The Russians have been aggressively moving in on that region for the last several years such that under the Obama administration, the United States was in no position to respond.
 Officially closed in 2006, Currently the Keflavík Airbase is being used by planes from the US and other NATO members (Iceland is a member nation). As Iceland does not have an army or an air force NATO allies periodically deploy fighter aircrafts to provide air policing. The plane crews are only a small fraction of the thousands of US servicemen that used to by stationed at Keflavík. The condos that they used to live in with their families have now been turned into a school campus, a hotel and other civilian facilities. More here.
Officially closed in 2006, Currently the Keflavík Airbase is being used by planes from the US and other NATO members (Iceland is a member nation). As Iceland does not have an army or an air force NATO allies periodically deploy fighter aircrafts to provide air policing. The plane crews are only a small fraction of the thousands of US servicemen that used to by stationed at Keflavík. The condos that they used to live in with their families have now been turned into a school campus, a hotel and other civilian facilities. More here.
***
Russian submarines are also patrolling the North Atlantic more frequently than at any time since the end of the Cold War
The United States has a long relationship with Iceland, and by treaty since 1951 continues to be responsible for the defense of the country. Iceland has no military, but the country’s coast guard fulfills most military missions, and is responsible for maintaining Keflavik as a military installation. More here.
BI: The Pentagon is preparing to spend millions of dollars to fix up a Cold War-era air base in Iceland as Washington rushes to keep an eye on a new generation of stealthy Russian submarines slipping into the North Atlantic.
Tucked away in the 2018 defense budget sitting on President Donald Trump’s desk is a provision for $14.4 million to refurbish hangars at Naval Air Station Keflavik to accommodate more U.S. Navy P-8 Poseidon reconnaissance aircraft, a key surveillance asset for locating and tracking submarines, a defense official confirms.
The move comes as new Russian nuclear and conventional submarines have been making more frequent trips through the area known as the “GIUK gap” — an acronym for Greenland, Iceland, and the United Kingdom — the route for the Russian Northern Fleet to enter the Atlantic Ocean.
The United States and Iceland have agreed to increase rotations of the American surveillance planes to Iceland next year, Pentagon spokesman Johnny Michael confirmed to Foreign Policy.
Inside the alliance, there is concern over NATO’s ability to locate and track the new Russian submarines as they move silently into the open ocean. NATO officials have admitted that the past two decades of anti-piracy operations near Africa and support for ground operations in the Middle East have distracted from the anti-submarine mission which was at the core of the Cold War mission in the Atlantic.
After allowing its naval forces to fall into disrepair in the 1990s, Russian President Vladimir Putin set out on a major military overhaul in the 2000s, clawing back capability by designing and building new diesel- and nuclear-powered boats, making them quieter, more lethal, and longer-legged than their Soviet predecessors.
Russia’s undersea fleet “is in the best state it has been in since the fall of the Soviet Union,” said Michael Kofman, a Russian military expert at the Center for Naval Analyses. “A lot of effort has been spent on drilling, training, and readiness.”
The Russian submarine force of about 50 hulls is a fraction of the 400 the Soviet Union floated during the Cold War, but they boast vastly improved technical capabilities that put them on par with their American rivals, experts said.
“This time they’re going for quality rather than quantity,” added Magnus Nordenman of the Atlantic Council.
In an unclassified assessment of Russian military strength issued earlier this year, the Pentagon’s Defense Intelligence Agency concluded that Moscow’s new nuclear-powered ballistic missile submarines are “capable of delivering nuclear warheads from thousands of kilometers away. This strategic capability puts the Russian Navy in the top tier of foreign navies.”
The pride of the Russian fleet is the nuclear-powered Yasen-class guided missile submarine, which can carry 32 Kalibr cruise missiles. While the missile’s range isn’t known for sure, Russian subs have fired the Kalibr into Syria from about 700 miles away.
Moscow has two Yasen-class subs operational, and plans to build an additional eight in coming years.
In late November the British first sea lord, Adm. Sir Philip Jones, said that the naval superiority Western navies have enjoyed in recent decades is disappearing and resurgent powers like Russia are testing the Royal Navy in home waters.
The Russian Yasen-class nuclear attack submarine Severodvinsk Wikimedia Commons
“It’s now clear that the peaks of Russian submarine activity that we’ve seen in the North Atlantic in recent years are the new norm,” he said.
France, Germany, Greece, Italy, Spain, and Turkey signed a letter of intent this summer to start development of new submarine-detecting aircraft. More airborne assets are needed because the number of sub-hunting ships that can patrol the waters on the North Atlantic, Baltic, and Mediterranean is far reduced since the Cold War.
Navies generally use frigates to conduct anti-submarine warfare — known as ASW operations — and the number of frigates in use by NATO allies has fallen to about 50, down from the 100 or so in the early 1990s.
