Staff Sgt. Stacy L. Pearsall/USAF
Staff Sgt. Stacy L. Pearsall/USAF
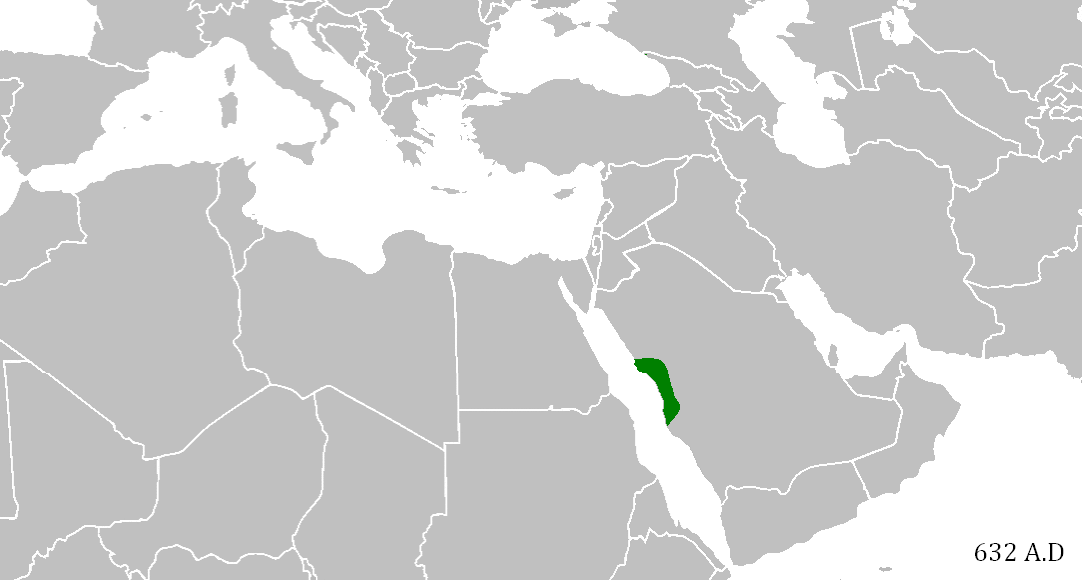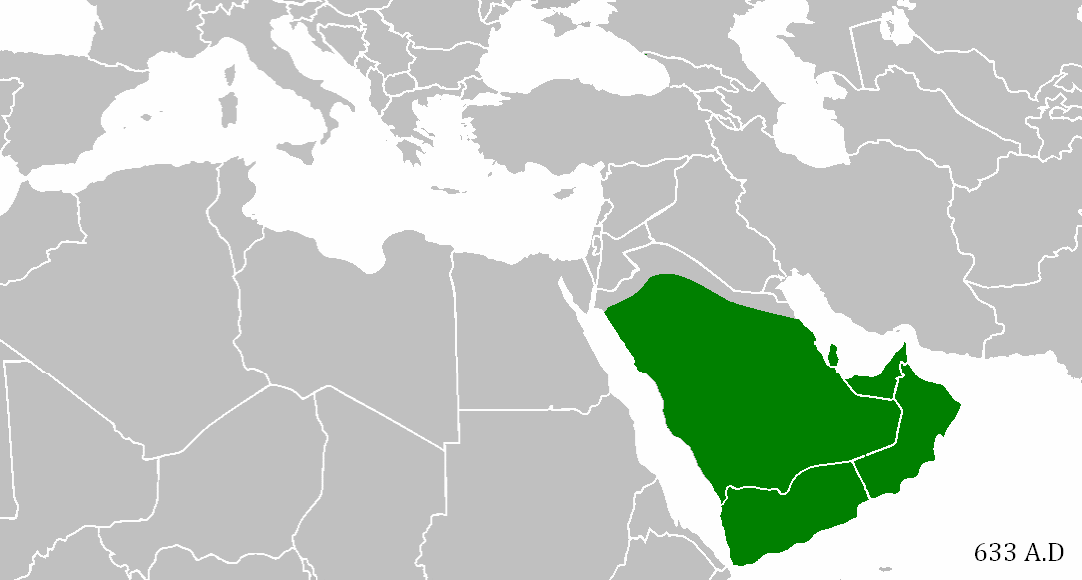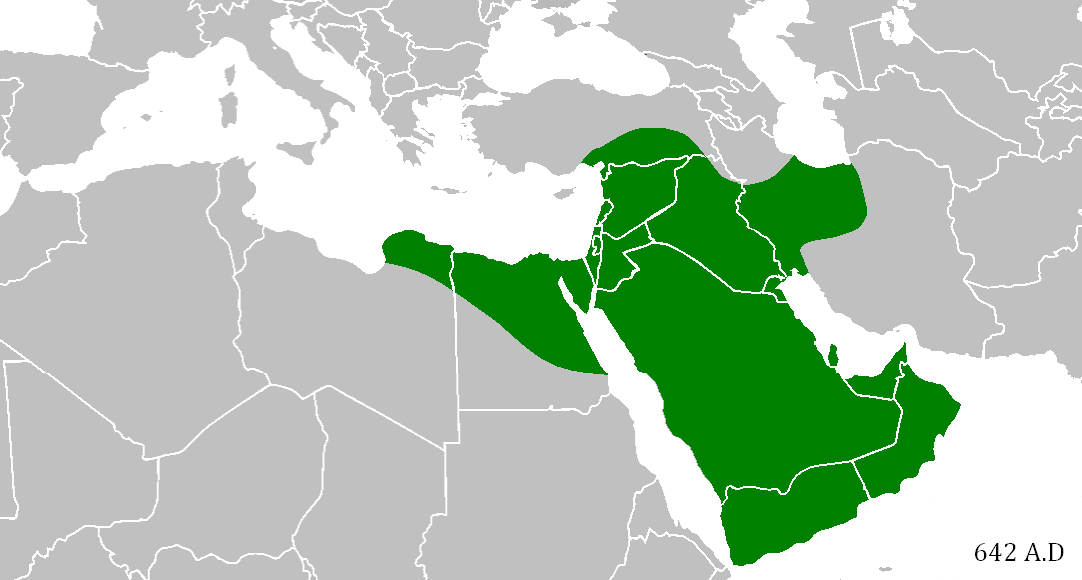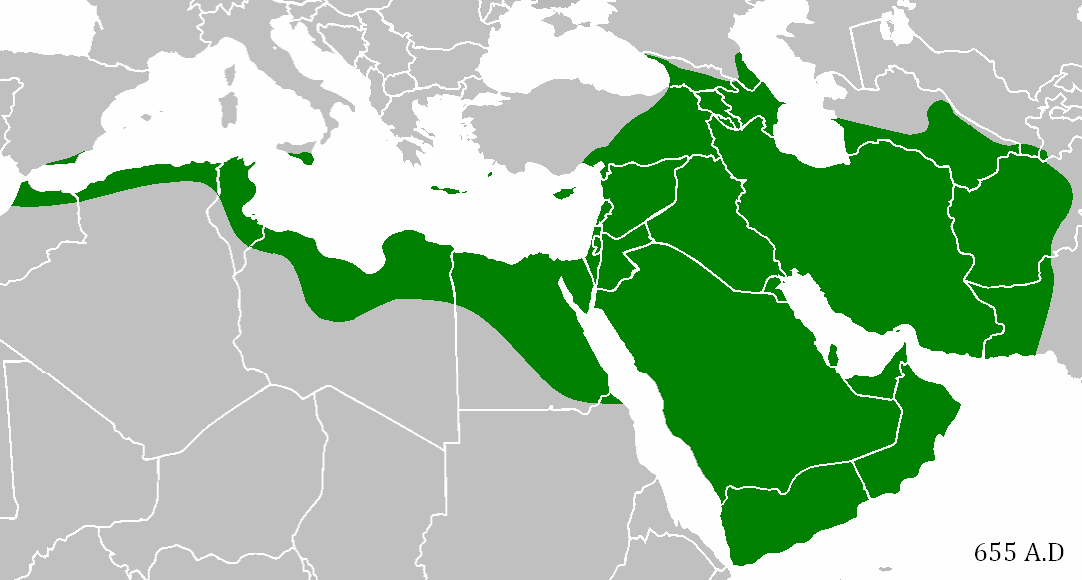
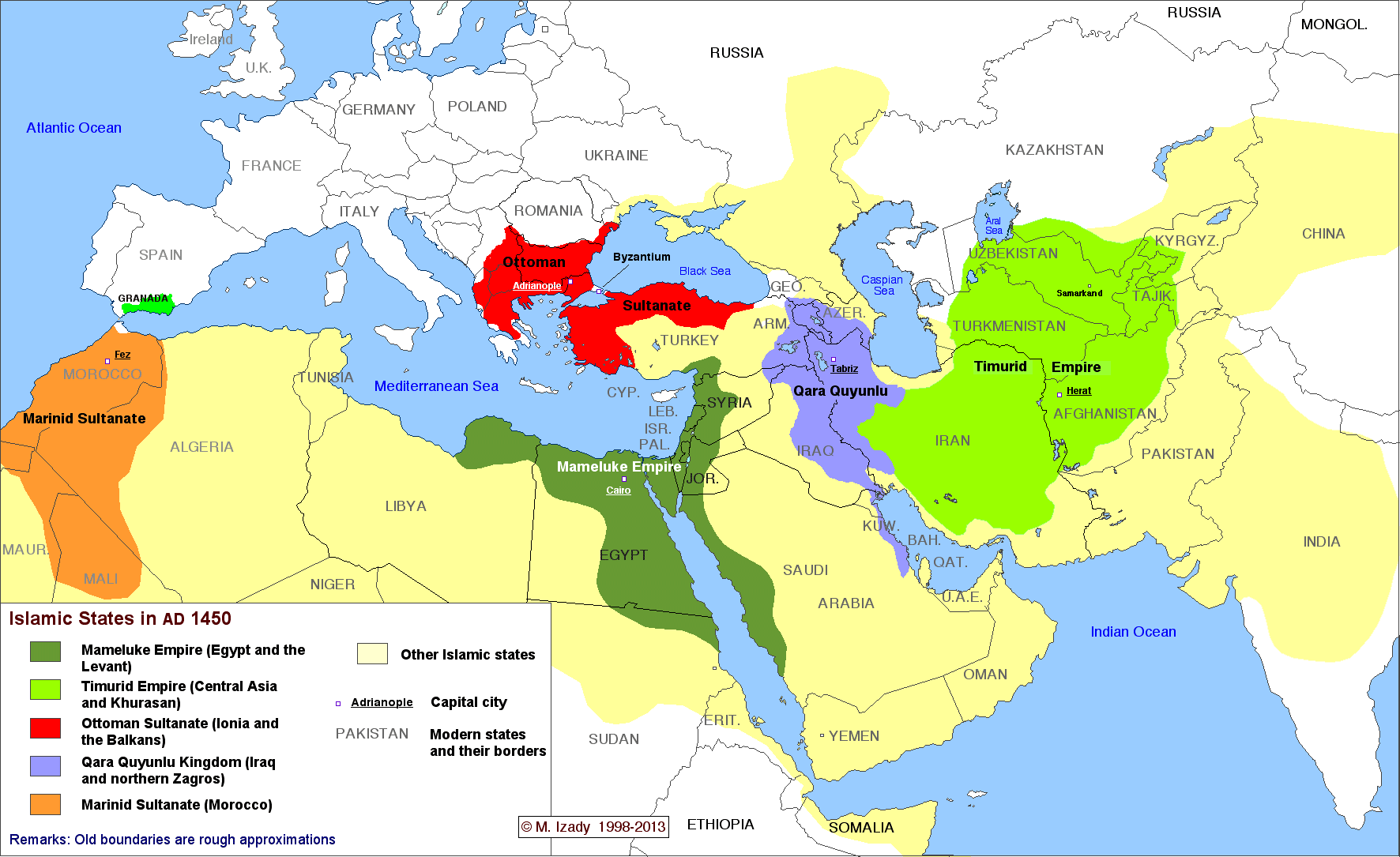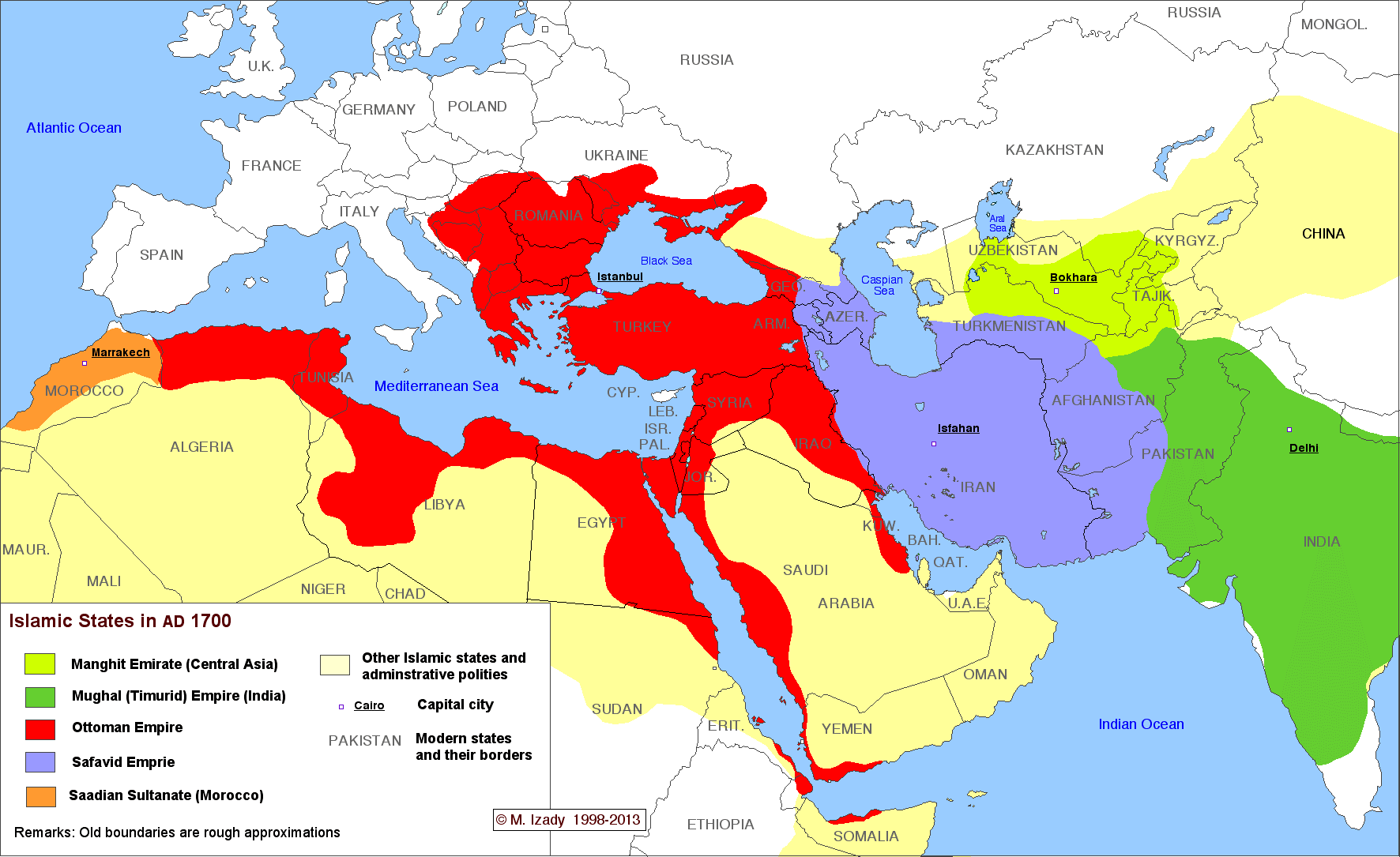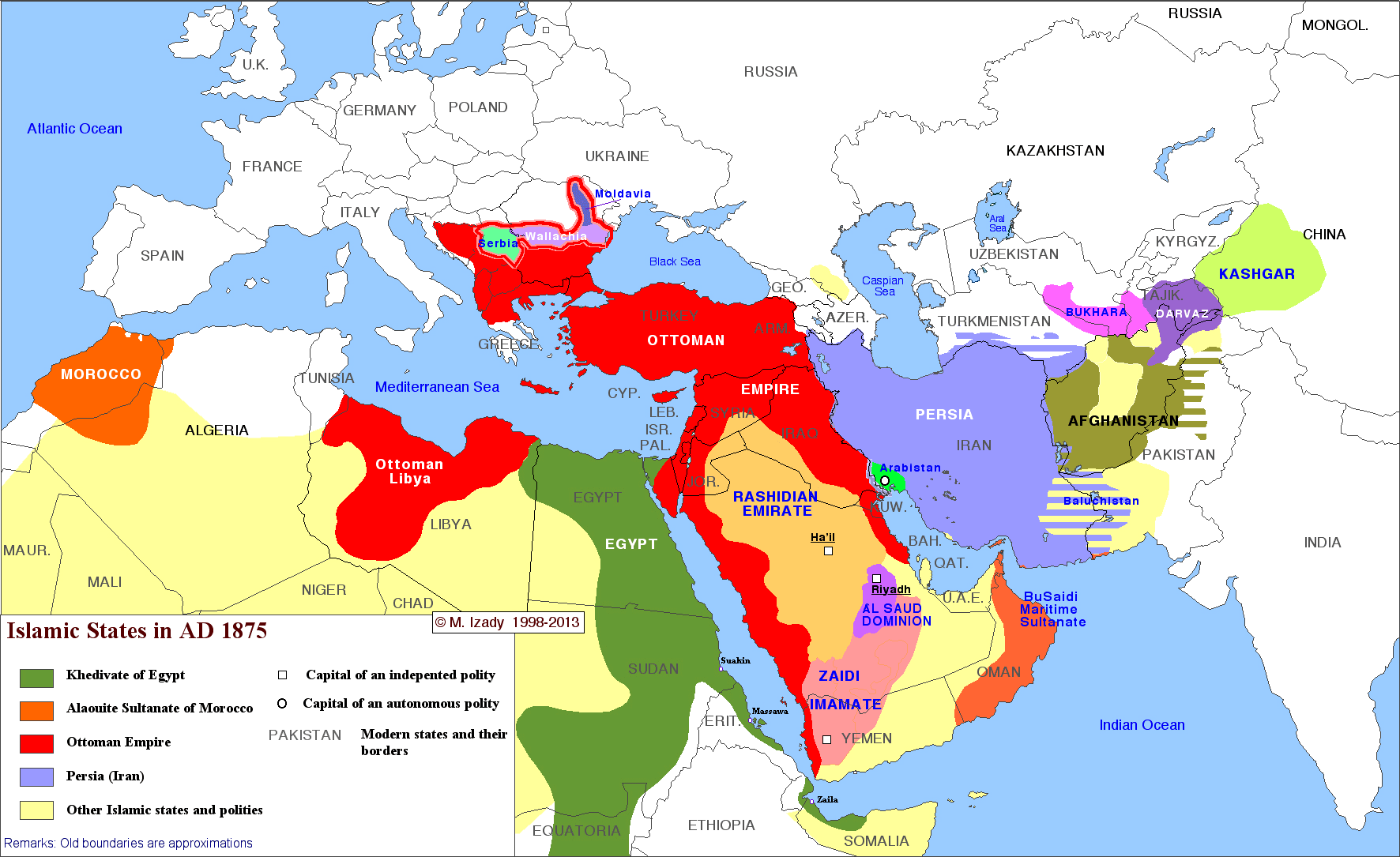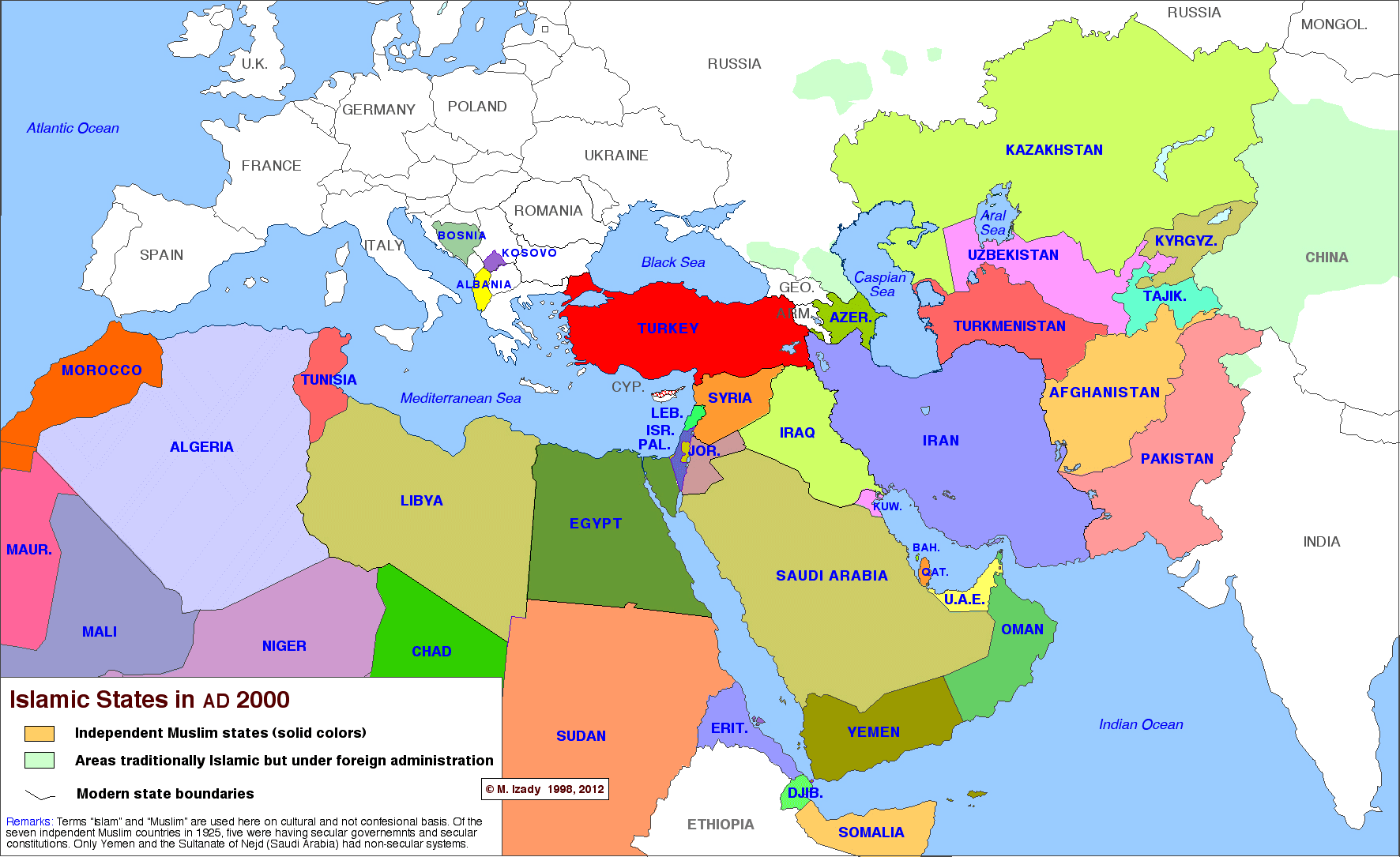
