Does Minneapolis, Minnesota look like it did 5 years ago? How about Lewiston, Maine or Cape Coral, Florida?

Forget Miami, Los Angeles and New York–America’s newest immigrant capitals are the country’s recent boom towns.
Top of the list: Cape Coral-Fort Myers, Fla., with a 122% increase in its foreign-born population from 2000 to 2007, according to a Brookings Institution analysis of U.S. Census Bureau information. Also ranking high are the metro areas of Nashville, Tenn., (74% increase), Indianapolis (71%), Orlando, Fla., (64%) and Raleigh, N.C. (62%).
It makes sense. Like everyone else, immigrants are drawn to places with jobs. These towns offer a relatively low cost of living, compared with their big-city brethren and, in recent years, ample opportunities for work in various fields. Raleigh is a hub of North Carolina’s “Research Triangle,” and in 2007, about 15% of its working immigrant population worked in professional, scientific and administrative occupations, according to the Census Bureau. Orlando, a major tourist destination, is a hub for service-sector jobs.

From Breitbart:
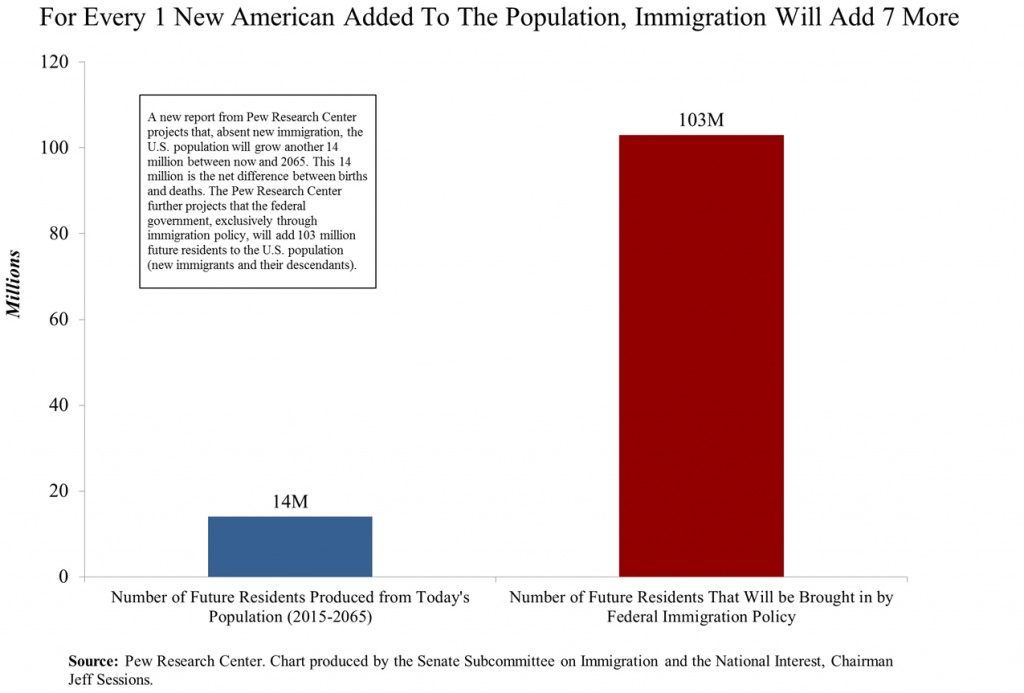
The following chart and background have been provided to Breitbart News exclusively from the Senate Judiciary Committee’s subcommittee on Immigration and the National Interest, which is chaired by Sen. Jeff Sessions (R-AL). The chart shows that for every 1 net American born to today’s population—births minus deaths—the federal government will add 7 more people to the country through future immigration.
