Primer:
The Justice Department on Tuesday announced plans to appeal a judge’s ruling that blocked President Donald Trump from shuttering a program that gave protections and work permits to some people who entered the U.S. illegally as children.
In a ruling last week, San Francisco-based U.S. District Court Judge William Alsup ordered the administration to resume accepting renewal applications for the Deferred Action for Childhood Arrivals program, better known as DACA. More here from Politico.
In part, highlights:
The Department has also implemented historic efforts to step up international cooperation. For the first time ever, DHS established a clear baseline for what countries must do to help the United States confidently screen travelers and immigrants from their territory. Every country in the world is now required to meet high security standards and to help us understand who is coming into our country.As required under President Trump’s Executive Order Protecting the Nation from Foreign Terrorist Entry into the United States (EO 13780), all foreign governments have been notified of the new standards, which include the sharing of terrorist identities, criminalhistory information, and other data needed to ensure public safety and national security, as well as the requirement that countries issue secure biometric passports, report lost and stolen travel documents to INTERPOL, and take other essential actions to prevent identity fraud.***Visa Waiver ProgramWe are also looking at ways to further strengthen the Visa Waiver Program (VWP). First and foremost, the VWP is a security partnership program. It mandates high and consistent standards from partner countries in the areas of national security, law enforcement, and immigration enforcement to detect and prevent terrorists, criminals, and other potentially dangerous individuals from traveling to the United States —while still facilitating legitimate travel and tourism.Currently, 38 countries participate in the VWP, which allows their citizens to travel to the United States for business or tourism for stays of up to 90 days after applying and being approved through the Electronic System for Travel Authorization (ESTA). In return, these countries must comply with program requirements to enter into information-sharing protocols that enable the relay of information concerning known and suspected terrorists and criminals; consistent and timely lost and stolen passport information reporting; and robust border and travel documentscreening. As a result of these program requirements, countries have adopted new laws, policies, and practices that strengthen our mutual security.The Visa Waiver Program Improvement and Terrorist Travel Prevention Act of 2015,combined with Secretarial action, have strengthened the VWP’s security provisions over the past two years.VWP countries are now required to issue high -security electronic passports (e-passports); implement information sharing arrangements to exchange terrorist identity information; establish mechanisms to validate e-passports at each key port of entry; report all lost and stolen passports to INTERPOL or directly to the United States no later than 24 hours after the country becomes aware of the loss or theft; and screen international travelers against the INTERPOL Stolen and Lost Travel Documents (SLTD) database and notices. As with other operational activities of DHS, a full discussion of the privacy impact of these initiatives and how we mitigate the risk to personal privacy is available on our website.Since enactment of the Visa Waiver Program Improvement and Terrorist Travel Prevention Act, DHS has realized an increase in the sharing of terrorist identity information. Several countries have increased the frequency of their reporting of lost and stolen passports —VWP countries account for over 70 percent of the almost 73 million lost and stolen travel documents reported to INTERPOL. All VWP countries are now issuing and using for travel to the United States fraud-resistant e-passports that meet or exceed the ICAO standards. Over 70,000 ESTA applicationshave been denied, cancelled or revoked under enforcement of the VWP Improvement Act’seligibility restrictions for VWP travel.Border SecurityIn compliance with Executive Order 13767: Border Security and Immigration EnforcementImprovements, DHS has conducted a comprehensive study of the security of the southern border that addresses all of the elements that provide an integrated solution for the Nation. Our first priority is to expand on our existing southern border wall system and close legal loopholes that encourage and enable illegal immigration and create a corresponding backlog in the courts. We currently have an immigration court backlog of more than 650,000 cases pending before the Department of Justice’s Executive Office for Immigration Review. We also have a massive asylum backlog with more than 270,000 pending cases before U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS).Recognizing the unsustainability of the asylum case backlog, USCIS has implemented efficiency measures designed to reduce adjudication times. Similarly, the Department of Justice has taken action to reduce unwarranted case continuances in immigration courts, which helps reduce the backlog while affording aliens full and fair hearings. To furtherreduce the “pull factors” and restore integrity