TechInsiders: There’s an unseen world war that has been fought for years with no clear battle lines, few rules of engagement, and no end in sight.
But it’s not a shooting war; not a war where combatants have been killed or wounded — at least not yet.
It’s a war that pits nations against each other for dominance in cyberspace, and the United States, like other nations employing professional hackers as “cyber soldiers,” sees it as a battlefield just like any other.
“It’s like an operational domain: Sea, land, air, space, and cyber,” Charlie Stadtlander, chief spokesperson for US Army Cyber Command, told Tech Insider. “It’s a place where our presence exists. Cyber is a normal part of military operations and needs to be considered as such.”
As US military leaders warn of the growing progress of Russia, China, and North Korea in cyberspace, the Pentagon has ramped up its own efforts in what it calls the “cyber domain” after the release of a new cyber strategy in April 2015.
“This ephemeral space that’s all around us, literally, is a space where operations can be performed against us,” Frank Pound, a program manager who leads DARPA’s “Plan X” cyber warfare platform, told Tech Insider. “And how do we defend against that? How do we detect that?”
Building a cyber army
In its cyber strategy, the military proposed 133 teams for its “cyber mission force” by 2018, 27 of which were directed to support combat missions by “generating integrated cyberspace effects in support of … operations.” (Effects is a common military term used for artillery and aircraft targeting, and soldiers proclaim “good effect on target” to communicate a direct hit).
The cyber mission force will comprise some 4,300 personnel. But only about 1,600 of those would be on a “combat mission team” that would likely be considered to be taking an offensive hacking role. They are up against China’s own “specialized military network warfare forces,” North Korea’s secretive Bureau 121 hacker unit, other nation-states, hacktivists like Anonymous, and criminal enterprises alike.
They have been further tasked with breaking into the networks of adversaries like ISIS, disrupting communications channels, stopping improvised explosive devices from being triggered through cellphones, or even, as one Marine general put it, just “trying to get inside the enemy’s [head].”