The Senate Subcommittee told Breitbart News:
October 3rd marked the 50th anniversary of the Immigration and Nationality Act. According to Pew Research, in the five decades since the Act’s adoption, 59 million immigrants have entered the United States. Pew further estimates that, including the descendants of those new arrivals, immigration policy added 72 million people to the population of the United States. In 1970, fewer than 1 in 21 Americans were foreign-born; today, nearly 1 in 7 are foreign-born. The United States has taken in four times more worldwide immigrants than any other nation on Earth. Over the next five decades, Pew projects that new immigration, including the descendants of those new immigrants, will add 103 million to the current U.S. population. The net addition of 103 million new persons is exclusively the result of new immigration of persons not currently in the U.S. The 103 million figure does not include any immigrants currently in the U.S. or their future children. (As a side note: Pew data shows that new foreign-born arrivals will not lower today’s median U.S. age of 38; Pew estimates the median age of the foreign-born in 2065 will approach 53.)
Pew also found that, by more than a 3-1 margin, Americans wished to see immigration rates reduced – not raised. Unless such reductions are enacted, the foreign-born share of the U.S. population will soon eclipse the highest levels ever recorded in U.S. history and will keep climbing to new all-time records every decade of the 21st century. Pew projects that by 2065, more than 1 in 3 U.S. residents will either be foreign-born or have foreign-born parents, assuming no law is passed to reduce immigration rates. By contrast, in the 20th century, after the foreign-born population share peak reached in 1910, immigration was reduced for the next six consecutive decades.
Lower-income workers, including millions of prior immigrants, are among those most severely impacted by the vast inflow of new workers competing for the same jobs at lower wages. Across the economy, average hourly wages are lower today than in 1973, while the share of people not working is at nearly a four-decade high. Yet the Senate’s Gang of Eight bill would have tripled green card issuances over the next decade (issuing more new green cards than the entire population of Texas) and the industry-backed I-squared bill would triple admission of new H-1B foreign workers provided to technology corporations as low-wage substitutes for their existing workers.
Sen. Jeff Sessions (R-AL), the chairman of the subcommittee, responded to the startling data his committee uncovered by telling Breitbart News there should be immigration controls put in place immediately.
“We should not admit people in larger numbers than we can reasonably expect to vet, assimilate, and absorb into our schools, communities, and labor markets,” Sessions said. “It is not compassionate but uncaring to bring in so many people that there are not enough jobs for them or the people already here. Over the last four decades, immigration levels have quadrupled. The Census Bureau projects that we will add another 14 million immigrants over the next decade. It is not mainstream, but extreme, to continue surging immigration beyond all historical precedent. It is time for moderation to prevail, and for us to focus on improving the jobs, wages, and security of the 300 million people already living inside our borders.”
The subcommittee also pointed to polling data that proves Americans are united entirely behind what Sessions wants to do.
“Polling from Kellyanne Conway shows that, by nearly a 10-1 margin, Americans of all backgrounds are united in their belief that companies should raise wages and improve working conditions for people already living in the United States – instead of bringing in new labor from abroad,” the subcommittee noted.
Sen. Sessions is appearing on Breitbart News Sunday on Sirius XM Patriot Channel 125 with Breitbart News Executive Chairman Stephen K. Bannon on Sunday evening to discuss this and more right at 7 p.m.
*** The same goes for Europe:
Tip of the iceberg: No end in sight to migrant wave
ZAGREB, Croatia (AP) — One month after the body of 3-year-old Aylan Kurdi washed up on a Turkish beach — and a week after the European Union agreed to secure its borders — the migrant crisis has largely fallen off the front pages and reporters are going home.
But the human tide keeps rolling northward and westward, and aid agencies are preparing for it to continue through the winter, when temperatures along the migrant trail will drop below freezing. They fear the crisis may get worse.
“One thing is clear, the movement is not going to die down,” said Babar Baloch, the U.N. refugee agency’s representative in the Balkans. “What we are seeing right now … it’s just the tip of the iceberg.”

While over a half million people have crossed the Mediterranean to Europe this year, more than double the figure for all of 2014, that is only a fraction of the people who are on the move. Some 4 million have fled Syria after more than four years of civil war, and 8 million have been displaced inside the country. And it’s not just Syrians. It’s Iraqis and Iranians, Afghans and Eritreans.
The EU acknowledged the scale of the problem last week, even after it approved a plan to toughen border controls and provide at least 1 billion euros ($1.1 billion) to help Turkey, Lebanon and Jordan care for refugees living in their countries. The first new border measures won’t take effect until November, and a proposal for strengthening the EU border agency is due in December.
