
 McCain and Graham both stated they were unaware of the operations in Niger, much less the other countries located in West Africa. The United States has an estimated 7000 troops operating in about 50 countries in Africa. Militant Islam has no boundaries globally.
McCain and Graham both stated they were unaware of the operations in Niger, much less the other countries located in West Africa. The United States has an estimated 7000 troops operating in about 50 countries in Africa. Militant Islam has no boundaries globally.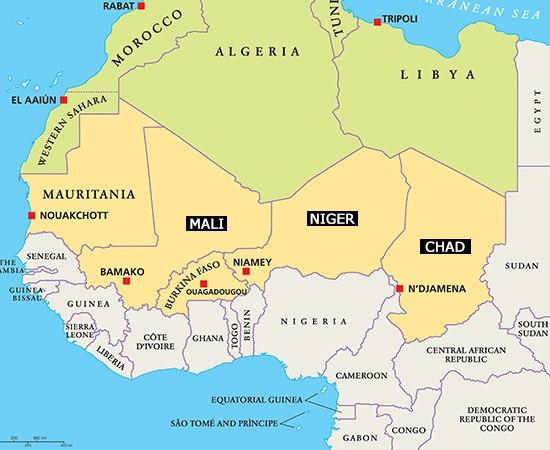
U.S. officials increasingly believe that the military unit ambushed by an Islamic State militant group (ISIS) affiliate in Niger was attacked as the result of being set up by people in a village sympathetic to local jihadis.
Details about the October 4 attack that left four U.S. soldiers—all Green Berets—dead are only now being revealed.
The militants were likely tipped off by at least one accomplice who may have lived within the local population, U.S. officials briefed on the case told NBC News. Almou Hassane, the mayor of the village in question, Tongo Tongo, told Voice of America that “the attackers, the bandits, the terrorists have never lacked accomplices among local populations.”
Nigerien authorities have detained the chief of the village, Mounkaila Alassane, adding to the suspicion that the dozens of ISIS-affiliated militants who attacked the unit had prior information about the soldiers’ movements.
A joint U.S. and Nigerien patrol spent the evening near the Malian border before the attack. Local reports indicate that the purpose of their mission may have been to locate an associate of Abu Adnan al-Sahraoui, a member of the Islamic State in the Greater Sahara, or ISGS, the affiliate suspected of the ambush.
“They must have spent the night in the northwest of Tongo Tongo,” Hassane said.
The soldiers met with elders of the village, which they knew was likely sympathetic toward ISIS, and officials told NBC News that villagers made efforts to delay the Green Berets’ departure.
When the soldiers left the village in unarmored vehicles, dozens of jihadis launched a sneak attack with machine-gun fire and then mortars and rocket-propelled grenades. The soldiers exited their vehicles and started to fire back, but were outnumbered and outgunned. They tried to retreat but were ambushed again a mile away.
On Monday, General Joseph Dunford, the U.S. military’s top officer, said he wanted to uncover what happened, for the public and for the relatives of those killed in the attack.
“We owe you more information; more importantly, we owe the families of the fallen more information,” Dunford said. “Did the mission change? It’s a fair question.”
He said the troops did not call for help from French special forces until an hour after coming into contact with the enemy in Niger. He said a U.S. drone responded in “minutes” but did not fire. He would not comment on whether it was armed or not.
“I make no judgment as to how long it took them to ask for support,” Dunford said. “I don’t know that they thought they needed support prior to that time. I don’t know how this attack unfolded. I don’t know what their initial assessment was of what they were confronted with.”
French jets arrived one hour after the call for assistance but did not strike because they did not have accurate intelligence about the combatants on the battlefield and were not liaising with the U.S. military. Dunford said at present there was no indication that the soldiers were acting outside their remit or orders from their superiors.
“I don’t have any indication right now to believe or to know that they did anything other than operate within the orders that they were given,” Dunford said. “That’s what the investigation’s all about. So I think anyone that speculates about what special operations forces did or didn’t do is doing exactly that—they’re speculating.”
The Islamic State in the Greater Sahara is a relatively new and local branch of ISIS that has conducted several small attacks in the region, particularly in Burkina Faso, which neighbors Niger. The jihadi affiliate gave its allegiance to ISIS and the group accepted its bayah, or pledge, in October 2016.
The ISIS affiliate in the area that stretches across six African countries from Senegal to Chad is overshadowed by more dominant radical Islamist groups, in this case Al-Qaeda’s affiliates—Al-Qaeda in the Islamic Maghreb, Ansar Dine and Al-Mourabitoun.






 photo
photo


