Declining Deportations and Increasing Criminal Alien Releases –
The Lawless Immigration Policies of the Obama Administration
Subcommittee on Immigration and the National Interest
May 19, 2016
Statement of Mark Krikorian
Executive Director, Center for Immigration Studies
Hearing May 19, 2016
Deportation is crucial. Credibility in immigration policy can be summed up in one sentence: Those who should get in, get in; those who should be kept out, are kept out; and those who should not be here will be required to leave.
– Barbara Jordan
CIS: The Obama administration has embraced a radical new approach to immigration law. It has, without the consent of Congress, transformed violation of immigration law into a “secondary offense.” That is to say, the goal is to ensure that an alien faces consequences for breaking immigration law only if he also breaks some other, “real,” law involving, say, violence or drug dealing. And even then, the primary violation has to be quite severe to warrant deportation for the (secondary) immigration offense.
This is comparable to the seat belt laws in many states; in places where failing to wear a seat belt is a secondary offense, a police officer cannot pull you over just for that, but if he pulls you over for speeding or some other primary offense, he can then also write a seat belt citation.
The administration’s November 2014 deportation priorities memo pretends this is not so; it includes ordinary violations of immigration law, but only as the lowest priority for deportation. And the collapse in interior removals of immigration violators shows that this third priority category is just for show.

John Sandweg, former acting director of ICE, stated the Obama administration position succinctly: “If you are a run-of-the-mill immigrant here illegally, your odds of getting deported are close to zero.”
This extra-legal shift in the conception of the immigration statute has been misleadingly packaged as “prosecutorial discretion.” True prosecutorial discretion is exercised by individual law enforcement officers in ways that do not undermine the agency’s mission. For instance, if a state trooper stops you for speeding and your documents are in order, you’ve interacted with him in a respectful manner, and your toddler in the back seat is crying because she needs her diaper changed — and he lets you off with a warning rather than a fine, that is prosecutorial discretion.
What the Obama administration has done is use discretion as a pretext for simply exempting the vast majority of immigration violators from any possibility of legal consequences.
The results of this transformation of immigration law are clear in the data. ICE statistics show that deportations from the interior (aliens arrested by ICE deportation officers and special agents, as opposed to the Border Patrol) have collapsed, from 236,000 in President Obama’s first year in office to 72,000 last year, a decline of 70 percent over the course of this administration:
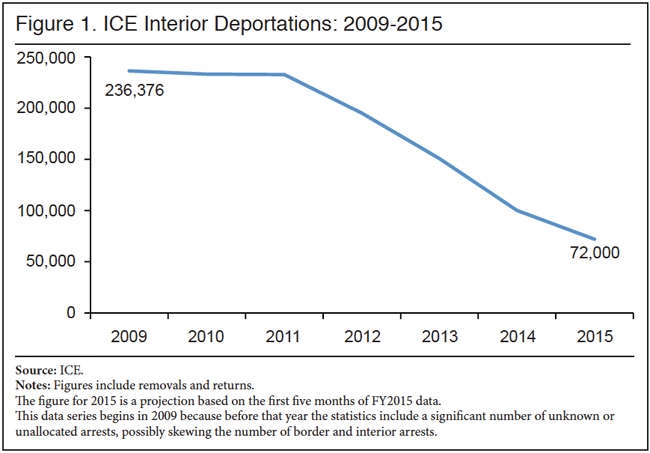
Not only have total interior deportations collapsed, but even the removal of
criminals has declined by more than half, from about 150,000 in 2010 and 2011 to about 63,000 last year — this despite the Obama administration’s claim of prioritizing such removals:
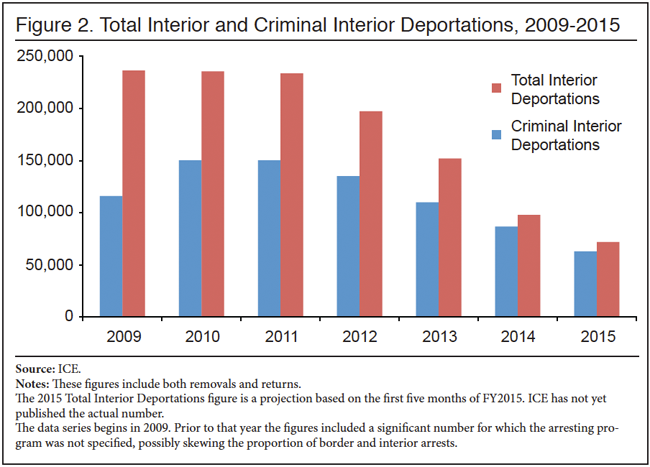