“Recently I visited refugee camps in Turkey and Jordan and I heard only one message — we are determined to get to Europe,” European Council President Donald Tusk said after the agreement was announced. “It is clear that the greatest tide of refugees and migrants is yet to come.”
While the UN High Commissioner for Refugees on Friday reported a “noticeable drop” in migrants entering Greece by sea — as weather conditions deteriorated this week — agency spokesman Adrian Edwards said “any improvement in the weather is likely to bring another surge in arrivals.”
About 1,500 people arrived in Greece on Thursday, down from 5,000 a day in recent weeks, UNHCR said.

The EU was spurred to act after photos of Aylan lying face down on a Turkish beach were published around the world, triggering outrage over the suffering of migrants fleeing war and poverty. Aylan drowned, along with his mother and brother, when their boat capsized on the journey from Turkey to the Greek island of Kos.
Before the EU can stop the influx, it must convince the world that it has regained control of its borders after months of news coverage showing the virtually unimpeded flow of people traveling from Turkey to Greece, then north through the Balkans to Austria, Germany and Sweden.
The surge came as donors cut back on funding for groups supporting Syrian refugees. The World Food Program in August said funding shortfalls forced it to cut food aid by 50 percent for 1.5 million refugees living in Jordan, Lebanon, Turkey, Iraq and Egypt. EU members pledged to restore funding for the WFP as part of their agreement last week.
The aid is important. Most refugees are unable to build new lives in their Middle Eastern host countries because they are barred from working. And as they watch their resources vanish, even people who hadn’t planned to go to Europe are now considering it.
“There’s no hope at all, so moving on seems the only option,” Baloch said. “It could be an exodus in the making.”
Take, for example, Zafer, a Syrian refugee who spoke on condition that his last name not be used for fear of reprisals. Zafer, 43, fled his country three years ago for Istanbul and is now contemplating Europe, encouraged by a friend who made the illegal crossing to Greece and is now in Germany.
“I don’t have a future here, it is very hard. I had a budget but it is running out,” he told The Associated Press. “I am worried about my children’s education. Now they are young, but what will happen later when they are older? I am worried.”
He isn’t alone.
With a migrant path clearly established, complete with signposts on how to get to Europe, aid groups say it’s almost as if a message has gone out: This is your chance. Now or never.
“In normal conditions, you will think twice about crossing the Mediterranean with your children because it is dangerous,” said Gianluca Rocco, western Balkans coordinator for the International Organization for Migration. “But now you go with the flow. The flow is there and it is moving very quickly.”
Macedonia, the main corridor for people traveling north from Greece, is preparing for the flood to continue through the winter.
Authorities are installing floors and heating in tents at the Gevgelija refugee camp, and aid agencies will provide warm clothes and blankets for the migrants, said Aleksandra Kraus, a spokeswoman for the UNHCR in Macedonia.
The Macedonian parliament in September extended the state of emergency on the country’s borders until June 2016. The country of 2 million people is spending about 1 million euros a month on migrants.
“Conditions and capacities for migrants depend on the budget,” said Ivo Kotevski, a police spokesman. “We appeal for assistance.”
All over the region, groups are already struggling to keep pace with arrivals, especially with winter drawing close.
“It will get much colder still, and the provision of adequate shelter is not even close to matching the number of people crossing into Serbia every day,” Doctors Without Borders President Meinie Nicolai told The Associated Press.
It’s unclear whether the EU actions will stem the flow, particularly in the short term.
Social media savvy asylum seekers are now aware the new border measures may take effect in November; and that effectively gives potential migrants a deadline that could spur them to make a dash for Europe, making the events of recent weeks a mere prelude to an even larger flood of humanity.
The EU is moving in the right direction, but the new programs will take time to implement, and the conditions that have pushed the refugees toward Europe haven’t changed, said Maurizio Albahari, author of “Crimes of Peace: Mediterranean Migrations at the World’s Deadliest Border,” and a social anthropologist at the University of Notre Dame.
“People in Turkey and in Libya are on top of the news. This includes both smugglers and refugees,” he said by email. “The winter months and the promise/threat of additional border control/patrols at the EU’s external borders might motivate them to move earlier than they would.”


