(AP) — A leaked recording of an exchange between an Iranian air-traffic controller and an Iranian pilot purports to show that authorities immediately knew a missile had downed a Ukrainian jetliner after takeoff from Tehran, killing all 176 people aboard, despite days of denials by the Islamic Republic.
Ukraine’s President Volodymyr Zelenskiy acknowledged the recording’s authenticity in a report aired by a Ukrainian television channel on Sunday night.
In Tehran on Monday, the head of the Iranian investigation team, Hassan Rezaeifar, acknowledged the recording was legitimate and said that it was handed over to Ukrainian officials. A transcript of the recording, published by Ukrainian 1+1 TV channel, contains a conversation in Farsi between an air-traffic controller and a pilot reportedly flying a Fokker 100 jet for Iran’s Aseman Airlines from Iran’s southern city of Shiraz to Tehran.
“A series of lights like … yes, it is a missile, is there something?” the pilot calls out to the controller.
“No, how many miles? Where?” the controller asks.
The pilot responds that he saw the light by the Payam airport, near where the Guard’s Tor M-1 anti-aircraft missile was launched from. The controller says nothing has been reported to them, but the pilot remains insistent.
“It is the light of a missile,” the pilot says.
“Don’t you see anything anymore?” the controller asks.
“Dear engineer, it was an explosion. We saw a very big light there, I don’t really know what it was,” the pilot responds.
The controller then tries to contract the Ukrainian jetliner, but unsuccessfully.
Publicly accessible flight-tracking radar information suggests the Aseman Airlines aircraft, flight No. 3768, was close enough to Tehran to see the blast.
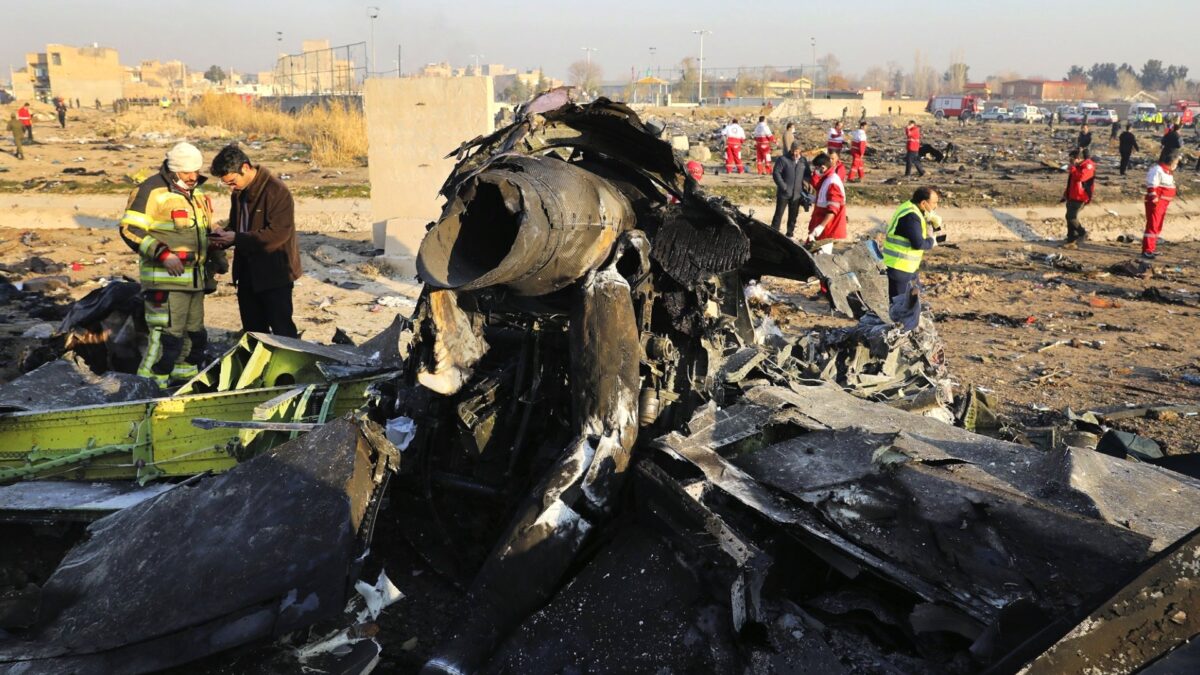

In part from the NYT’s: Around midnight on Jan. 7, as Iran was preparing to launch a ballistic-missile attack on American military posts in Iraq, senior members of the Islamic Revolutionary Guards Corps deployed mobile antiaircraft defense units around a sensitive military area near Tehran’s Imam Khomeini Airport.