This decline has occurred despite increases in the number of criminal aliens identified by ICE, largely from the nationwide implementation of the Secure Communities program, which screened the fingerprints of aliens arrested by local law enforcement agencies. This successful program, which was tremendously popular with local law enforcement agencies, was dismantled by the president’s November 2014 executive actions, and replaced by the Priority Enforcement Program (PEP). ICE removal officers are still alerted to the arrest of criminal aliens by local police, but are prohibited by the White House and subservient ICE political leadership from acting on that information.

This collapse in deportations is not because we’ve run out of illegal aliens. After declining in 2007-2009 because of new enforcement efforts at the end of the Bush administration, followed by the recession, the number of illegal aliens has remained essentially constant at between 11 and 12 million. Many of these are new illegal arrivals — we estimate that some 2.5 million new illegal immigrants settled here during the first six years of the Obama administration, offset mainly by departures and legalizations.
Nor is the steep drop in deportations due to a lack of resources. Last year the Obama administration re-programmed $113 million that Congress had provided to ICE/ERO for enforcement and gave it to other agencies within DHS. The White House 2017 budget request actually seeks a decrease in funding for immigration enforcement, most notably a decrease of $100 million in funding for detention beds — from 34,000 beds to 30,900 — and a 15 percent decrease in funding for fugitive operations (i.e., the effort to locate the roughly 900,000 people ordered deported who simply ran off).
Rather, the collapse in enforcement is a policy choice of the Obama administration. Its strategic vision is, as I described above, to downgrade the immigration law to a secondary status. Among the tactics that serve this strategy, especially with regard to criminals, is the termination of the successful Secure Communities program and its replacement with the Priority Enforcement Program (PEP). There are three ways PEP suppresses enforcement:
- The new, more restrictive PEP prioritization scheme exempts a larger number of criminal aliens from deportation. Essentially, under PEP the only aliens ICE officers can target for deportation are people convicted of felonies, multiple “serious” misdemeanors, certain gang members, terrorists, and recent deportees. This exempts large numbers of criminal aliens from deportation.
- PEP imposes new logistical hurdles for ICE, most notably the requirement that an alien be convicted before ICE takes custody — which can enable a criminal alien to abscond from facing charges, or in some cases walk out of a courthouse or jail before ICE is aware that the offender is being released; and
- PEP explicitly allows local governments to impose non-cooperation or sanctuary policies on local law enforcement agencies. In 2014, local sanctuary jurisdictions released more than 10,000 aliens that local ICE field officers were seeking to deport.
As a result of these policies, fewer deportable aliens (and criminal aliens) are being removed from the country and criminal aliens who formerly would have been removed are now being released back to our communities only to commit new crimes.
There is an enormous public safety cost to these enforcement suppression policies. Since 2013 ICE has released approximately 85,000 criminal aliens from its custody. Many of these aliens have gone on to commit additional crimes. More than 125 have since been charged with homicide.
