But there already is domestic terrorism law…meanwhile it was not applied to BLM or ANTIFA as those protests still go on….just a few arrests have been made while people and small business were not only terrorized but hundreds or maybe thousands lost their businesses. It is okay however, as VP -Elect Kamala Harris is good with that and supported it all.
Just one day ago –> it is terrorism but they call it unlawful assembly.
Portland rioters smash courthouse window, damage businesses before police declare unlawful assembly
Portland police arrived on the scene and told the crowd it had declared an unlawful assembly.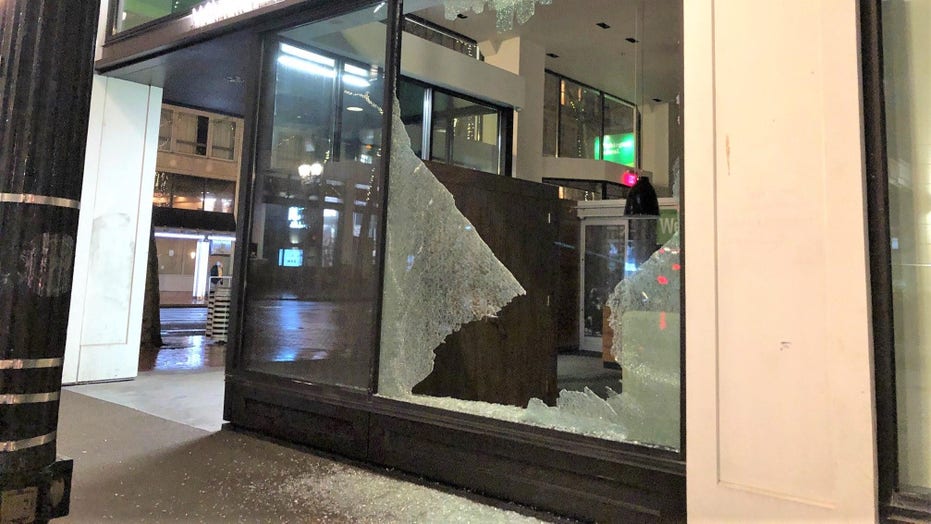
We’re aware of a direct action event outside the Justice Center tonight calling for demonstrators to “spread fire.” We will not tolerate criminal activity that jeopardizes or threatens the safety of deputies, officers, adults in custody, employees and community members.
— Multnomah Co. Sheriff’s Office (@MultCoSO) January 7, 2021
So why the new proposed legislation? Hardly balanced application of the law and that is good with the new administration and progressive members of Congress.
The Patriot Act 2.0 coming your way.
Note:
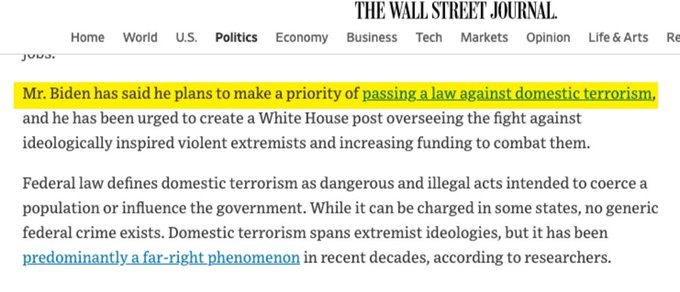
Today, legislation introduced by Congressman Brad Schneider (IL-10) to address the threat of domestic terrorism passed the House Judiciary Committee by a vote of 24-2. The Committee’s markup and bipartisan vote reports H.R. 5602, the Domestic Terrorism Prevention Act of 2020, out of the House Judiciary Committee.
“The rising tide of domestic terror across our country, particularly from violent far-right extremists and white supremacist organizations, demands a response from Congress,” said Schneider. “It is not enough to just condemn hate, we need to equip law enforcement with the tools needed to identify threats and prevent violent acts of domestic terrorism. The Domestic Terrorism Prevention Act improves coordination between our federal agencies and makes sure they are focused on the most serious domestic threats. I thank Chairman Nadler and Chairwoman Bass for their leadership on this issue and my colleagues on both sides of the aisle for supporting this legislation in markup. I look forward to building support for a vote by the full House as soon as possible.”
The Domestic Terrorism Prevention Act of 2020 would enhance the federal government’s efforts to prevent, report on, respond to, and investigate acts of domestic terrorism by authorizing offices dedicated to combating this threat; requiring these offices to regularly assess this threat; and providing training and resources to assist state, local, and tribal law enforcement in addressing it.
According to the Anti-Defamation League, in 2019, domestic extremists killed at least 42 people in the United States in 17 separate incidents. This number makes 2019 the sixth deadliest year on record for domestic extremist-related killings. Last year, a Trump Administration Department of Justice official wrote in a New York Times op-ed that “white supremacy and far-right extremism are among the greatest domestic-security threats facing the United States. Regrettably, over the past 25 years, law enforcement, at both the Federal and State levels, has been slow to respond.”
H.R. 5602 would authorize three offices, one each within the Department of Homeland Security (DHS), the Department of Justice (DOJ), and the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI), to monitor, investigate, and prosecute cases of domestic terrorism. The bill also requires these offices to provide Congress with joint biannual reports assessing the state of domestic terrorism threats, with a specific focus on white supremacists. Based on the data collected, H.R. 5602 requires these offices to focus their resources on the most significant threats..
H.R. 5602 also codifies the Domestic Terrorism Executive Committee, which would coordinate with United States Attorneys and other public safety officials to promote information sharing and ensure an effective, responsive, and organized joint effort to combat domestic terrorism. The legislation requires DOJ, FBI, and DHS to provide training and resources to assist state, local, and tribal law enforcement agencies in understanding, detecting, deterring, and investigating acts of domestic terrorism and white supremacy. Finally, H.R. 5602 directs DHS, DOJ, FBI, and the Department of Defense to establish an interagency task force to combat white supremacist infiltration of the uniformed services and federal law enforcement.
The Domestic Terrorism Prevention Act of 2020 has been endorsed by the following organizations: Anti-Defamation League, Arab American Institute, Bend the Arc: Jewish Action, Center for the Study of Hate & Extremism, Human Rights Campaign, Lawyers’ Committee for Civil Rights Under Law, The Leadership Conference on Civil and Human Rights, Muslim Advocates, NAACP, NAACP Legal Defense and Educational Fund, Inc., Sikh Coalition, Southern Poverty Law Center Action Fund, and Unidos. .
The legislation has more than 100 co-sponsors in the House. A Senate companion bill is led by Sen. Dick Durbin (D-IL).

/https://public-media.si-cdn.com/filer/5a/cf/5acf1c49-c598-40f7-8f35-8d282a43536e/reichstagsbrand-web.jpg)
 s
s



