NIN is not Nine Inch Nails but rather the Supreme Leader’s tightly controlled internet platform known as the National Internet Network. It operates somewhat like an fee based system, those that can afford and pay more for access and usage get the best speed and less government oversight. The poorer class and the dissenters are controlled by the regime and not only vulnerable to the throttling of service but are subject to phishing operations, hacks and DDoS outages, all at the direction of the regime.
It almost sounds like a marriage between the U.S. version/marriage of Google, Facebook and NSA, right? Well it is.
The NIN can filter key words and phrases and send users only to the sites it approved, according to the CHRI report. The government has also limited access to thousands of sites and platforms, including Facebook and YouTube. It is attempting to replace search engines like Google with its own state-approved versions.
Iran has also been able to influence how people use the internet through pricing. While there are private internet service providers (ISPs), they are still under government control, allowing state-run infrastructure companies to set up a tiered plan where access to international internet sites costs more than domestic. This drives traffic away from the global internet and to the NIN.
It’s not just internet censorship that Iranians are facing. The report also highlights state-sponsored cyberattacks and phishing schemes. State security agencies like the Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps, a branch of the armed forces meant to protect the Islamic system, have hacked into individual and private online communications and arrested people on the basis of their content, which is technically illegal under Iranian law.
DDoS attacks, which aim to make specific websites unavailable or limit access to information by flooding them with illegitimate traffic, have become more prominent during politically sensitive times as well, according to the report. During the election in 2016, reformist and centrist candidates like Gaam-e Dovvom faced multiple attacks. The report said many of these are also internal attacks through the government.
Meanwhile, Iranians are not blind to the extensive surveillance they are facing online. As we’ve reported, many internet users use VPNs and other apps to try and circumvent the censorship. And millions of Iranians have turned to the Toronto-born Psiphon app to use the internet during the protests in December and this month. More here.
***  photo
photo
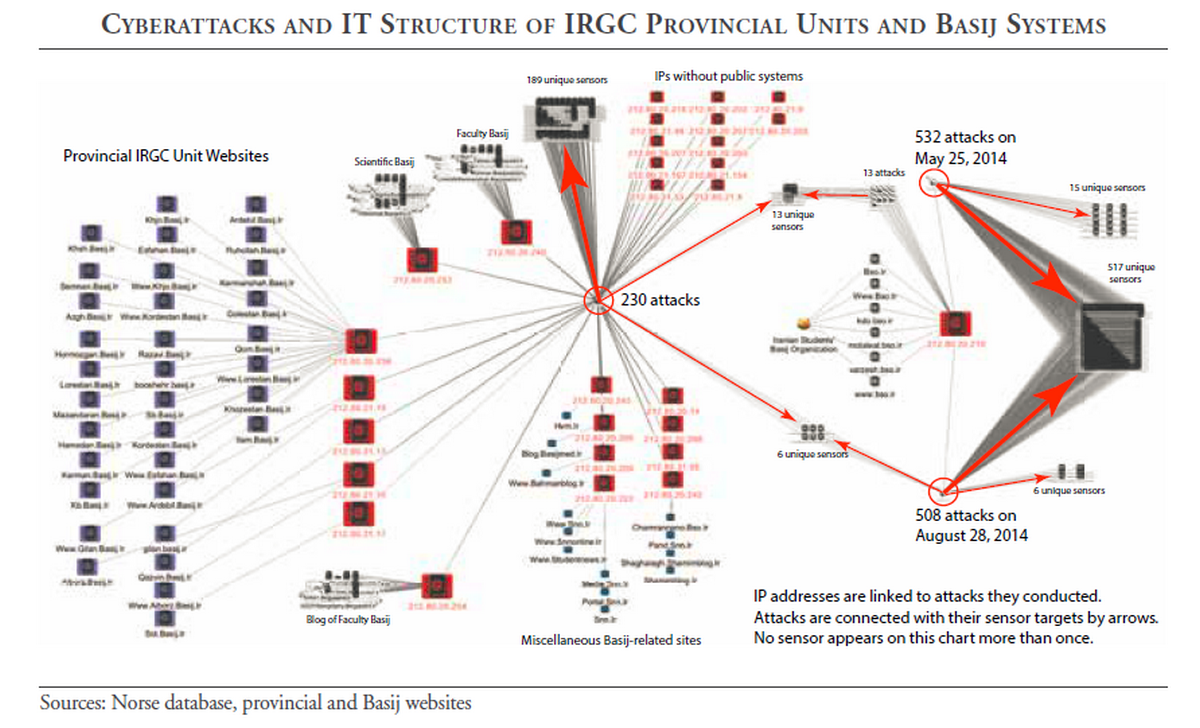
Tehran has become increasingly adept at conducting cyber espionage and disruptive attacks against opponents at home and abroad, ranging from Iranian civil society organizations to governmental and commercial institutions in Israel, Saudi Arabia, and the United States.