Online hacks can lead to offline outcomes, and the military has become keenly aware of that power. In 2009, the US and Israel reportedly infected Iranian computers with the Stuxnet malware that destroyed roughly one-fifth of the country’s nuclear centrifuges. And as recently as February, hackers were used against ISIS as others fought on the ground, quite possibly for the first time ever.
“These are strikes that are conducted in the war zone using cyber essentially as a weapon of war,” Defense Secretary Ash Carter told NPR. “Just like we drop bombs, we’re dropping cyber bombs.”
As one Army officer said during a 2015 training exercise, the cyber war seems to just be getting started: “Future fights aren’t going to be guns and bullets. They’re going to be ones and zeroes.”
 Brian Rodan/US ArmySoldiers work together during a training exercise in 2011.
Brian Rodan/US ArmySoldiers work together during a training exercise in 2011.
‘Prepping the battlefield’
That the Pentagon would employ specialists to defend itself in cyberspace is not surprising, since government and military systems are attacked regularly by nations trying to read soldier’s email, or others who want to uncover personal details on millions who undergo background checks for security clearances.
But the defense of networks — while still an important function — has been supplanted in some cases by an offensive strategy. That is, soldiers hacking into computers overseas for intelligence or to disrupt the enemy on the battlefield — a kind of digital tit-for-tat.
“If there’s something that you can do to prep the battlefield before a kinetic attack or to disrupt defenses during kinetic attacks, why wouldn’t a combatant commander turn to that?” Stadtlander said.
Stadtlander couldn’t talk about ongoing operations that Army Cyber Command is involved in, mainly due to the unique nature of cyber warfare. An enemy who knows the US is developing a next-generation fighter jet might develop something in response that could take years, but with a cyberattack, a fix can be developed sometimes within days.
“The unique thing about cyber activity and defense is you’re talking about building a couple thousand lines of code or having a certain electronic device, or some sort of cyber capability. And just based on the nature of this space, a lot of times it can only be used once,” he said. “Once it’s known … it’s no longer a viable tool.”
Still, some insight into what the US military is capable of can be found within its own training manuals, presentations, and the few news stories by the military’s own writers. And it’s likely that hackers with Army Cyber Command, subordinate to US Cyber Command and NSA, benefit from top secret initiatives to infect “millions” of computers with malware in an effort aimed at “owning the net.”
“Denying the ability to coordinate, communicate, and assess,” Stadtlander said. “That’s an advantage that we might be able to leverage.”
Inside the Army’s cyber warfare ‘Bible’
Perhaps one of the most important publications on cyber warfare was released with little fanfare in Feb. 2014. Known as Army Field Manual 3-38 Cyber Electromagnetic Activities, it proclaimed itself as the “first doctrinal field manual of its kind,” unifying a number of other publications on network operations, electronic warfare, and intelligence into one 96-page document.
In FM 3-38, the Army defined offensive cyberspace operations as actions “intended to project power by the application of force in or through cyberspace,” while noting they are to be carried out in support of command objectives and within legal frameworks.
But what can soldiers do in cyberspace that can affect what happens on the battlefield? Quite a bit, according to the manual.
 US Army
US Army
“A cyberspace attack may be employed in conjunction with” other methods of attack “to deceive, degrade, destroy, and disrupt a specific enemy integrated air defense system or enemy safe haven,” it says.
As an example, the manual offers an early warning radar site as a target which, if soldiers can get inside the network, could possibly be destroyed or degraded.
That’s just what students trained for during an exercise in March, according to the Fort Gordon Globe. Acting just as they would on the battlefield, cyber soldiers patrolled to their objective — a simulated enemy air defense control system — then searched for their target’s wireless network so it could be exploited or neutralized.
There’s little need for stealth coating on aircraft when a guy behind a computer can disable the radar site for you. The manual also offers other systems Army hackers may consider breaking into, such as enemy telephone networks, servers, and smartphones.
“Even if you think about the way that IEDs are triggered,” Stadtlander said, using the acronym for improvised explosive devices. “Or an adversary’s [intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance], a lot of these are done through electronics and with internet connections.”
Getting into the Army’s ‘hacker university’
Located just southwest of Augusta, Georgia is Fort Gordon, an Army installation that brings together most of the service’s cyber warriors under one roof. In 2013, the Army chose the site as the home base of its Cyber Command after the unit was established in 2010.