to our immigration benefits adjudication process, we must tighten case processing standards, including the “credible-fear” standard, impose and enforce penalties for fraud, and ensure applicants are fully vetted before they are allowed access to the United States.In addition, visa-overstays account for roughly 40 percent of all illegal immigration in theUnited States. In FY 2016, more than 628,000 aliens overstayed their visas. By increasingoverstay penalties and expanding ICE’s enforcement tools, we can help ensure that foreignworkers, students, and visitors respect the terms of their temporary visas. We need Congress to authorize the Department to raise and collect fees from immigration benefit applications to fund additional enhancements to our immigration system called for by the President’s Executive Orders.Enforcing Immigration LawsWe are also prioritizing the enforcement of our immigration laws in the interior of our country.There are nearly one million aliens with final orders of removal across the country—meaning these removable aliens were afforded due process of law, had theirday in court, and were ultimately ordered removed by a judge — yet they remain in our nation and ICE only has 6,000 Deportation Officers to arrest and remove them. The Administration looks to strengthen law enforcement by hiring 10,000 more ICE officers and agents, and supports the request from the Department of Justice to hire 300 more federal prosecutors.To further protect our communities, we must end so-called “sanctuary” jurisdictions. Hundreds of state and local jurisdictions across the country that do not honor requests from ICE to hold criminal aliens who are already in state and local custody. Instead, they allow them back into their communities, where they are allowed to commit more crimes. This also poses a greater risk of harm to ICE officers, who must locate and arrest these criminals in public places, and increases the likelihood that the criminal aliens can resist arrest or flee. Rather than enhancing public safety, sanctuary jurisdictions undermine it.The only “sanctuary” these jurisdictions create is a safe haven for criminals. States and localities that refuse to cooperate with federal authorities should be ineligible for funding from certain grants and cooperative agreements.Authorizing and incentivizing states and localities to enforce immigration laws would further help ICE with its mission and make all communities safer.In FY 2017, 1,761 criminal illegal aliens were released from ICE custody because of a 2001Supreme Court decision that generally requires ICE to release certain removable aliens with final orders of removal—including violent criminals—within 180 days, if they have not been removed and there is no significant likelihood of removal in the reasonably foreseeable future. Legally insupportable judicial interpretations of the law regarding the detention and removability of criminal aliens have eroded ICE’s authority to keep aliens in custody pending removal.Pursuant to this Executive Order, USCIS announced it will take a more targeted approach to combatting fraud and abuse in the employment -based visa programs, including the H-1B program. To help end H-1B petitioner fraud and abuse, USCIS has established a Targeted Site Visit and Verification Program (TSVVP). Targeted site visits allow USCIS to focus its resources where fraud and abuse of certain programs are more likely to occur. TSVVP initially focused on H-1B petitions filed by companies that are H-1B dependent (as defined by statute), employers petitioning for H-1B workers who will be placed off -site at another company’s location, or cases where USCIS cannot validate the H-1B petitioner’s business information through commercially -available data.USCIS has also taken great strides to improve transparency with the public about employment -based immigration programs. The agency has published new data on its website to give the public more information regarding the use of nonimmigrant workers in the H-1B, H-2B, and L nonimmigrant programs. Information about the use and legal authority for employment authorization documents has also been published.Most low-skilled immigration into the United States occurs legally through ourimmigrant-visa system, which, unlike many other countries’ systems, prioritizes family-based chain-migration. Each year, the United States grants lawful permanent resident status (greencards) to more than one million people; two-thirds of that total is based on a person having a sponsoring relative in the United States, regardless of the new immigrant’s skills, education, English language proficiency, or ability to successfully assimilate. This system of chain-migration has accounted for more than 60 percent of immigration into the United States over the past 35 years. We must end chain-migration, and limit family -based green cards to spouses and the minor children of U.S. citizens and lawful permanent residents.We must also eliminate the “diversity visa” lottery. Every year, through this lottery, 50,000green cards are awarded at random to foreign nationals. Many of these lottery beneficiaries have absolutely no ties to the United States, no special skills, and limited education. The random lottery program has not been adopted by other countries and does not adequately serve our national interest. Full opening summary here.