A new report by carnegiendowment.org evaluates Iran’s Cyber threat environment. Just as Iran uses proxies to project its regional power, Tehran often masks its cyber operations using proxies to maintain plausible deniability. Yet such operations can frequently be linked to the country’s security apparatus, namely the Ministry of Intelligence and Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps.
While Iran does not have a public strategic policy with respect to cyberspace, its history demonstrates a rationale for when and why it will engage in attacks. Iran uses its capabilities in response to domestic and international events. As conflict between Tehran and Washington subsided after the 2015 nuclear deal, so too did the cycle of disruptive attacks. However, Iran’s decisionmaking process is obscured and its cyber capabilities are not controlled by the presidency, as evident in cases of intragovernmental hacking.
The report claims that the United States is reliant on an inadequately guarded cyberspace and should anticipate that future conflicts, online or offline, could trigger cyber attacks on U.S. infrastructure. The first priority should be to extend efforts to protect infrastructure and the public, including increased collaboration with regional partners and nongovernmental organizations targeted by Iran. More details here.
The U.S. Army War College recently included this concern: In late-2011, the executive chairman of Google stated, “The Iranians are unusually talented in cyber war for some reason we don’t fully understand.”3 Stopping a cyber adversary from disrupting activity or stealing intellectual property has been the primary concern of government and private sector organizations, but in the military and intelligence communities, there are other concerns about Iran.
Prior to 2009, much of Iran’s cyber efforts were focused internally on countering government dissidence. The influential Iranian Revolutionary Guard Corp (IRGC) proposed the development of an Iranian Cyber Army in 2005 to combat internal threats. It sought out professional hackers through voluntary means or by using blackmail and threats to boost its ranks. In early March 2012, Supreme Leader of Iran Ayatollah Ali Khameni publicly announced to state media the creation by decree of a new Supreme Council of Cyberspace charged “to oversee the defense of the Islamic Republic’s computer networks and develop new ways of infiltrating or attacking the computer networks of its enemies.”7 It included heads of intelligence, militia, security, media chiefs, and the IRGC. It has its own budget and offices along with the power to enact laws. Additionally, the IRGC stated that a secure internal network for high-level command and control called “Basir” (Persian for perceptive) was created to counter outside threats to online activities.8 However, it is clear from its actions against opposition influences and dissident groups that the regime continues internal censorship and monitoring as well. Furthermore, Reporters Without Borders, in its 2012 annual report of countries that restrict internet access, filter content, and imprison bloggers, “ranked Iran the number one enemy of the Internet…ahead of 11 other countries—including Saudi Arabia, Bahrain, Syria, China, and Belarus.”9




 Over the weekend, a former chairman of the joint chiefs of staff under two presidents said the U.S. is closer to nuclear war with North Korea “than we have ever been.” | AP Photo
Over the weekend, a former chairman of the joint chiefs of staff under two presidents said the U.S. is closer to nuclear war with North Korea “than we have ever been.” | AP Photo