Primer: Amendment IV
The right of the people to be secure in their persons, houses, papers, and effects, against unreasonable searches and seizures, shall not be violated, and no warrants shall issue, but upon probable cause, supported by oath or affirmation, and particularly describing the place to be searched, and the persons or things to be seized. Does this only apply to the Federal government or State government?
Humm read on….
The Mark Zuckerberg apology tour continues. There was the 87 million compromised accounts where privacy was ignored. Then there was the fact that Facebook employees track communications in the private message feature. But why would Facebook contact hospitals asking for patient information? Sheesh, really?
Facebook asked hospitals for anonymized data about their patients for a proposed research project, CNBC reported on Thursday.
The social media platform reportedly intended to compare the data, which included prescription information and illnesses, with its own data that it collected from users, in order to flag users that may need hospital care.
The proposal was paused after Facebook revealed that Cambridge Analytica improperly took data from 50 million of its users’ profiles, and reportedly never made it beyond initial planning stages.
“This work has not progressed past the planning phase, and we have not received, shared, or analyzed anyone’s data,” a Facebook spokesperson told CNBC.
The social media company discussed its plan with organizations including Stanford Medical School and American College of Cardiology.
The data the company would have collected would have been completely anonymous and only available for medical research, according to the report.
Cathleen Gates, the interim CEO of the American College of Cardiology, said in a statement provided to CNBC that Facebook’s proposed data project could help medical research.
“As part of its mission to transform cardiovascular care and improve heart health, the American College of Cardiology has been engaged in discussions with Facebook around the use of anonymized Facebook data, coupled with anonymized ACC data, to further scientific research on the ways social media can aid in the prevention and treatment of heart disease—the #1 cause of death in the world,” she said.
News of the proposed medical data collection comes amid scrutiny over how a British research firm hired by the Trump campaign, Cambridge Analytica, improperly took user data through Facebook.
Controversy over matter has sparked an outcry about Facebook’s data collection and privacy practices.
Lawmakers have been particularly vocal on the issue. Facebook CEO Mark Zuckerberg is set to testify before them on Capitol Hill in hearing on Tuesday and Wednesday during Senate and House hearings about data privacy.
*** Gonna be some interesting hearings on The Hill right? Perhaps Android should be included….
A software developer — who didn’t want to be identified — told News.com.au the social media giant should be the least of our worries, saying Android apps available on Google Play are often “saturated by spyware.”
“Google has given apps a wide open ‘side-door’ to collect personal info to all apps if users simply download and accept the listed permissions,” he said. “Of course, if you notice, the permissions are actually hard to find and Google downplays what they can do.”
He pointed to third-party keyboards as an example.
“Third-party keyboards not only have access to all dangerous permissions, but they also have access to all keystrokes — including account names and passwords,” he said.
We’ve already seen evidence of this blowing up in recent months.
In December, the popular virtual keyboard app AI.type leaked the personal data of over 31 million customers online.
Security researchers at the Kromtech Security Center said the server wasn’t password-protected, allowing anyone to access the company’s massive database.
The app stated that any text entered on its keyboard stays “encrypted and private.”
But researchers found users must allow “Full Access” to all of their data stored on the iPhone, including all keyboard data.
This meant the app would theoretically have access to all your secure usernames and passwords.
“If you look at all the top Android keyboards and look at their requested permissions, it is alarming,” the developer said. “They often can run at start-up, prevent the device from sleeping, and have access to an extensive amount of a user’s personal data.
“They can send encrypted data anywhere in the world without scrutiny.”
A ZDNet investigation into AI.type found the company kept complete records on the device’s IMSI and IMEI number, the device’s make and model, its screen resolution, and the device’s specific Android version.
It also included the user’s phone number, the name of their mobile phone provider, and in some cases their IP address and internet provider.
As the app developer said, third-party keyboards can access the highest level of Android permissions, including personal data like passwords and credit card numbers.
According to ZDNet, one table contained more than 8.6 million entries of text that had been entered using the keyboard, which included phone numbers, email addresses and corresponding passwords, and web search terms.
It found that — for apps that contained a paid and free version, the latter was more concerning; a free version would be more likely to collect data than the paid, which the company would use to monetize with advertising.
“Other keyboards have also been found to have been collecting unsettling data, while none have been removed from Google Play,” he said.
Both the free and paid versions of AI.type are still available on Google Play.
“What is most disturbing to me is that Google apparently blindly ignores this problem, and has built in this open ‘side door’ to facilitate their won apps that collect lots of data on us. If they shut this down, they would shut down their own intrusive apps.”
‘Trading privacy for profits’
Cybersecurity expert, professor Nigel Phair, from the University of Canberra in Australia, shared several of these concerns.
He said it’s surprisingly difficult to log out of a Google service, which explains how they can store your data consecutively over many years.
“What concerns me most is that we’re not making informed decisions,” he told News.com.au. “We get free email, free apps, free directions … but people aren’t consciously making informed consent. It’s not just Google. Apple [does] the same thing.”
But he said Android users were particularly at risk. “If you go into the Facebook app on your Android device and look at the permissions, it’s broader than that of Apple devices, and can include text messages and phone calls. Android is a completely uncurated, open-sourced platform.”