Category Archives: Gangs and Crimes
UN Declaration, Regular, Constant Global Migration = Insurgency
Berlin – A new series launched by the Global Migration Data Analysis Centre (GMDAC) of IOM, the UN Migration Agency, aims to summarize the existing evidence on migration in an accurate and accessible fashion, to support discussions and any follow-up activities of the Global Compact for Safe, Orderly and Regular Migration.
Note the words orderly and regular….if the United Nations and peacekeeping operations as well as the aid, education, construction and protection campaigns were successful, migration would not be required especially in non-war torn countries. Right? Or how about all these other global human interest organizations….they failing too? Those like the Clinton Foundation or hey how about the Gates Foundation, which is a private foundation founded by Bill and Melinda Gates. It was launched in 2000 and is said to be the largest private foundation in the US, holding $38 billion in assets, improving lives from Seattle to South Africa….ahem.
Check here for the largest 10 organizations…. if all this work and money and resources were effective, then why the migration at all?
For the first time on 19 September 2016 Heads of State and Government came together to discuss, at the global level within the UN General Assembly, issues related to migration and refugees. This sent an important political message that migration and refugee matters have become major issues in the international agenda. In adopting the New York Declaration for Refugees and Migrants, the 193 UN Member States recognized the need for a comprehensive approach to human mobility and enhanced cooperation at the global level.
What are the aims of the global compact for migration?
The global compact is framed consistent with target 10.7 of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development in which member States committed to cooperate internationally to facilitate safe, orderly and regular migration and its scope is defined in Annex II of the New York Declaration. It is intended to:
- address all aspects of international migration, including the humanitarian, developmental, human rights-related and other aspects;
- make an important contribution to global governance and enhance coordination on international migration;
- present a framework for comprehensive international cooperation on migrants and human mobility;
- set out a range of actionable commitments, means of implementation and a framework for follow-up and review among Member States regarding international migration in all its dimensions;
- be guided by the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development and the Addis Ababa Action Agenda; and
- be informed by the Declaration of the 2013 High-Level Dialogue on International Migration and Development.
The development of the global compact for migration – an open, transparent and inclusive process
The Modalities Resolution for the intergovernmental negotiations of the global compact for safe, orderly and regular migration outline the key elements and timeline of the process. The global compact will be developed through an open, transparent and inclusive process of consultations and negotiations and the effective participation of all relevant stakeholders, including civil society, the private sector, academic institutions, parliaments, diaspora communities, and migrant organizations in both the intergovernmental conference and its preparatory process.
US Treasury to Publish Russian Oligarch Corruption Index
In December of 2015, Obama took aggressive action expelling Russian diplomats over hacking and political intrusion.
“In addition, the Russian Government has impeded our diplomatic operations by, among other actions — forcing the closure of 28 American corners which hosted cultural programs and English-language teaching; blocking our efforts to begin the construction of a new, safer facility for our Consulate General in St Petersburg; and rejecting requests to improve perimeter security at the current, outdated facility in St Petersburg.” Some additional actions and those expelled include:
Two Russian intelligence agencies, the GRU and the FSB, four GRU officers and three companies “that provided material support to the GRU’s cyber operations”.
The White House named Igor Valentinovich Korobov, the current chief of the GRU; Sergey Aleksandrovich Gizunov, deputy chief of the GRU; Igor Olegovich Kostyukov, a first deputy chief of the GRU; and Vladimir Stepanovich Alexseyev, also a first deputy chief of the GRU. The Obama Executive Order is here.
Russia’s Oligarchs Brace for U.S. List of Putin Friends
(Bloomberg) — The U.S. Treasury Department is finishing its first official list of “oligarchs” close to President Vladimir Putin’s government, setting off a flurry of moves by wealthy Russians to shield their fortunes and reputations.
