Okay, let us start with ‘catch and release’. Actually under GW Bush and Michael Certoff, it was a policy of ‘catch and return’. That is until many home countries refused to take back their citizens. During that time, the United States had to have detention facilities to house these people until their case(s) could be worked through the varied systems. Then the left decided there needed to be a lawsuit on the whole detention thing. Yup, it went to the Supreme Court and the decision was a time limit of 6 months of detention and then the case had to be resolved. Well, there were not enough judges, so ‘catch and release’ was tried, hoping they would show up to court….well 80% did not show up. Catch and release now remains.
Now we continue to hear new labels applied to people entering the United States by various methods including across the borders, by air and by ship. In fact more enter by air than any other means and overstay the visa. So, advertisement float around the world and especially in Central and South America on who to contact to get to the United States, how much it costs, what to do, what to say, what to have. Yup, advertisements and sadly that does include our diplomatic posts and embassies in regions of conflict(s). The buzzword today is ‘asylum’. Here is the rub on that…
People applying for asylum must first apply after they are provided an alien status and must prove why they cannot be returned to their home country. Over the years, that process has become twisted an no real proof or approval of the application is necessary especially in states where it is well known there are humanitarian issues. It should also be understood that asylum status is NOT a forever status as conditions can change, thus making it favorable for return to the home country. If that still proves impossible, coordination can be made with other countries that are not of origin to accept these people. President Clinton in 1994 when it came to Haitian and Cuban refugees, he worked a deal to have many go to Suriname, Grenada, Barbados and St. Lucia. Further, he did a remarkable and clever thing, for those wanting to get out of their failed home state, he held hearings for their cases in their home country or aboard ships, such that they would not enter the U.S. in the first place.
The United States has about a 16 year waiting list for cases to get through the immigration court process, that is if and when people do show up.
Now for the international pressures of refugees like from Honduras, Guatemala, Syria, Libya or Iran. The United States is a signatory to the United Nations Protocol Relating to the Status of Refugees. That DOES not force the United States to accept any refugee. It is time for the United States to make an annex condition stating a new and updated policy with regard to foreign nationals and refugees.
Check this: The Illegal Immigrant Reform and Immigrant Responsibility Act of 1996 (IIRIRA, P.L. 104-208) made substantial changes to the asylum process: establishing expedited removal proceedings; codifying many regulatory changes; adding time limits on filing claims; and limiting judicial review in certain circumstances, but it did not alter the numerical limits on asylee adjustments. Okay, so we need a quota system perhaps, well we have quota systems, so we need one that is law and enforced.
While we are at it, we need updated and concise cogent definitions of asylum. It cannot just be the word fear….that does not work or apply anymore. Heck people are borrowing children to fabricate a family and claim fear if forced to return…who is lying to who? Ever wonder why these people dont apply to Mexico, Peru, or Sri Lanka for refugee or asylum status? Just being snarky….Read more details here.
Now let us take a sample country like Honduras.
According to the State Department website, Honduras has some of the highest favorabilty ratings to the United States in the Western hemisphere. Sheesh they should…why?
Several of our federal agencies give big money to Honduras like the Department of Commerce and the Department of Agriculture. Then we have this agency that I watch constantly, The Millennium Challenge. Just in 2013 alone, that MCC gave Honduras $15.6 million to improve public financial management and to create more effective and transparent public-private partnerships. What the heck does that mean? Trade between the United States and Honduras in 2015 was $10 billion.
Now, USAID gives money to Honduras, along with climate change money and military subsidies….oh yeah, did you know we have full control of our own air base in Honduras that we kinda share with the Honduran military? We have an estimated 700-1000 military personnel assigned to Soto Cano Air Base, of which our troops were living in air conditioned huts until about two years ago until we built condos for them….this time with running water.

So, what does our military even do in Honduras? Counter-narcotics….oh wait …isn’t that the reason all these Hondurans are leaving due to violent drug operations? We also do medical stuff like pediatric nutrition and dentisty via our military at Soto Cano, as well as weather prediction, fire protection and aircraft maintenance. From time to time we do patrol(s).