Partly to fill that gap, the U.S. Navy is working to rush a new class of 20 frigates into service beginning in 2020. Last month, the service issued a notice to the defense industry to come up with a multi-mission frigate design that could be built within the next two years capable of conducting air defense and anti-submarine operations.
Russia has traditionally been constrained in its access to the open ocean, and the loss of the Baltic states and Poland, and of Black Sea ports in Romania and Bulgaria, mean modern Russia has a harder time getting out to sea than the Soviet Union did.
In the event of conflict with the West, Moscow’s Baltic and Black Sea fleets would likely be bottled up by NATO, “so that leaves the Northern Fleet as their power-projection fleet — it’s how they get out into the Atlantic,” the Atlantic Council’s Nordenman said.
While the Northern Fleet has primarily been designed to hold NATO at a distance from Russia, or exact a cost for any push by NATO forces, the increasing ability of its stealthy submarines to slip past American surveillance and pop up off the U.S. Eastern seaboard unannounced is a major concern for policymakers.
“The U.S. Navy needs to have a clear answer as to how they’re going to track these submarines,” said Kofman.
“Iceland is key,” Nordenman added. During the Second World War, U.S. anti-submarine forces in Iceland helped hunt down German U-boat wolf packs that had enjoyed a safe haven in the middle of the ocean, a role the island seems set to reprise.
“It’s the unsinkable aircraft carrier in the middle of the Atlantic that you can fly from,” Nordenman said.



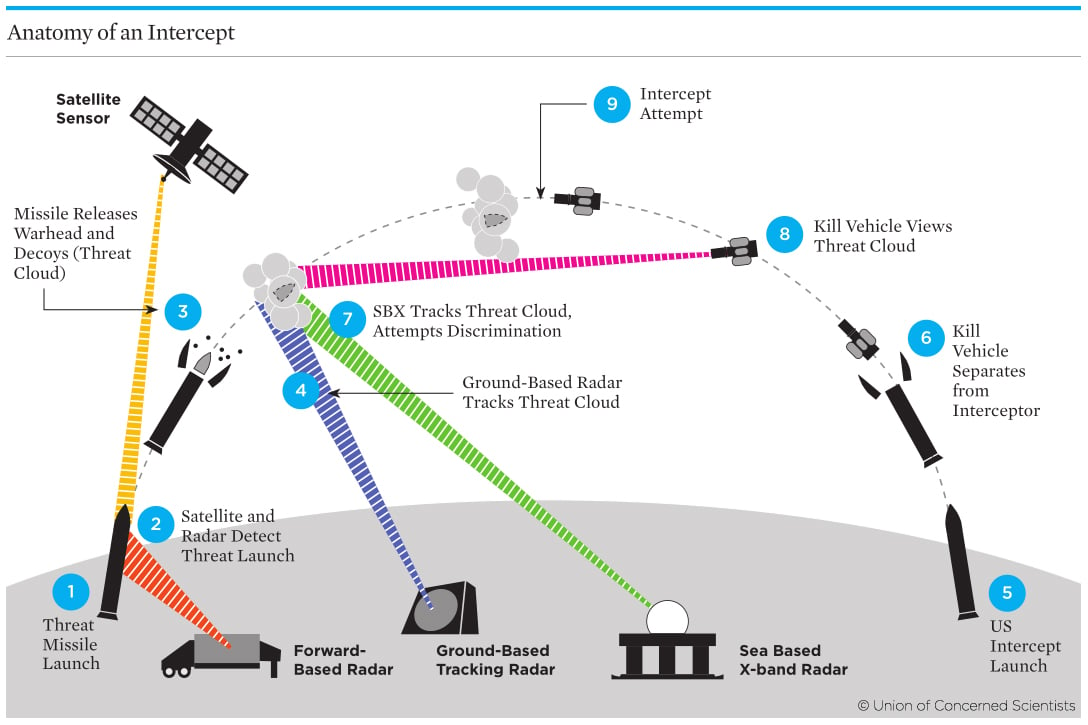 ICBM launches have three distinct phases of flight. During the boost phase, a rocket launches the warhead at high speeds above the atmosphere, where it continues in free-fall through the vacuum of space. The midcourse phase begins with the rocket separating from the warhead, which continues unguided and unpowered, hundreds of miles above the Earth. The reentry, or terminal, phase sees the warhead descend at high speeds back through the Earth’s atmosphere toward the ground.
ICBM launches have three distinct phases of flight. During the boost phase, a rocket launches the warhead at high speeds above the atmosphere, where it continues in free-fall through the vacuum of space. The midcourse phase begins with the rocket separating from the warhead, which continues unguided and unpowered, hundreds of miles above the Earth. The reentry, or terminal, phase sees the warhead descend at high speeds back through the Earth’s atmosphere toward the ground.