Some people who think they’re likely to land on the list have stress-tested the potential impact on their investments, two people with knowledge of the matter said. Others are liquidating holdings, according to their U.S. advisers.
Russian businessmen have approached former Treasury and State Department officials with experience in sanctions for help staying off the list, said Dan Fried, who previously worked at the State Department and said he turned down such offers.
Some Russians sent proxies to Washington in an attempt to avoid lobbying disclosures, according to one person that was contacted.
The report is expected to amount to a blacklist of Russia’s elite. It was mandated by a law President Donald Trump reluctantly signed in August intended to penalize the Kremlin for its alleged meddling in the 2016 election.
A rare piece of legislation passed with a bipartisan veto-proof margin, the law gave Treasury, the State Department and intelligence agencies 180 days to identify people by “their closeness to the Russian regime and their net worth.”
That deadline is Jan. 29.
Shamed Oligarchs
The list has also become a headache within Treasury, where some officials are concerned it will be conflated with sanctions, a person familiar with the matter said.
Treasury officials are considering keeping some portions of the report classified — which the law allows — and issuing it in the form of a letter from a senior official, Sigal Mandelker, instead of releasing it through the Office of Foreign Assets Control, which issues sanctions.
That would help distinguish it from separate lists of Russians subject to U.S. economic penalties, said the person, who spoke on condition of anonymity.
“You’re going to have people getting shamed. It’s a step below a sanction because it doesn’t actually block any assets, but has the same optics as sanctions — you’re on a list of people who are engaged in doing bad things,” said Erich Ferrari, who founded Ferrari & Associates in Washington and has helped people get removed from the sanctions designation list.
Corruption Index
The report must include “indices of corruption” with the oligarch’s names and list any foreign assets they may own. Lawmakers expect the list to provide a basis for future punitive actions against Russia.
“Because of the nervousness that the Russian business community is facing, a number of oligarchs are already beginning to wind back businesses, treating them as if they are already designated, to stay ahead of it,” said Daniel Tannebaum, head of Pricewaterhousecoopers LLP’s global financial sanctions unit.
He advises a handful of wealthy Russian individuals and some businesses who he declined to identify.
Treasury’s terrorism and financial intelligence unit is working with the State Department and Office of National Intelligence to complete the report, said a spokesman who declined to elaborate on the criteria for the list or whether it would be made public.
“It should be released in the near future,” Treasury Secretary Steve Mnuchin said at a White House briefing. ‘It’s something we’re very focused on.”
‘Allows Mischief’
The list’s impact will depend on how it’s released, said Adam Smith, a former senior adviser in Treasury’s sanctions unit and now a partner at Gibson, Dunn & Crutcher LLP in Washington.
The law is “written in a way that it allows mischief if the administration wanted to go a different way,” Smith said. “If the president wanted to provide little or a lot and be very selective, he has the ability to do that.”
That discretion partly flows from the criteria used to assemble the list, which Congress left up to Treasury.
Senator Ben Cardin of Maryland, the ranking Democrat on the committee on foreign relations, said he would like to see “as much transparency as possible” from Treasury when it finishes the list.
Russia has sought to defend its elites. Putin warned of worsening U.S. sanctions last month and introduced a capital amnesty program to encourage wealthy nationals to repatriate some of their overseas assets.
He also approved a plan to issue special bonds designed to give the wealthy a way to hold their dollar assets out of reach of the U.S. Treasury.
‘Disgusting’ Relations
While compilation of the list doesn’t mean there’ll be a new round of tit-for-tat sanctions, Russia will react to any punitive measures against its business people, Kremlin spokesman Dmitry Peskov told reporters on a conference call Friday.
“The principle of reciprocity remains,” and it would be for Putin to decide on the best response, he said.
Prime Minister Dmitry Medvedev, a Putin lieutenant for two decades, called the state of the relationship “disgusting” in November.