Iran was about to retaliate for the American drone strike that had killed Iran’s top military commander, Gen. Qassim Suleimani, in Baghdad five days earlier, and the military was bracing for an American counterstrike. The armed forces were on “at war” status, the highest alert level.
But in a tragic miscalculation, the government continued to allow civilian commercial flights to land and take off from the Tehran airport.Gen. Amir Ali Hajizadeh, commander of the Guards’ Aerospace Force, said later that his units had asked officials in Tehran to close Iran’s airspace and ground all flights, to no avail.
Iranian officials feared that shutting down the airport would create mass panic that war with the United States was imminent, members of the Guards and other officials told The Times. They also hoped that the presence of passenger jets could act as a deterrent against an American attack on the airport or the nearby military base, effectively turning planeloads of unsuspecting travelers into human shields.
After Iran’s missile attack began, the central air defense command issued an alert that American warplanes had taken off from the United Arab Emirates and that cruise missiles were headed toward Iran.
The officer on the missile launcher near the airport heard the warnings but did not hear a later message that the cruise missile alert was a false alarm.
The warning about American warplanes may have also been wrong. United States military officials have said that no American planes were in or near Iranian airspace that night.
When the officer spotted the Ukrainian jet, he sought permission to fire. But he was unable to communicate with his commanders because the network had been disrupted or jammed, General Hajizadeh said later.The officer, who has not been publicly identified, fired two missiles, less than 30 seconds apart.
General Hajizadeh, who was in western Iran supervising the attack on the Americans, received a phone call with the news.
“I called the officials and told them this has happened and it’s highly possible we hit our own plane,” he said later in a televised statement.General Hajizadeh advised the generals not to tell the rank-and-file air defense units for fear that it could hamper their ability to react quickly if the United States did attack.
“It was for the benefit of our national security because then our air defense system would be compromised,” Mr. Hajizadeh said in an interview with Iranian news media this week. “The ranks would be suspicious of everything.”The military leaders created a secret investigative committee drawn from the Guards’ aerospace forces, from the army’s air defense, and from intelligence and cyberexperts. The committee and the officers involved in the shooting were sequestered and ordered not to speak to anyone.
The committee examined data from the airport, the flight path, radar networks, and alerts and messages from the missile operator and central command. Witnesses — the officer who had pulled the trigger, his supervisors and everyone involved — were interrogated for hours.
The group also investigated the possibility that the United States or Israel may have hacked Iran’s defense system or jammed the airwaves.Senior commanders discussed keeping the shooting secret until the plane’s black boxes — the flight data and cockpit voice recorders — were examined and formal aviation investigations completed, according to members of the Guards, diplomats and officials with knowledge of the deliberations. That process could take months, they argued, and it would buy time to manage the domestic and international fallout that would ensue when the truth came out.
The government had violently crushed an anti-government uprising in November. But the American killing of General Suleimani, followed by the strikes against the United States, had turned public opinion around. Iranians were galvanized in a moment of national unity.
The authorities feared that admitting to shooting down the passenger plane would undercut that momentum and prompt a new wave of anti-government protests.
“They advocated covering it up because they thought the country couldn’t handle more crisis,” said a ranking member of the Guards who, like others interviewed for this article, spoke on condition of anonymity to discuss internal deliberations. “At the end, safeguarding the Islamic Republic is our ultimate goal, at any cost.”