Here are some of the most egregious examples of crimes committed by illegal aliens released from ICE custody because of the president’s prioritization rules:
Sarah Root. In Omaha, Nebraska, on January 31, 2016, an illegal alien named Eswin Mejia, age 19, who had entered illegally as an “unaccompanied minor” but was allowed to stay with his brother, was drag racing while drunk and crashed his pick-up truck into the back of a car driven by Sarah Root, age 21. She died in the hospital soon after, just a day after her graduation from college. Mejia was arrested several days later for felony motor vehicle homicide. He had prior infractions as well. Bail was set at $50,000. Knowing Mejia was an illegal alien, local police contacted ICE five times to urgently request a detainer, fearing he would flee after making bail. ICE refused, saying that Mejia “did not meet ICE’s enforcement priorities.” As the local police feared, Mejia disappeared after posting bail.
Grant Ronnebeck. A 21-year-old man who was murdered while working at a convenience store in Mesa, Arizona. Ronnebeck’s killer was an illegal alien who was released by ICE in 2013 after conviction for a burglary and kidnapping involving drug dealing, to await an immigration hearing years in the future.
Katerin Gomez. This 35-year-old mother of three children under age 13 was killed in Chelsea, Massachusetts, on October 18, 2014, by a stray bullet through her window. The gun was fired during a street brawl allegedly by Hector Ramires, a 21-year old illegal alien member of the notoriously violent MS-13 gang, who was at large awaiting trial for two prior arrests for armed robbery (one with a gun, one with a knife), in which his illegal status and gang membership were noted. The police report also includes mention of prior criminal involvement in his home country of Honduras. ICE did not issue a detainer or initiate deportation proceedings after either prior arrest, nor did it make an effort to charge Ramires as an illegal alien in possession of a firearm, which is a felony punishable by up to 10 years in prison.
Greg Morton. This Frederick County (Maryland) sheriff’s deputy was attacked last November while sitting in his vehicle by Jose Misael Reyes-Reyes, an 18-year-old illegal alien who had entered as an unaccompanied minor. The attacker was a member of the notoriously violent MS-13 gang and had prior arrests, including one for carrying a dangerous weapon. ICE declined to take him into custody after the prior arrests because he was already awaiting an immigration court hearing.
* * *Prioritizing enforcement resources is not, in itself, the problem we face in immigration. Applying any body of law requires trade-offs and choices. The Treasury Department, for instance, devotes significant resources to the detection of money-laundering by organized crime or funding for terrorists. But it also has parallel initiatives of routine enforcement, to serve as a deterrent for ordinary taxpayers who might be tempted to cheat. Likewise in traffic enforcement; a driver doing 100 miles per hour through a school zone, firing a gun out the window, will obviously be top priority — but at the same time, there are parallel, routine enforcement efforts — speed traps and the like — to deter ordinary people from endangering others with unsafe driving.
If the IRS were to issue memos exempting anyone who’s not a mobster or terrorist from paying taxes, Congress would be aghast. Yet that is precisely what ICE has been ordered to do in the immigration context.
Some might object that the anticipated “raids” to take Central American illegal aliens into custody prove that the administration has not relegated immigration law to secondary status. Unfortunately, the opposite is true. The first round of “raids,” in January, netted a whopping 121 people — out of thousands of recent Central American illegal aliens — and only 70 of them were actually deported. Even if this next round of apprehensions is several times larger, it still amounts to nothing more than “enforcement theater.” It’s not even good enforcement theater. These Kabuki raids are too small — microscopic would be more accurate — to change the perception in Central America that if you get into the United States it’s unlikely you’ll ever be required to leave.
Despite staged disagreements with the administration over immigration enforcement, Congresswoman Pelosi concisely articulated the view she shares with the White House when she said in 2013 that “Our view of the law is that … if somebody is here without sufficient documentation, that is not reason for deportation.”
This is very different from an earlier Democratic congresswoman, Barbara Jordan, a civil rights pioneer and champion of the rule of law. As head of the bipartisan U.S. Commission on Immigration Reform, Jordan testified before Congress that “Credibility in immigration policy can be summed up in one sentence: Those who should get in, get in; those who should be kept out, are kept out; and those who should not be here will be required to leave.”