Congress has also requested that Treasury submit an impact analysis of potential sanctions on Russian sovereign bonds. A Treasury spokesman said its international affairs office is working on the analysis.
U.S. sanctions on the bonds would deal a major blow to Russia’s finances, raising the prospect of a selloff in the bond market, posing a risk to the ruble and the potential for higher borrowing costs.
The Russian Finance Ministry relies on debt to cover budget shortfalls and is seeking to borrow $18 billion domestically in 2018.
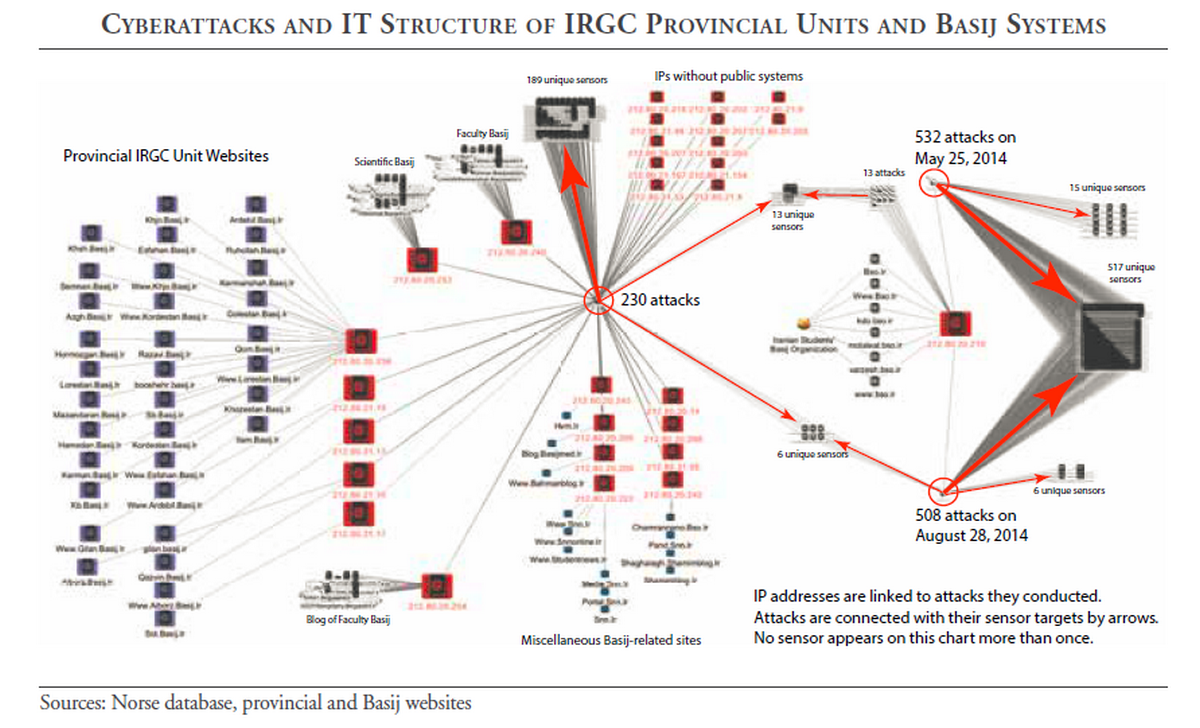
Iran’s Cyber Forces under IRGC Target Dissenters/Enemies
NIN is not Nine Inch Nails but rather the Supreme Leader’s tightly controlled internet platform known as the National Internet Network. It operates somewhat like an fee based system, those that can afford and pay more for access and usage get the best speed and less government oversight. The poorer class and the dissenters are controlled by the regime and not only vulnerable to the throttling of service but are subject to phishing operations, hacks and DDoS outages, all at the direction of the regime.
It almost sounds like a marriage between the U.S. version/marriage of Google, Facebook and NSA, right? Well it is.
