So, while we are continuing to learn only some of the actions inside the United States by the Chinese Communist Party that include:
Senator Dianne Feinstein and her husband
The entire Biden Family
Congressman Eric Swalwell
… we are now finding that Georgia Senate candidate, Jon Ossoff in a contentious run-off race lied about his Chinese Communist Party business deal and finally came clean after he was about to be sued over his false financial disclosures.

There is much more to bubble to the surface as noted by the shuttering of the Chinese Consulate in Houston a few months ago and the soon to be revealing of more details. Meanwhile, U.S. corporations are also very tied to the Chinese Communist Party least of which is Apple, Google and Facebook. But what about slaves?
Few people understand that China has re-education camps and slaves known as Uighurs and the treatment of this Turkic ethnic group which is native to China.
A very large and detailed investigation completed has noted below:
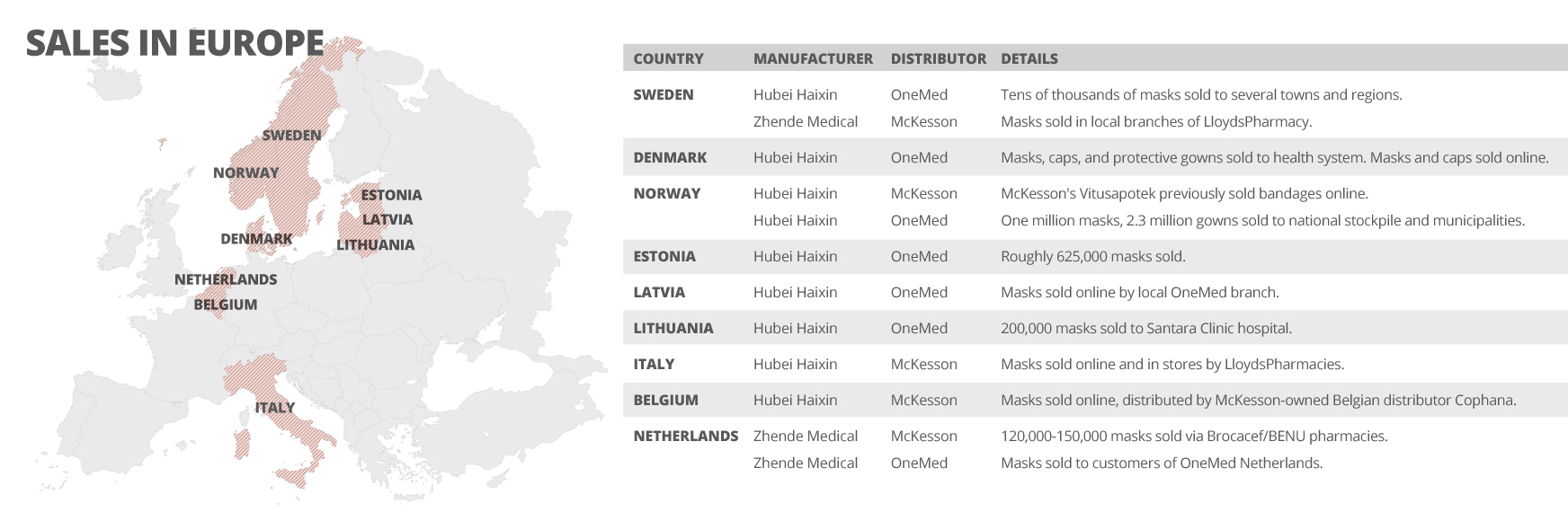
Medical masks and protective equipment made by Uighur laborers in China are being sold across Europe by at least two major distributors, and have been bought by governments and health bodies in at least five countries, an investigation by OCCRP and partners has found.
The workers are ethnic Uighurs from the western Chinese region of Xinjiang who have been sent to factories in other parts of the country under a controversial “labor transfer” program that experts say is coercive and prone to abuses.
China’s government has embarked on a campaign to stamp out unrest among Uighurs in Xinjiang via a campaign of mass surveillance and detention.
