Remember? During the Christmas holiday in 2015, so you easily could have missed the news or just forgotten it due to spiked eggnog.
Washington (AFP) – Iran sent a major shipment of low-enriched uranium materials to Russia on Monday, a key step in Tehran’s implementation of this year’s historic nuclear accord with world powers.
The United States hailed the move, which Secretary of State John Kerry said marked “significant progress” in Tehran’s fulfillment of a deal to stop it developing nuclear weapons.
The Russian foreign ministry confirmed the report after Ali Akbar Salehi, head of Iran’s Atomic Energy Organization, told the ISNA news agency: “The fuel exchange process has taken place.”
According to ISNA’s report, Iran had sent 8.5 tons of low-enriched nuclear material to Russia and received “around 140 tons of natural uranium in return.”
State Department spokesman Mark Toner described the cargo as a 25,000-pound “combination of forms of low-enriched uranium materials” including five and 20 percent enriched uranium, scrap metal and unfinished fuel plates. More here.
Kerry said that Iran’s shipment to Russia had already tripled the amount of time it would take to produce enough fuel for a bomb from two or three months up to six or nine.
And he dubbed it “a significant step toward Iran meeting its commitment to have no more than 300 kilograms of low-enriched uranium by Implementation Day.”
Now the question is, where is it now? Was this transaction for real in the first place? Any congressional investigation? Ambassador Stephen Mull before Congress stated the following:
Iran shipped out almost all of its enriched uranium stockpile. Pre-JCPOA, Iran had approximately 12,000 kilograms of enriched uranium. Now, Iran can have no more than 300 kilograms of up to 3.67% enriched uranium for the next 15 years. This, combined with Iran’s dismantlement of two-thirds of its centrifuges, has effectively cut off Iran’s uranium pathway to a nuclear weapon.
Iran removed the core of its Arak reactor and rendered it inoperable by filling it with concrete. This cut off the path by which Iran could have produced significant amounts of weapons grade plutonium. Now, the Arak reactor will be redesigned, in cooperation with a working group established under the JCPOA, ensuring that the reactor is used solely for peaceful purposes going forward. Read more here to see how the Obama administration punked the whole story and then read below. Has anyone asked Norway? They assisted.
The U.S. Has No Clue Where Iran’s 8.5 Tons Of Enriched Uranium Are
At a February 11, 2016 hearing before the U.S. House Foreign Affairs Committee, Amb. Mull acknowledged that Washington had lost track of the enriched uranium, which, he said, was now “on a Russian ship, in Russian custody, under Russian control” – that is, no longer under IAEA oversight.
Indeed, in response to Rep. Chris Smith’s (R-NJ) question at the hearing, “Do we have any on site accountability? Can we go and verify ourselves, or?” Amb. Mull replied: “We cannot.” Rep. Smith said: “We cannot. Who does?” to which Amb. Mull replied: “…Russia is responsible for maintaining access and controls.”
Rep. Smith then asked, “Where has it been put?” and Amb. Mull answered: “It has not been fully, according to our information it has not yet been decided where exactly Russia will put this.”
To Rep. Smith’s question “But where did it go? I mean it has to be somewhere,” Amb. Mull replied: “…I believe, if it has not arrived yet, it will very soon.”
In reply to Rep. Smith’s comment that “we are then trusting the Russians to say that they have it under their purview, that they are watching it? I mean they are so close to Iran, they have doubledealed us and especially the Middle East, the Syrians, I don’t know why we would trust them. Could you tell us where it is going?” Amb. Mull replied: “That is a Russian Government responsibility to decide where it goes. We do not have concerns about Russian custody of this material. What is important in this deal is will it go back to Iran? And I can guarantee there are sufficient controls in place that if one piece of dust of that material goes back into Iran we are going to be aware of it.”
Rep. Smith then asked, “But again, can the IAEA go to that ship and verify that it is there and follow it as it goes to its final resting place?” To this, Amb. Mull responded: “IAEA has different monitoring arrangements with each, each country in the world.” (As noted, Mull had stated that the uranium was now in “Russian custody, under Russian control” – that is, not under IAEA oversight.)
To Rep. Smith’s statement that “… it is not even in a place, it is not in any city that you say. It is not in any, it is not somewhere in Russia that we could say there it is. We don’t even know where it is,” Amb. Mull replied: “The IAEA verified the loading of all of this material…”
In response to Rep. Smith’s pointing out that “loading and where does it end up is very important,” Amb. Mull said, “That is the Russian Government’s responsibility to decide where it goes.”
Rep. Smith concluded, “That is a flaw, in my opinion.”
***
Watching that ship, the Mikhail Dudin….
Norwegian participation
Norway played a key role in the agreement by helping ensure that Iran’s enriched uranium was replaced by natural uranium. Oslo paid some $6 million for transporting 60 tons of natural uranium from Kazakhstan to Iran by plane.
