The author of this site has mentioned for several months the reason for the recent failed missile launches of North Korea. There are two distinct causes and both point to the United States. They are cyber operations and electronic warfare.
Over the past decade of conflict, the U.S. Army has deployed the most capable communications systems in its history. U.S. forces dominated cyberspace and the electromagnetic spectrum (EMS) in Afghanistan and Iraq against enemies and adversaries lacking the technical capabilities to challenge our superiority in cyberspace. However, regional peers have since demonstrated impressive capabilities in a hybrid operational environment that threaten the Army’s dominance in cyberspace and the EMS.
The Department of Defense information network-Army (DODIN-A) is an essential warfighting platform foundational to the success of all unified land operations. Effectively operating, securing, and defending this network and associated data is essential to the success of commanders at all echelons. We must anticipate that future enemies and adversaries will persistently attempt to infiltrate, exploit, and degrade access to our networks and data. A commander who loses the ability to access mission command systems, or whose operational data is compromised, risks the loss of lives and critical resources, or mission failure. In the future, as adversary and enemy capabilities grow, our ability to dominate cyberspace and the EMS will become more complex and critical to mission success.
Incorporating cyberspace electromagnetic activities (CEMA) throughout all phases of an operation is key to obtaining and maintaining freedom of maneuver in cyberspace and the EMS while denying the same to enemies and adversaries. CEMA synchronizes capabilities across domains and warfighting functions and maximizes complementary effects in and through cyberspace and the EMS. Intelligence, signal, information operations (IO), cyberspace, space, and fires operations are critical to planning, synchronizing, and executing cyberspace and electronic warfare (EW) operations. CEMA optimizes cyberspace and EW effects when integrated throughout Army operations. More here.
You can be assured there is acute cooperation between the military and other Federal agencies including the CIA and NSA when it comes to North Korea. What do we know that media is not sharing?
North Korea’s proliferation of missile technology and expertise is another serious concern for the United States. Pyongyang has sold missile parts and/or technology to several countries, including Egypt, Iran, Libya, Burma, Pakistan, Syria, United Arab Emirates, and Yemen.53 Sales of missiles and telemetric information from missile tests have been a key source of hard currency for the Kim regime.
North Korea and Iran have cooperated on the technical aspects of missile development since the 1980s, exchanging information and components.54 Reportedly, scientific advisors from Iran’s ballistic missile research centers were seen in North Korea leading up to the December 2012 launch and may have been a factor in its success.55 There are also signs that China may be assisting the North Korean missile program, whether directly or through tacit approval of trade in sensitive materials. Heavy transport vehicles from Chinese entities were apparently sold to North Korea and used to showcase missiles in a military parade in April 2012, prompting a U.N. investigation of sanctions violations.56 More here.
Security experts and U.S. officials have voiced increasing concern about North Korea’s improving cyberattack capabilities. In March 2013, an attack on the computer systems of several South Korean media and financial institutions disrupted their functioning for days, in one of the most significant cyberattacks in the country’s history; cybersecurity analysts identified North Korean hackers as the culprit.68 The FBI determined that North Korean hackers were responsible for the November 2014 cyberattack on Sony Pictures Entertainment, an intrusion that disrupted the company’s communication systems, released employees’ personal information, and leaked yet-to-be released films. (Some reports speculate that the cyberattack on Sony Pictures could have been an attempt to punish the company for its production of a comedy in which American journalists assassinate Kim Jong-un at the instigation of the Central Intelligence Agency.) Perhaps in response to doubts about the attribution of the cyberattack to North Korea, U.S. officials revealed that the National Security Agency had penetrated North Korean computer networks years in advance of the Sony hacking.69
*** Much has been printed in recent months, the WikiLeaks release of the CIA/NSA toolkit that demonstrates abilities of both agencies ability to intrude and intercept adversaries and allies in the cyber realm. Due to private citizens fear of unauthorized and possible access to personal data and internet activities, many Americans are angry. That anger is not misplaced, however, consider, do we want our agencies to have cyber skills to penetrate such rogue regimes as North Korea, Syria, Iran or militant factions such as al Qaeda and Islamic State? The answer is likely yes.
The UK Sunday Times reports: ”
A missile test by North Korea that failed seconds after launch may have been sabotaged by a US cyber-attack, a former foreign secretary has said.
The US said a ballistic missile “blew up immediately” after firing near the port of Sinpo on the east coast early today.
“It could have failed because the system is not competent enough to make it work, but there is a very strong belief that the US through cyber methods has been successful on several occasions in interrupting these sorts of tests and making them fail,” Sir Malcolm Rifkind, the former foreign and defence secretary, told the BBC.”.