The NIN can filter key words and phrases and send users only to the sites it approved, according to the CHRI report. The government has also limited access to thousands of sites and platforms, including Facebook and YouTube. It is attempting to replace search engines like Google with its own state-approved versions.
Iran has also been able to influence how people use the internet through pricing. While there are private internet service providers (ISPs), they are still under government control, allowing state-run infrastructure companies to set up a tiered plan where access to international internet sites costs more than domestic. This drives traffic away from the global internet and to the NIN.
It’s not just internet censorship that Iranians are facing. The report also highlights state-sponsored cyberattacks and phishing schemes. State security agencies like the Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps, a branch of the armed forces meant to protect the Islamic system, have hacked into individual and private online communications and arrested people on the basis of their content, which is technically illegal under Iranian law.
DDoS attacks, which aim to make specific websites unavailable or limit access to information by flooding them with illegitimate traffic, have become more prominent during politically sensitive times as well, according to the report. During the election in 2016, reformist and centrist candidates like Gaam-e Dovvom faced multiple attacks. The report said many of these are also internal attacks through the government.
Meanwhile, Iranians are not blind to the extensive surveillance they are facing online. As we’ve reported, many internet users use VPNs and other apps to try and circumvent the censorship. And millions of Iranians have turned to the Toronto-born Psiphon app to use the internet during the protests in December and this month. More here.
***  photo
photo
Tehran has become increasingly adept at conducting cyber espionage and disruptive attacks against opponents at home and abroad, ranging from Iranian civil society organizations to governmental and commercial institutions in Israel, Saudi Arabia, and the United States.
A new report by carnegiendowment.org evaluates Iran’s Cyber threat environment. Just as Iran uses proxies to project its regional power, Tehran often masks its cyber operations using proxies to maintain plausible deniability. Yet such operations can frequently be linked to the country’s security apparatus, namely the Ministry of Intelligence and Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps.
While Iran does not have a public strategic policy with respect to cyberspace, its history demonstrates a rationale for when and why it will engage in attacks. Iran uses its capabilities in response to domestic and international events. As conflict between Tehran and Washington subsided after the 2015 nuclear deal, so too did the cycle of disruptive attacks. However, Iran’s decisionmaking process is obscured and its cyber capabilities are not controlled by the presidency, as evident in cases of intragovernmental hacking.
The report claims that the United States is reliant on an inadequately guarded cyberspace and should anticipate that future conflicts, online or offline, could trigger cyber attacks on U.S. infrastructure. The first priority should be to extend efforts to protect infrastructure and the public, including increased collaboration with regional partners and nongovernmental organizations targeted by Iran. More details here.
The U.S. Army War College recently included this concern: In late-2011, the executive chairman of Google stated, “The Iranians are unusually talented in cyber war for some reason we don’t fully understand.”3 Stopping a cyber adversary from disrupting activity or stealing intellectual property has been the primary concern of government and private sector organizations, but in the military and intelligence communities, there are other concerns about Iran.
Prior to 2009, much of Iran’s cyber efforts were focused internally on countering government dissidence. The influential Iranian Revolutionary Guard Corp (IRGC) proposed the development of an Iranian Cyber Army in 2005 to combat internal threats. It sought out professional hackers through voluntary means or by using blackmail and threats to boost its ranks. In early March 2012, Supreme Leader of Iran Ayatollah Ali Khameni publicly announced to state media the creation by decree of a new Supreme Council of Cyberspace charged “to oversee the defense of the Islamic Republic’s computer networks and develop new ways of infiltrating or attacking the computer networks of its enemies.”7 It included heads of intelligence, militia, security, media chiefs, and the IRGC. It has its own budget and offices along with the power to enact laws. Additionally, the IRGC stated that a secure internal network for high-level command and control called “Basir” (Persian for perceptive) was created to counter outside threats to online activities.8 However, it is clear from its actions against opposition influences and dissident groups that the regime continues internal censorship and monitoring as well. Furthermore, Reporters Without Borders, in its 2012 annual report of countries that restrict internet access, filter content, and imprison bloggers, “ranked Iran the number one enemy of the Internet…ahead of 11 other countries—including Saudi Arabia, Bahrain, Syria, China, and Belarus.”9
DoJ’s Bruce Ohr Demoted Again, Project Cassandra?

