The Taliban are watching all things Washington DC, especially Secretary of Defense Mattis and the White House.
Context: U.S. Defense Secretary Jim Mattis told reporters on Monday that the Trump administration was “very, very close” to a decision on Afghanistan, adding that all options were on the table. However, U.S officials believe it could take weeks for a South Asia strategy to be approved.
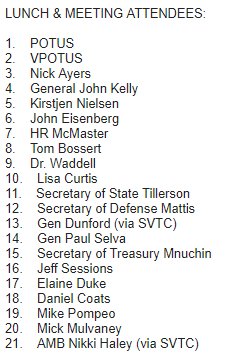
While the meetings could be delayed or rescheduled, the officials told CNN that the ongoing review appears to be drawing to a close.
LWJ: The Taliban has published an “open letter” to President Donald Trump, urging him to “adopt the strategy of a complete withdrawal from Afghanistan instead of a troops increase.” The letter was clearly penned with the Trump administration’s ongoing debate over the war in Afghanistan in mind.
Senior administration officials have reportedly prepared several plans, ranging from a complete withdrawal to a small increase of several thousand American troops. Lt. Gen. H.R. McMaster, the national security adviser, favors the latter while alternative scenarios have also been presented to the president.
President Trump has been reticent to commit additional forces, as he would then take ownership of the longest war in America’s history. The Taliban obviously knows this and is trying to influence the debate inside the US.
But readers should keep in mind that the new letter is propaganda and should be read as such. The letter is laced with erroneous and self-serving statements. And some of its key points, crafted for Western readers, are contradicted by the facts.
Allied with al Qaeda, which exports terrorism around the globe
The Taliban describes itself as a “mercy for Afghanistan, [the] region and the world because the Islamic Emirate does not have any intention or policy of causing harm to anyone and neither will it allow others to use the Afghan soil against anyone.”
Although the Taliban does not explicitly mention al Qaeda, the group likely wants readers to assume that this sentence means there is a clear distinction between the Taliban’s operations inside Afghanistan and jihadist threats outside of the country. In reality, there is no such clear line of demarcation.
Ayman al Zawahiri, the head of al Qaeda, remains openly loyal to the Taliban’s overall leader. Zawahiri swore allegiance to Mullah Mansour in Aug. 2015. Mansour, the successor to Taliban founder Mullah Omar, described al Qaeda’s leaders as the “heroes of the current jihadist era” and Osama bin laden as the “leader of mujahideen.” Mansour publicly accepted the “esteemed” Dr. Zawahiri’s fealty shortly after it was offered.
After Mansour was struck down by an American drone strike in Pakistan in May 2016, Zawahiri quickly rehearsed the same oath to Mullah Haibatullah Akhundzada, who still presides over the Taliban. Akhundzada’s son carried out a suicide bombing in Helmand province in July. The attack was just the latest piece of evidence confirming that the Taliban emir is a committed ideologue, not a prospective peace partner.
Under Akhundzada’s leadership, the Taliban is hardly bashful about its continuing alliance with al Qaeda. The Taliban celebrated the relationship in a Dec. 2016 video, which contained images of Osama bin Laden alongside Mullah Omar. One such image from the production can be seen below:
Other al Qaeda figures are also proudly featured in the Taliban video, such as Al Qaeda in the Arabian Peninsula’s (AQAP) Khalid al Batarfi, a veteran jihadist who plays an important ideological role. Batarfi praised the Taliban for harboring and supporting al Qaeda. And he directly connected the Taliban’s war in Afghanistan to the jihad against the US.
“Groups of Afghan Mujahideen have emerged from the land of Afghans that will destroy the biggest idol and head of kufr of our time, America,” Batarfi said in the Taliban’s video. The “Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan was sacrificed and even vanished in support of our sacred religion, but they (the Taliban) did not trade off their religion.” Batarfi crowed that the jihadists can finally “see [the] light of victory,” as governance according to the “rule of Sharia” law is “even stronger in Afghanistan than before.”
While the Taliban is often portrayed as a nationalist group (this is the intended implication of the group’s letter to President Trump), the Dec. 2016 video portrayed the Taliban’s struggle as part of the global jihad and the effort to reclaim all Muslim lands.
Akhundzada’s top deputy is the aforementioned Sirajuddin Haqqani, a longtime al Qaeda ally. The Haqqanis have been in bed with al Qaeda since the 1980s. Sirajuddin’s father, Jalaluddin, was one of Osama bin Laden’s earliest and most influential backers. Files recovered during the May 2011 raid on bin Laden’s compound reveal that al Qaeda’s men have fought alongside Sirajuddin’s forces for years. This is especially significant because Haqqani oversees the Taliban’s military operations.
There are numerous other ties. In Sept. 2014, for instance, Zawahiri publicly announced the creation of Al Qaeda in the Indian Subcontinent (AQIS), which brought together existing al Qaeda-allied groups. AQIS has repeatedly made it clear that its men fight under the Taliban’s banner and that its primary goal is to restore the Taliban’s Islamic Emirate to power in Afghanistan. In Oct. 2015, US and Afghan forces raided two massive al Qaeda training camps in southern Afghanistan. One of the camps, approximately 30 square-miles in size, may be the largest al Qaeda training camp in Afghanistan’s history. Both of the camps were supported by the Taliban. AQIS conducts operations in Bangladesh, Pakistan, India and elsewhere.