*** The UK Telegraph tells us in part: U.S. Pacific Command detected and tracked what it assessed to be a North Korean ballistic missile launch at 11:21 a.m. Hawaii time (2121 GMT) on Saturday, said U.S. Navy Commander Dave Benham, a spokesman for Pacific Command.
“The missile blew up almost immediately. The type of missile is still being assessed,” he said.
It was launched from a base at Sinpo, a port city on the North Korean east coast. The North’s previous attempted missile launch, on April 5, also suffered an in-flight failure before the weapon crashed into the Sea of Japan. Experts have suggested that the United States may be carrying out “left-of-launch” attacks on the missiles using electromagnetic propagation or cyber attacks, including through infected electronics aboard the weapon that confuse its command and control or targeting systems. More here.
*** So, while we tend to panic and push back on the cyber toolkit of Federal agencies which WikiLeaks tells us to do, perhaps we should look wider and deeper to the positive affects of those operations as Japan and S. Korea are most at risk if North Korea is remotely successful. Can and do Federal agencies exploit cyber tools and electronic warfare against American citizens and is there evidence of abuse? Not so much yet, but this site does invite readers to offer evidence.
*** Some other items of interest with regard to North Korea:
- Chinese troops are always stationed in the northeast near North Korea, and Yun Sun, a senior associate with the East Asia Program at the Stimson Center, told Business Insider that “Chinese troop movements happen often along that border” when North Korean nuclear and missile provocations seem imminent.