Also home to a 604,000 square foot operations center for the National Security Agency, Gordon is where cyber warriors are taught their craft at what the Army calls its Cyber Center of Excellence. But before they get to the military’s “hacker university,” enlisted soldiers need to score high technical scores on the military entrance exam, and sign on for five years of service, instead of the normal four-year tour.
 US ArmyInsider Fort Gordon’s Cyber Operations Center.
US ArmyInsider Fort Gordon’s Cyber Operations Center.
Due to the classified nature of their work, cyber training is often conducted in secure compartmented information facilities (SCIFs) where cell phones and other outside recording devices are not allowed, and all soldiers will have to obtain a Top Secret clearance prior to being assigned to their unit.
Soldiers go through a lengthy period of training after basic training: Six months spent at the Navy’s Center for Information Dominance in Pensacola, Florida followed by six months at Fort Gordon.
Army officers go through their own training program at the Georgia base, called Cyber Basic Officer Leader Course. The course takes nearly nine months to complete and is the longest officer training program in the Army.
Enlisted soldiers train with members of all military branches over six months at the Navy’s Cyber Analysis Course, according to Bloomberg. Since students can come from a variety of skill sets and backgrounds, the first two-thirds of classroom time focuses on basic programming, mathematics, and how networks and operating systems function. But later on they learn the steps to research and infiltrate targets, defend networks, and even hack a simulated network with Metasploit, a common tool hackers have used since its release in 2004.
Meanwhile, officers receive similar training, though their position merits other coursework in leading operations as opposed to carrying them out. Though a cyber officer can likely step in and be more than capable, given the certifications they obtain, to include Cisco’s Certified Network Associate (CCNA) and the independent Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP) credential.
“They are really valuably trained after that [schooling],” Stadtlander said.
So valuable in fact that the Army is seeing a challenge in retaining its talent from heavyweights in Silicon Valley.
Is hacking considered an ‘act of war’?
 via Flickr
via Flickr
“There is no international standing or framework that is binding over any one nation-state in terms of offensive cyber operations,” Bradley P. Moss, a national security lawyer, told Tech Insider. “It’s whatever rules we put in place for ourselves.”
In essence, the US, China, Russia, and others are operating in a sort-of “digital Wild West” with few overarching guidelines outside of the Law of War that predates our interconnected world.
Cyber warfare continues unabated because there is no governing body such as the United Nations telling nations not to hack one another. Not that that would necessarily make a difference, as a 2014 UN report criticized mass surveillance programs employed by NSA and others as violating privacy rights “guaranteed by multiple treaties and conventions,” The Intercept reported.
Still, Moss explained that nations are less concerned with the legalities of hacking each other, and instead, worry about the potential diplomatic and political fallout should they be exposed.
“More or less, we all engage in some manner of warfare these days, we just don’t go to ‘war’ over it,” Moss said.
How foreign nations would likely respond to being hacked by the US is something that is considered before any offensive operation, according to a top secret presidential policy directive leaked by ex-NSA contractor Edward Snowden.
The document, made public in 2013, listed cyber attacks resulting in “loss of life, significant responsive actions against the United States, significant damage to property, serious adverse US foreign policy consequences, or serious economic impact” as requiring presidential approval.
And for US military hackers who may be on a battlefield in Iraq, Syria, or elsewhere, their self-imposed rules for cyber attacks are clear:
“Military attacks will be directed only at military targets,” reads the Pentagon’s cyberspace operations document.
 US Army
US Army
But what of cyber attacks that have potentially devastating effects on foreign nations, such as US-made worms that cause nuclear centrifuges to fall apart, or alleged Russian-made malware that knocks out power and heat to people in the dead of winter?
Are these “acts of war”?
“From a strictly legal matter, you could designate the US Army hacking the Russian Army’s [computer] system as an act of war,” Moss said. “Just as much as if we were to have infiltrated and damaged a Russian bomber, that would be an act of war.”
But, he added: “There’s nothing that necessarily stops us, except the political and diplomatic ramifications.”
Hostile groups are acquiring the capability to launch devastating attacks, warns Hannigan Credit: TELEGRAPH
ISIS sent out a message on encrypted chat app Telegram with instructions to avoid being hacked Photo: Huffington Post UK