That evening, the spokesman for the Joint Armed Forces, Brig. Gen. Abolfazl Shekarchi, told Iranian news media that suggestions that missiles struck the plane were “an absolute lie.”
 source, Aljizeera
source, Aljizeera
On Thursday, as Ukrainian investigators began to arrive in Tehran, Western officials were saying publicly that they had evidence that Iran had accidentally shot down the plane.A chorus of senior Iranian officials — from the director of civil aviation to the chief government spokesman — issued statement after statement rejecting the allegations, their claims amplified on state media.
The suggestion that Iran would shoot down a passenger plane was a “Western plot,” they said, “psychological warfare” aimed at weakening Iran just as it had exercised its military muscle against the United States.
But in private, government officials were alarmed and questioning whether there was any truth to the Western claims. Mr. Rouhani, a seasoned military strategist himself, and his foreign minister, Javad Zarif, deflected phone calls from world leaders and foreign ministers seeking answers. Ignorant of what their own military had done, they had none to give.
Domestically, public pressure was building for the government to address the allegations.
Among the plane’s passengers were some of Iran’s best and brightest. They included prominent scientists and physicians, dozens of Iran’s top young scholars and graduates of elite universities, and six gold and silver medal winners of international physics and math Olympiads.
There were two newlywed couples who had traveled from Canada to Tehran for their weddings just days earlier. There were families and young children.
Their relatives demanded answers. Iranian social media began to explode with emotional commentary, some accusing Iran of murdering its own citizens and others calling such allegations treason.
Persian-language satellite channels operating from abroad, the main source of news for most Iranians, broadcast blanket coverage of the crash, including reports from Western governments that Iran had shot down the plane.
Mr. Rouhani tried several times to call military commanders, officials said, but they did not return his calls. Members of his government called their contacts in the military and were told the allegations were false. Iran’s civil aviation agency called military officials with similar results.
“Thursday was frantic,” Ali Rabiei, the government spokesman, said later in a news conference. “The government made back-to-back phone calls and contacted the armed forces asking what happened, and the answer to all the questions was that no missile had been fired.”
On Friday morning, Mr. Rabiei issued a statement saying the allegation that Iran had shot down the plane was “a big lie.”
Several hours later, the nation’s top military commanders called a private meeting and told Mr. Rouhani the truth.
Mr. Rouhani was livid, according to officials close to him. He demanded that Iran immediately announce that it had made a tragic mistake and accept the consequences.
The military officials pushed back, arguing that the fallout could destabilize the country.
Mr. Rouhani threatened to resign.
Canada, which had the most foreign citizens on board the plane, and the United States, which as Boeing’s home country was invited to investigate the crash, would eventually reveal their evidence, Mr. Rouhani said. The damage to Iran’s reputation and the public trust in the government would create an enormous crisis at a time when Iran could not bear more pressure.
As the standoff escalated, a member of Ayatollah Khamenei’s inner circle who was in the meeting informed the supreme leader. The ayatollah sent a message back to the group, ordering the government to prepare a public statement acknowledging what had happened.
Mr. Rouhani briefed a few senior members of his government. They were rattled.Mr. Abdi said the government’s actions had gone “far beyond” just a lie.
“There was a systematic cover-up at the highest levels that makes it impossible to get out of this crisis,” he said.
Iran’s National Security Council held an emergency meeting and drafted two statements, the first to be issued by the Joint Armed Forces followed by a second one from Mr. Rouhani.
As they debated the wording, some suggested claiming that the United States or Israel may have contributed to the accident by jamming Iran’s radars or hacking its communications networks.
But the military commanders opposed it. General Hajizadeh said the shame of human error paled compared with admitting his air defense system was vulnerable to hacking by the enemy.
Iran’s Civil Aviation Agency later said that it had found no evidence of jamming or hacking.



 source, Aljizeera
source, Aljizeera




 August 2018: Members of the Friends of Ukraine Network (FOUN), the Ukrainian-American community, the U.S.-Ukraine Foundation and other supporters of Ukraine met on August 7th to discuss pending and future legislative action on Capitol Hill regarding Ukraine.
August 2018: Members of the Friends of Ukraine Network (FOUN), the Ukrainian-American community, the U.S.-Ukraine Foundation and other supporters of Ukraine met on August 7th to discuss pending and future legislative action on Capitol Hill regarding Ukraine.