“When North Korea acts up with some sort of provocation, the Chinese in the past have moved their troops to reinforce their deployments in the northeast for military preparedness,” Yun said.
“On the other hand,” Yun said, “I think it does signal that the Chinese are concerned about a potential escalation, or even potential conflict” between the US and North Korea, as North Korea plans a nuclear test and the USS Carl Vinson aircraft carrier pulls up to Korea’s coast.
- North Korea forces citizens to work outside the country in often slave labor conditions and the regime keeps 85% of the revenue. “150,000 N.Koreans Sent to Slave Labor Abroad,” Chosun Ilbo, November 13, 2014. This often amounts to $1 billion a year in revenue.
- North Korea selling arms to Hamas and advises on tunnel systems.
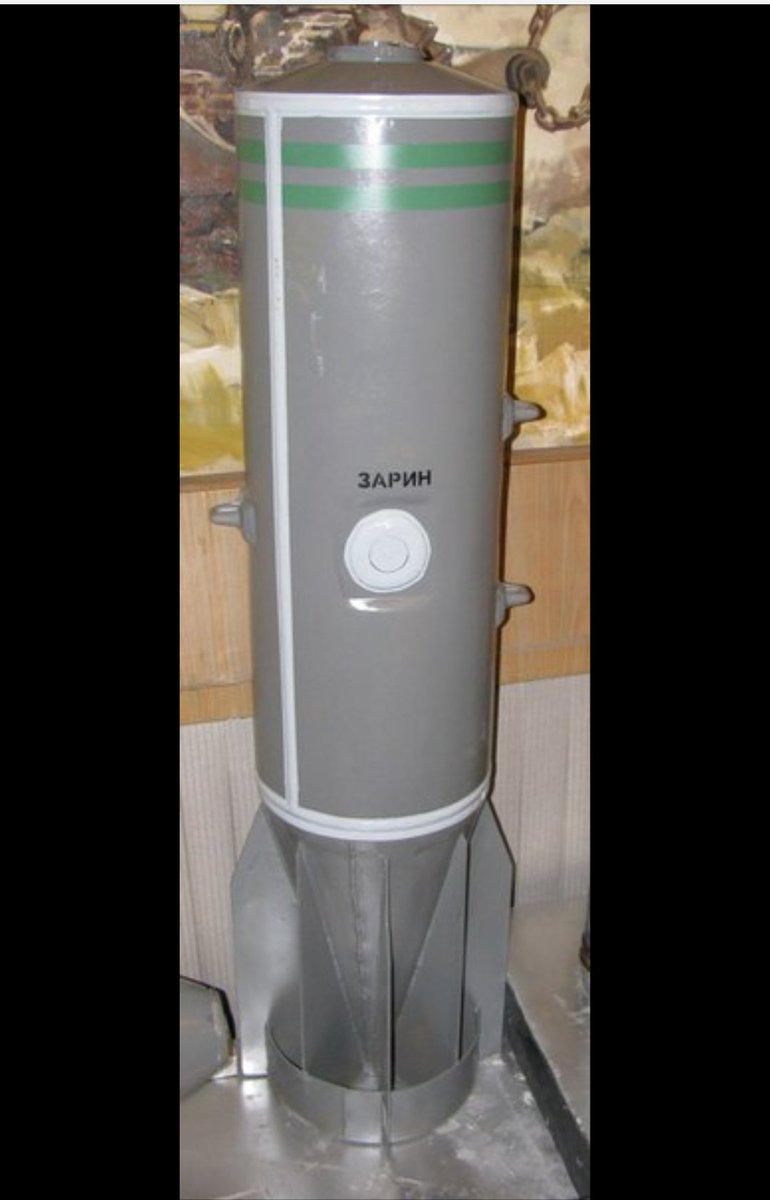
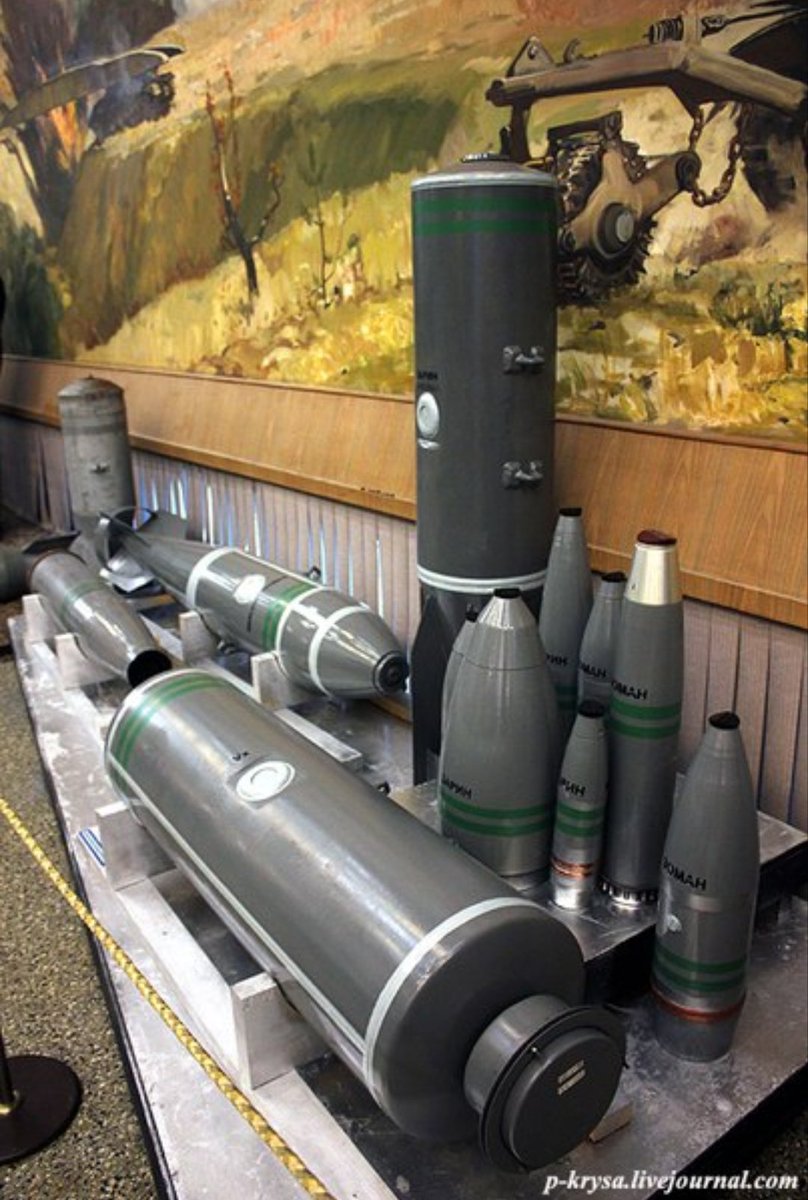
- North Korea has a sizeable inventory and robust program in both chemical and biological weapons. While the DPRK possesses considerable capabilities to deliver CW agents, it is unclear whether comparable munitions are available to deliver BW agents. Although the DPRK has advanced missile technology, the fragile nature of biological agents complicates the task of using missiles as a means of delivery and dispersal. While the ROK government has estimated that half of the DPRK’s long-range missiles and 30 percent of its artillery pieces are capable of delivering chemical or biological warheads, it is not known whether biological payloads would survive and be effectively dispersed by these missiles. More here.