That’s it? On second thought, keep him employed to cough up the goods on Project Cassandra. More on that below. As an aside, in late December, Jeff Sessions ordered a complete review of Project Cassandra.
FNC: A Justice Department official demoted late last year for concealing his meetings with the men behind the anti-Trump “dossier” has been stripped of yet another title, Fox News has learned.
Bruce Ohr is no longer head of the Organized Crime Drug Enforcement Task Force.
Separately, sources familiar with the discussions tell Fox News that the Justice Department is expected to comply with demands from the House Intelligence Committee to provide Ohr for an interview. He is scheduled to visit the committee on Jan. 17, sources said.
Fox News first reported in December that Ohr had been demoted from the position of associate deputy attorney general, after it was revealed he had conducted undisclosed meetings with dossier author Christopher Steele and Glenn Simpson of Fusion GPS, the opposition research firm that produced the salacious document.
Fox News also reported that his wife Nellie Ohr worked for Fusion GPS, specifically on research related to the dossier.
At the time of his demotion, DOJ officials told Fox News that Bruce Ohr had been “wearing two hats,” and would fall back to his other title and portfolio – as head of OCDETF.
Now, Ohr has been stripped of that role as well; former deputy director Thomas Padden is now acting director. It is unclear where Ohr has landed, only that he is still an employee with the Department of Justice.
One DOJ insider joked that Ohr might end up in “one of those offices without a phone.”
Fox News has also confirmed that Bruce Ohr, as the head of OCDETF, was directly involved with Project Cassandra, the interagency investigation spearheaded by the DEA that tracked a massive international drug and money laundering scheme allegedly run by Hezbollah.
The project recently was the subject of a critical and lengthy Politico report looking at how the Obama administration may have hampered the investigation. Those closest to Project Cassandra, including Derek Maltz, the now-retired supervisory DEA agent who was a major player in the operation, claim the project and its potential prosecutions were sidelined by senior Obama administration officials who didn’t want to upset Iran in the lead-up to the historic nuclear deal with Tehran in 2015.
Attorney General Jeff Sessions has promised to look into what happened with the investigation.
He said in a statement last month: “While I am hopeful that there were no barriers constructed by the last admission to allowing DEA agents to fully bring all appropriate cases under Project Cassandra, this is a significant issue for the protection of Americans. We will review these matters and give full support to investigations of violent drug trafficking organizations.”
Sources close to the attorney general told Fox News that he was recently made aware of Ohr’s role in Project Cassandra and that Sessions is personally involved in the review and frequently asks for updates.
The 76 page criminal complaint for Project Cassandra is here.
Hezbollah Business Affairs Component 85 tons of cocaine was sold to Los Zetas one of the most violent Mexican cartels. Bruce Ohr was head of the teams assigned to Project Cassandra.
The United States Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA) (2016) announced significant enforcement activity including arrests targeting Lebanese Hizballah’s External Security Organization Business Affairs Component (BAC), which is involved in international criminal activities such as drug trafficking and drug proceed money laundering. These proceeds are used to purchase weapons for Hizballah for its activities in Syria. This ongoing investigation spans the globe and involves numerous international law enforcement agencies in seven countries, and once again highlights the dangerous global nexus between drug trafficking and terrorism.
This effort is part of DEA’s Project Cassandra, which targets a global Hizballah network responsible for the movement of large quantities of cocaine in the United States and Europe. This global network, referred to by law enforcement as the Lebanese Hizballah External Security Organization Business Affairs Component (BAC), was founded by deceased Hizballah Senior Leader Imad Mughniyah and currently operates under the control of Abdallah Safieddine and recent U.S.-designated Specially Designated Global Terrorist (SDGT) Adham Tabaja. Members of the Hizballah BAC have established business relationships with South American drug cartels, such as La Oficina de Envigado, responsible for supplying large quantities of cocaine to the European and United States drug markets. Further, the Hizballah BAC continues to launder significant drug proceeds as part of a trade based money laundering scheme known as the Black Market Peso Exchange.