This explains why Android phones were the subject of Facebook’s recent phone-scraping scandal.
So how is it that apps logging your keyboard entries and other data haven’t been shut down yet?
Phair stressed that it comes down to the open permissions laid out in the terms and conditions — which, let’s face it, very few people read. The sheer impracticality of doing so may well be the apps’ strategy.
“There’s nothing illegal about collecting data,” said Phair. “Take Facebook. By signing up, you’re basically agreeing to the terms and conditions, which are basically ‘we can do whatever we want with your data.’ That’s the get-out-of-jail-free card. If you’re going to use our servers, we’re going to collect and sell your data to third-party affiliates.”
In a recent interview, Facebook chief executive Mark Zuckerberg said Facebook’s current problems were partly because the company was so focused on connecting people during its first decade and that it didn’t pay enough attention to potential consequences around privacy.
Last week, technical consultant and web developer Dylan Curran posted a thread on Google and Facebook’s data storing that quickly went viral.
Curran posted photos of the personal data collected by Google (which users are able to download). The file was 5.5 gigabytes — the equivalent of about three million Word documents.
He said it included “every email I’ve ever sent, that’s been sent to me, including the ones I deleted or were categorized as spam.”
“Every image I’ve ever searched for and saved, every location I’ve searched for or clicked on, every news article I’ve ever searched for or read, and EVERY SINGLE Google search I’ve made since 2009.”
He found Google was storing his location every time he turned on his phone, his search history (even if he deleted this), every app and extension he used, his YouTube history, calendar, hangout sessions and the music he listened to.
Spooky stuff.
INDEED!






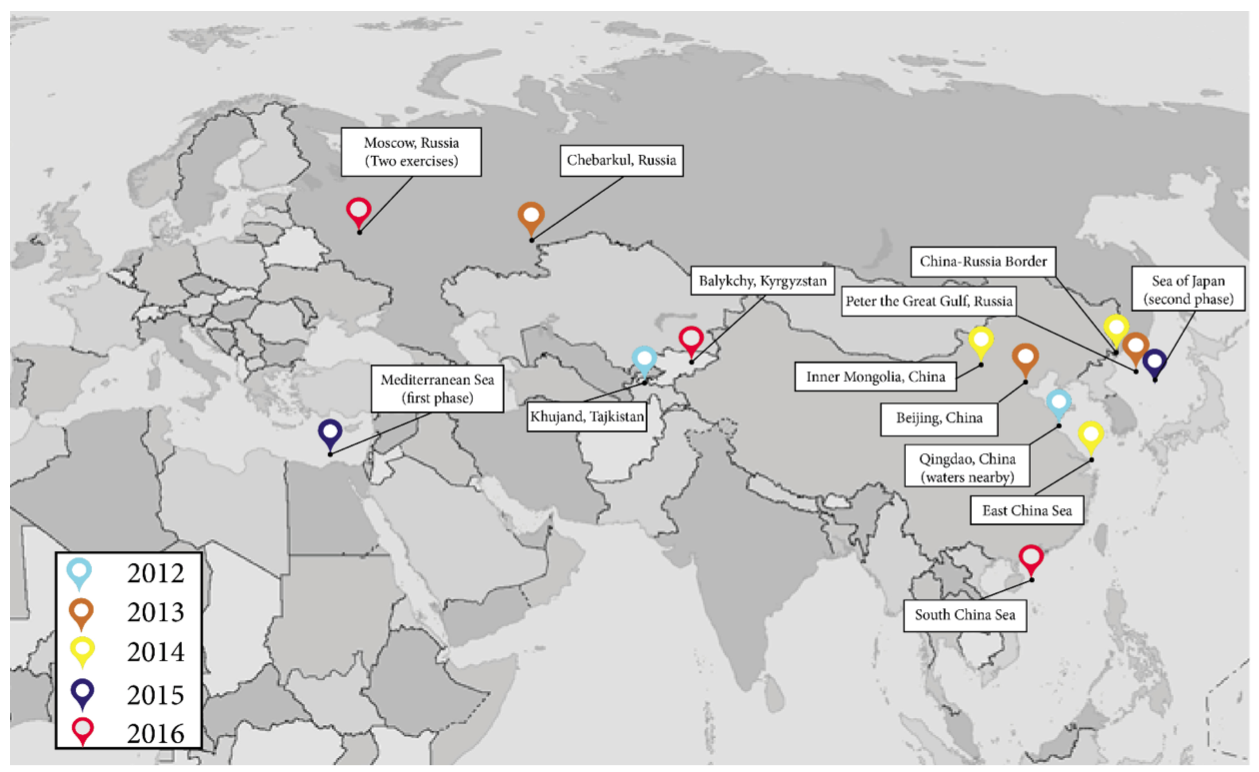 Before Russia and China began their recent series of bilateral exercises, the key tie between Moscow and Beijing was arms sales and military technology cooperation — totaling about $26 billion from 1992 to 2006 — according to estimates cited in the report.
Before Russia and China began their recent series of bilateral exercises, the key tie between Moscow and Beijing was arms sales and military technology cooperation — totaling about $26 billion from 1992 to 2006 — according to estimates cited in the report.
