There are several sources reporting this crisis including retailers. Big box stores are working to even send their own charter ships and aircraft to release the inventory.Large, empty spaces have returned to store shelves as consumers return to stockpiling essential items and supply chain issues slow deliveries.
Costco has reimposed limits on the purchase of toilet paper, paper towels, and bottled water — limits first imposed during the early days of the pandemic when panicked consumers overstocked their pantries.
With the spread of the Delta variant, some consumers are returning to that buying pattern. However, retail analysts say some consumers never changed their behavior and continue to buy in larger quantities than before the pandemic.
Supply chain bottlenecks
Overbuying isn’t the only reason for the growing gaps on supermarket shelves. The empty spaces in the soft drink aisle are caused by nagging supply chain bottlenecks that continue to slow both production and delivery.
According to the Economic Times (ET), Vietnam is a source of persistent supply chain problems. The U.S. depends on that country for a large amount of food and consumer product manufacturing. It’s one of the Asian nations currently struggling to contain the Delta variant.
“Shipping containers are in the wrong place. Sea freight costs are up tenfold. If goods do arrive at the destined ports, there are too few truck drivers to transport them to retailers,” ET reported. “Shortages of workers to harvest and prepare foods are also adding to the pressures.”
Slowed production has also led to fewer choices in the soft drink aisle. Soft drink manufacturers are dealing with a shortage of packaging, including aluminum cans. There is also a shortage of C02, which produces carbonation. That problem has been felt the most so far in the U.K.
Other products in short supply
Other categories experiencing increased demand are coffee, school supplies, consumer electronics, and pet food. Retailers report that the shortages have been caused by both increased demand from consumers and delivery problems.
With school starting up again, demand for Kraft Heinz’s Lunchables” packaged snack/meal product has created shortages at grocery stores. The food manufacturer told KIRO-TV in Seattle that the product is seeing double-digit sales growth for the first time in five years.
Economists say shortages inevitably lead to higher prices, which are already being seen in some food and beverage categories. The Federal Reserve has acknowledged the presence of inflation but predicted it will be “transitory” in nature.
Economist Joel Naroff, president of Naroff Economics, says manufacturers are paying more to produce their products. Unfortunately, they will likely pass those costs along to consumers at some point. He says labor shortages and supply chain issues could keep prices higher for longer than expected.
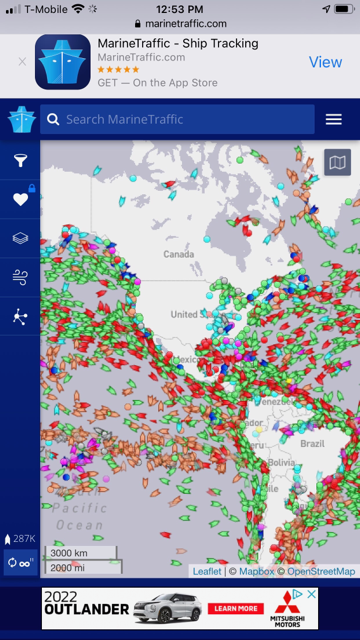
BI: The Southern California ports that are responsible for almost half of all US imports hit a new record every day last week.
Over the past week, the queue of ships waiting to unload at the ports in Los Angeles and Long Beach have lengthened by 10 ships. On Friday, the ports had 65 cargo ships stuck at anchor or in drift areas waiting for spots to open up to dock and unload. The ports, which are a primary thoroughfare for key imports between Asia and the US, had 147 ships in the locations, including 95 hulking cargo ships on Friday — both new records.
The average wait time for the vessels is about 8.7 days — about 2.5 days longer than the same time the month before, Los Angeles port data indicated. So far, the ports have handled about 862,000 imports in 2021.
The locations hit new records for the number of ships in the port, as well as the number of container ships waiting to undock every day last week, the Marine Exchange of Southern California said.
The ports have hit seven new records in less than four weeks as shipping delays continue to surge past early pandemic levels. When the ports hit an all-time high in late August, it was the first time since February, when the onset of pandemic shutdowns and the panic-buying frenzy wreaked havoc on global supply chains.
“The normal number of container ships at anchor is between zero and one,” Kip Louttit, the executive director of the Marine Exchange of Southern California, told Insider in July.
Freightos told Bloomberg that the average time it takes for an ocean freight to go door-to-door has increased 43% over the past year, from 50 days to 71.5 days.
At the same time, shipping costs have skyrocketed. Last week, Judah Levine, the head of research at Freightos, told Insider that the price for transporting a 40-foot container between the US and Asia jumped 500% from this time last year to $20,586.
Ultimately, the ports are facing backlogs as a result of COVID-19 disruptions and a labor shortage paired with spikes in demand.
Executives have warned that rising transportation costs would increase shortages of goods, as well as necessitate more price hikes. Last week, Scott Price, UPS’s president, said the company anticipated that supply-chain snags would continue through 2022.
Meanwhile, many companies have already begun raising their prices to offset the transportation costs.
“When we see these massive increases in transportation costs, it’s clear somebody will have to pay for it,” Douglas Kent, the executive vice president of strategy and alliances at the Association for Supply Chain Management, told Insider.
“One more disruption could send it into complete chaos,” he said of the global supply chain.
This photo is a screen shot taken a few minutes ago that demonstrates the issue.


 Getty Images
Getty Images
