are Saudi fears of Iranian influence and of the spread of Shiite Islam.
The Saudi Embassy in Tehran sent daily reports on local news coverage of Saudi Arabia. One cable suggested the kingdom improve its image by starting a Persian-language television station and sending pro-Saudi preachers to tour Iran.
Other cables detailed worries that Iran sought to turn Tajikistan into “a center to export its religious revolution and to spread its ideology in the region’s countries.” The Saudi ambassador in Tajikistan suggested that Tajik officials could restrict Iranian support “if other sources of financial support become available, especially from the kingdom.”

The fear of Shiite influence extended to countries where Muslims are small minorities, like China, where a Saudi delegation was charged with “suggesting practical programs that can be carried out to confront Shiite expansion in China.” And documents from the Philippines, where only 5 percent of the population is Muslim, included suggested steps to “restrict the Iranian presence.”
In 2012, Saudi ambassadors from across Africa were told to file reports on Iranian activities in their countries. The Saudi ambassador to Uganda soon filed a detailed report on “Shiite expansion” in the mostly Christian country.
A cable from the predominantly Muslim nation of Mali warned that Iran was appealing to the local Muslims, who knew little of “the truth of the extremist, racist Shiite ideology that goes against all other Islamic schools.”
Many of those seeking funds referred to the Saudi-Iranian rivalry in their appeals, the cables showed.
One proposal from the Afghan Foundation in Afghanistan said that it needed funding because such projects “do not receive support from any entities, while others, especially Shiites, get a lot of aid from several places, including Iran.”