The labor transfer program ostensibly provides Uighurs in Xinjiang with new opportunities to leave home for factory jobs in other provinces. But rights workers say they are often coerced into complying, amid a crackdown that has seen over a million Uighurs and other Muslim minorities sent to re-education camps. Campaigners have been pushing for Western companies and governments to stop buying products made with Uighur labor.
Earlier this year, the New York Times revealed that medical masks made by Uighurs at a factory in Hubei province were being sold in the U.S. Now, OCCRP and its partners have found that some of Europe’s biggest medical distributors are also selling masks and protective equipment from this manufacturer, Hubei Haixin Protective Products. Publicly available documents show that Hubei Haixin until recently employed at least 130 Uighur workers transferred from Xinjiang.
The distributors include local branches of McKesson, a multinational giant that owns some of Europe’s largest pharmacy chains and medical wholesalers, and Swedish medical supply firm OneMed, which sold masks to health authorities and national stockpiles across the Nordic and Baltic regions.
Both McKesson and OneMed continued selling Hubei Haixin products throughout 2020, even after the Chinese company was named earlier this year by the New York Times and a think tank, the Australian Strategic Policy Institute (ASPI), as using potentially forced labor by Uighurs.
Reporters also found McKesson and OneMed sold products made by Zhende Medical, a publicly traded Chinese company that has been flagged as risky by rights experts because it has supply chains and subsidiaries in Xinjiang.
In a brief response sent to reporters, McKesson Europe’s public affairs director, Ronan Brett, said: “McKesson Europe is committed to good corporate citizenship and ethical sourcing. Suppliers must agree to McKesson Sustainable Supply Chain Principles (MSSP) which covers compliance with appropriate laws along with adherence to our strict policies on protecting workers, preparing for emergencies, identifying and managing environmental risk, and protecting the environment.” He did not respond to a request for further comment.
Credit: Henrik Myhr Nielsen / NRK Norwegian Prime Minister Erna Solberg welcomes a shipment of protective equipment by OneMed on March 23, 2020. The shipment included goods from Hubei Haixin.
OneMed’s head of operations, Robert Schmidt, said the company found out in late 2019 that the Hubei Haixin factory employed workers from Xinjiang, but continued its relationship with the producer after finding no evidence they were being coerced or mistreated.
“OneMed’s overall assessment is that there is no forced labor or discrimination against the Uighur minority population in our supply chain,” he said. “But we will of course continue to follow the issue and act if we should receive any new information.”
According to documents obtained by reporters, OneMed contacted Hubei Haixin with concerns about Uighur workers in January, and the Chinese factory promised to return them to their homes in Xinjiang at the end of their contract in March. But in reality, the factory continued to employ them until this September, claiming that pandemic movement restrictions prevented the workers from going home. OneMed continued buying the products.
Neither Hubei Haixin nor Zhende Medical responded to requests for comment, but in a statement sent to one of its European distributors, and obtained by reporters, Zhende said, “It is not acceptable in Zhende to engage in or support the use of forced or compulsory labor.”
“The so-called ‘human rights abuses’ in Xinjiang or ‘persecution of ethnic minorities’ are lies of the century made up by extremist anti-China forces,” a representative of the Chinese Embassy in Oslo, Yang Yiding, wrote in a statement to reporters.
China’s Foreign Ministry did not respond to requests for comment.
Credit: Matteo Civillini Hubei Haixin masks ordered from LloydsPharmacy Italy bear the name of McKesson Global Sourcing Ltd, a U.K. subsidiary of McKesson.
“Violation of Virtually Any Kind of Ethical Policy”
Over a million Uighurs and other Muslim minorities are believed to have been detained in newly built detention camps in recent years. China describes the camps as re-education facilities intended to combat Islamic radicalism, following a series of deadly inter-ethnic riots in Xinjiang and attacks by Uighur militants on ethnic-majority Han throughout China.
Uighurs have been documented working both in factories within Xinjiang’s detention camps, as well as being sent to regular factories throughout China via labor transfer programs, which are billed as a way of alleviating poverty and countering religious extremism.
It is important to keep reading the full summary found here.