“These drug trafficking and money laundering schemes utilized by the Business Affairs Component provide a revenue and weapons stream for an international terrorist organization responsible for devastating terror attacks around the world,” said DEA Acting Deputy Administrator Jack Riley. “DEA and our international partners are relentless in our commitment to disrupt any attempt by terrorists and terrorist organizations to leverage the drug trade against our nations. DEA and our partners will continue to dismantle networks who exploit the nexus between drugs and terror using all available law enforcement mechanisms.”
Beginning in February 2015, based on DEA investigative leads, European authorities initiated an operation targeting the network’s criminal activities in that region. Since then, law enforcement authorities, closely supported by DEA, have uncovered an intricate network of money couriers who collect and transport millions of euros in drug proceeds from Europe to the Middle East. The currency is then paid in Colombia to drug traffickers using the Hawala disbursement system. A large portion of the drug proceeds was found to transit through Lebanon, and a significant percentage of these proceeds are benefitting terrorist organizations, namely Hizballah.
This investigation is a result of leads developed during the investigation into the Lebanese Canadian Bank.
The combination of aggressive international law enforcement investigations and Treasury’s ongoing sanctions (see below) pressure shows the scope of the global commitment to diminish the ability of Hizballah and its financial supporters to move funds worldwide.
Enforcement Action
With DEA and Customs and Border Protection (CBP) working closely with foreign counterparts in France, Germany, Italy and Belgium, authorities arrested top leaders of the European cell of this Lebanese Hizballah External Security Organization BAC last week. The most significant arrest was of the U.S.-designated SDGT Mohamad Noureddine, a Lebanese money launderer who has worked directly with Hizballah’s financial apparatus to transfer Hizballah funds via his Lebanon-based company Trade Point International S.A.R.L. and maintained direct ties to Hizballah commercial and terrorist elements in both Lebanon and Iraq.
The CPB National Targeting Center partnered with DEA and international counterparts such as Europol in this investigation. CBP’s continued cooperation with the DEA , and European law enforcement counterparts is a vital component in dismantling complex global drug trafficking and money laundering networks as well as enhancing the security of the United States border.
U.S. Treasury Sanctions
Separately, the U.S. Department of the Treasury announced sanctions last week targeted Hizballah’s financial support network by designating Hizballah-affiliated money launderers Noureddine and Hamdi Zaher El Dine, as well as Trade Point International S.A.R.L, a company owned or controlled by Noureddine, pursuant to Executive Order 13224. This order targets terrorists and those providing support to terrorists or acts of terrorism. Noureddine and El Dine were designated for providing financial services to or in support of Hizballah, a Specially Designated Global Terrorist. Trade Point International S.A.R.L. was designated for being owned or controlled by Noureddine. As a result of Treasury’s action, all assets of the designated individuals or entities that are located in the United States or in the possession or control of U.S. persons are frozen, and U.S. persons are generally prohibited from engaging in transactions with them.
As part of its designation, Adam J. Szubin, Acting Under Secretary for Terrorism and Financial Intelligence, stated that, “Hizballah needs individuals like Mohamad Noureddine and Hamdi Zaher El Dine to launder criminal proceeds for use in terrorism and political destabilization. We will continue to target this vulnerability, and expose and disrupt such enablers of terrorism wherever we find them.”
Participating offices and agencies:
DEA Philadelphia, DEA Miami, DEA Newark, DEA New York, DEA Special Operations Division, DEA Bilateral Investigative Unit, DEA country offices in Europe, as well as Bogota and Cartagena
U.S. Customs and Border Protection
U.S. Treasury Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN)
U.S. Treasury Office of Foreign Assets Control (OFAC)
EUROPOL
EUROJUST