So, ask yourself, if the United States was not located in Honduras, or if USSCOM via Joint Task Bravo was not in Honduras for the last 35 years…what state would that state be in today? Well, in 2011, we should remember Operation Castaway. That was the Honduras version of Operation Fast and Furious. Ah yes, we do have FBI and ATF in Honduras even as recently as 2017 where trafficking weapons from places like North Carolina flows in and out of Honduras.
Perhaps is it time we fix the real problems in these home countries with the money we do send there under our management and begin to stop failed nations like Honduras and the exodus problem causing our homeland problems.
Definitions, policies, laws and agreements need to be cleaned up for sure, country by country, document by document, agency by agency.






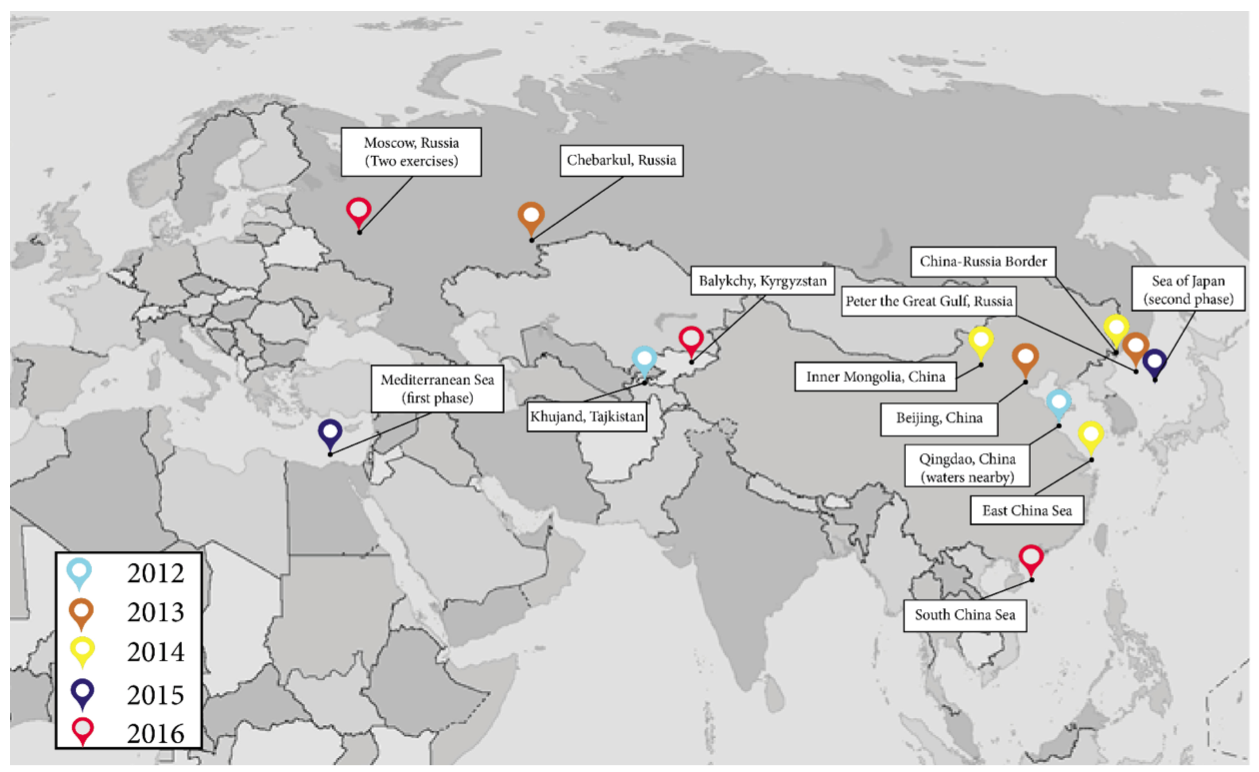 Before Russia and China began their recent series of bilateral exercises, the key tie between Moscow and Beijing was arms sales and military technology cooperation — totaling about $26 billion from 1992 to 2006 — according to estimates cited in the report.
Before Russia and China began their recent series of bilateral exercises, the key tie between Moscow and Beijing was arms sales and military technology cooperation — totaling about $26 billion from 1992 to 2006 — according to estimates cited in the report.