Rune Bjåstad with the press office of the Norwegian Ministry of Foreign Affairs says to the Independent Barents Observer that Norway only had inspectors following the transport of natural uranium to Iran, not the transport of material out.
“Regarding the enriched uranium transported out of Iran, there were no Norwegian representatives present. The control was done by a team of inspectors from the IAEA,” Bjåstad informs.
He says Norwegian representatives were in contact with the inspectors from IAEA who participated in the packing and sealing of the cargo that left Bushehr. The shipment from Iran to St. Petersburg is not paid with Norwegian money.
Voyage route across Scandinavian waters confirmed
Director of Norway’s Radiation Protection Authorities, Ole Harbitz, confirms in an SMS to the Independent Barents Observer that the cargo is en route to St. Petersburg.
It was U.S. Secretary of State, John Kerry, who in a statement on December 28 confirmed that the shipment takes place on board the vessel “Mikhail Dudin”, The New York Times reported.
Kerry said the cargo includes the uranium that is closest to bomb-grade quality, enriched to 20 percent purity.
The agreement, where Norway played a key role, can in the longer run indirectly open for increased transport of highly radioactive spent nuclear fuel along the coast of Norway to the Arctic.
With the deal ensuring no nuclear weapons projects can continue, Iran can again continue to expand its civilian nuclear energy program.
More spent nuclear fuel to sail outside Norway
Simultaneously as Norway in secret assisted with the transportation of natural uranium to Iran, Russia started to construct two more civilian nuclear reactors at existing Russian built Bushehr nuclear power plant. The plant will get uranium fuel from Russia.
That fuel will later have to be shipped back to Russia.
Currently, Murmansk on Russia’s Arctic Barents Sea coast is the port used to take back spent nuclear fuel arriving from other countries. Over the last three years, several shipments of spent nuclear fuel from Soviet built research reactors in Europe have been sailed back to Russia along the coast of Norway to Murmansk. Like in September 2014, when “Mikhail Dudin” secretly transported a load of highly enriched uranium from Poland to the Atomflot base north of Murmansk.
St. Petersburg is the port used when other kinds of radioactive material, like the enriched uranium from Iran, are imported back to Russia.
Back to Russia for reprocessing
Iran is not the only country where Russia’s state nuclear corporation Rosatom will built new nuclear reactors. Deals are signed or under negotiations with China, India and Vietnam. From China, spent nuclear fuel in return to Russia can be sent by railway, but all shipments from Iran, India and Vietnam will have to go by sea.
Rosatom is currently building 19 reactors abroad and has increased its foreign contracts by 60 percent over the last two years to $66,5 billion.
Uranium fuel is normally in the reactors for 3-4 years before being replaced. Then, the fuel will have to be cooled for some years in an on-site pool before it can be transported back to Russia for reprocessing.
The reason why Murmansk is used as import harbor for spent nuclear fuel is because of its suitable infrastructure for loading the special designed containers directly from vessels to railway wagons at Atomflot, the repair base for Russia’s fleet of civilian nuclear icebreakers. From Murmansk, the wagons take the uranium fuel to the Mayak plant north of Chelyabinsk in the South Urals where Russia has its reprocessing plant.
Anyone still trusting all of this years later? Anyone?

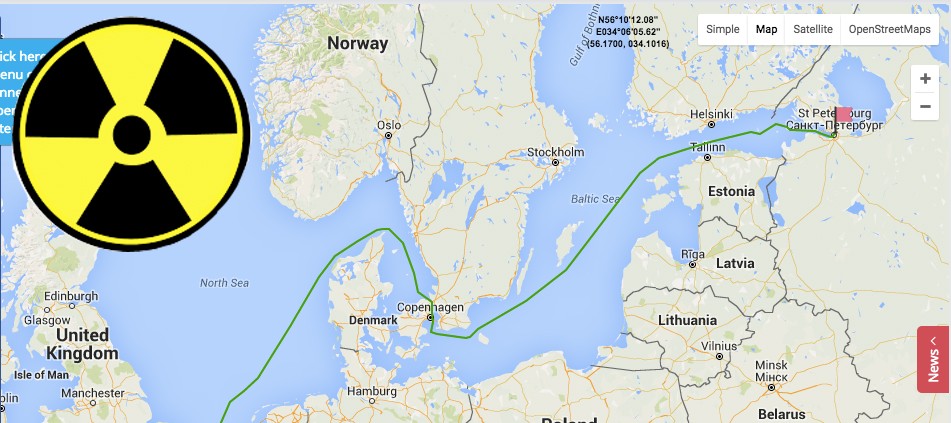



 Photo: Alex Brandon AP
Photo: Alex Brandon AP