Just over two weeks before the 2016 presidential election, the US hunted down a top al Qaeda commander known as Farouq al-Qahtani in eastern Afghanistan. Qahtani not only commanded jihadists fighting alongside the Taliban, he was planning attacks inside the United States at the time of his demise.
All of these details, and more, belie the Taliban’s claim that it won’t “allow others to use the Afghan soil against anyone.”
State sponsors and enablers of the Taliban-led insurgency
The Taliban claims that the US government has concluded that the “mujahideen” are entirely self-sufficient and do not receive any foreign support. “Your intelligence agencies admit that our Mujahideen are not being supported by any country and neither can they produce any proof in the contrary,” the letter reads.
This is obviously false — Pakistan’s support for the Taliban is longstanding and well-known. Other countries, such as Iran and Russia, provide some level of assistance. Wealthy benefactors in the Gulf have contributed rich sums to the Taliban cause as well.
In July, the US State Department once again confirmed that Pakistan harbors the Taliban, including the so-called Haqqani Network (HQN), which plays an integral role within the organization. “Pakistan did not take substantial action against the Afghan Taliban or HQN, or substantially limit their ability to threaten US interests in Afghanistan, although Pakistan supported efforts to bring both groups into an Afghan-led peace process,” State’s Country Reports on Terrorism 2016 reads. A “number” of attacks inside Afghanistan throughout 2016 “were planned and launched from safe havens in Pakistan.”
In a report submitted to Congress in June, the Defense Department also explained the enduring importance of the jihadists’ Pakistani safe havens. “Attacks in Afghanistan attributed to Pakistan-based militant networks continue to erode the Afghanistan-Pakistan relationship,” the Pentagon noted. “Militant groups, including the Taliban and Haqqani Network, continued to utilize sanctuaries inside Pakistan.”
The Afghan Taliban is not operating under the radar in Pakistan, but instead receives assistance from parts of the government. “Afghan-oriented militant groups, including the Taliban and Haqqani Network, retain freedom of action inside Pakistani territory and benefit from support from elements of the Pakistani Government,” the report reads (emphasis added).
This is consistent with Pakistan’s “Good Taliban” vs. “Bad Taliban” policy, which favors jihadists who are focused on attacking the Afghan government and allied forces, including the US. Only the “Bad Taliban” — that is, those jihadists operating against the Pakistani state — are regularly targeted by Pakistani security. The effects of this policy are plain to see. The Quetta Shura Taliban (QST) earned its name because the group’s most senior leaders have been able to operate openly in the city. It is well-known, too, that the Haqqanis have cozy relations with the Pakistani military and intelligence establishment. Sirajuddin Haqqani has been the Taliban’s top deputy leader since 2015.
Pakistan isn’t the only regional player supporting the Taliban-led insurgency. The Iranian government is as well.
“Iran provides some support to the Taliban and Haqqani Network and has publicly justified its relationships as a means to combat the spread of the ISIS-K threat in Afghanistan,” the Pentagon reported in June. Although the Iranians attempt to justify their policy as a form of realpolitik, a necessary consequence of fighting the Islamic State’s Wilayah Khorasan (Khorasan “province,” or ISIS-K), the reality is that they first forged a working relationship with their former foes in the Taliban immediately after the 9/11 hijackings. [See FDD’s Long War Journal report, Analysis: Iran has supported the Taliban’s insurgency since late 2001.]
A striking example of Iranian complicity in the Afghan insurgency was revealed in May 2016, when the Taliban’s leader, Mullah Mansour, was killed in an American airstrike. The US followed Mansour from Iran, where he was holding meetings, across the Pakistani border into Baluchistan, where he was struck down. Mansour’s ability to travel freely inside Iran speaks volumes about the ongoing relationship.
At a minimum, Russia has rhetorically backed the Taliban. “Russian-Afghan relations suffered due to Russia’s public acknowledgment of communications with the Taliban and support of the Taliban’s call for coalition withdrawal from Afghanistan,” the Pentagon has said. Press reports continue to point to evidence that Russian-supplied weapons are helping to fuel the Taliban-led insurgency. Asked about these reports in April, Gen. John Nicholson, the Commander of Resolute Support and US Forces Afghanistan, refused to refute them.
There are other obvious problems with the Taliban’s letter. The group accuses President Trump’s generals of lying about the American casualties incurred. The “[g]enerals are concealing the real statistics of your dead and crippled however the Afghans can easily count the coffins being sent your way on a daily basis,” the letter reads. This is nonsensical, as American casualties are readily verified. Moreover, the Taliban frequently lies about the number of Americans killed or wounded in combat.
The Taliban says that it could “conquer many provincial capitals currently under siege,” if it “were not for fear of civilian casualties.” There is no question that the Taliban currently threatens multiple provincial capitals, but its concern about civilian casualties is mostly cosmetic. The United Nations has repeatedly documented the Taliban’s culpability in killing and wounding innocents. The group is responsible for more civilian casualties in Afghanistan than any other actor.
The US approach to the war in Afghanistan should be based on a rational assessment of the situation, not the Taliban’s misleading claims.





 For a comprehensive timeline and names,
For a comprehensive timeline and names,  Ships set out from Northern Fleet headquarters in Severomorsk. Photo: mil.ru
Ships set out from Northern Fleet headquarters in Severomorsk. Photo: mil.ru

