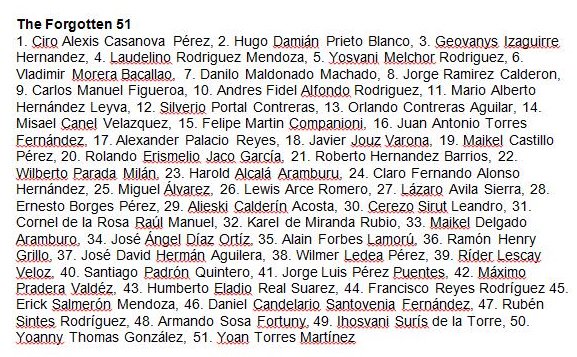
Primer for consideration:
North Korea’s Next Missile Test Could Kill
Chang/DailyBeast: Firing back with ‘unprecedented’ provocations against joint South Korean and American annual military exercises, Kim Jung Un could make a dangerously wrong move.On Monday, North Korea fired five short-range missiles eastward. The projectiles fell into the Sea of Japan, what Koreans call the East Sea. The provocation followed Friday’s launch of two Nodong medium-range missiles, which can put a dent anywhere in South Korea and parts of Japan.
The Democratic People’s Republic of Korea has launched 15 projectiles on four separate occasions since early last month in apparent shows of anger.
Friday’s and Monday’s belligerent acts follow a series of threats to kill all the residents of Manhattan and launch “preemptive and offensive” nuclear strikes. The regime has also taken the unprecedented step of releasing photographs of leader Kim Jong Un standing next to what it implied is a thermonuclear device. Full article here.
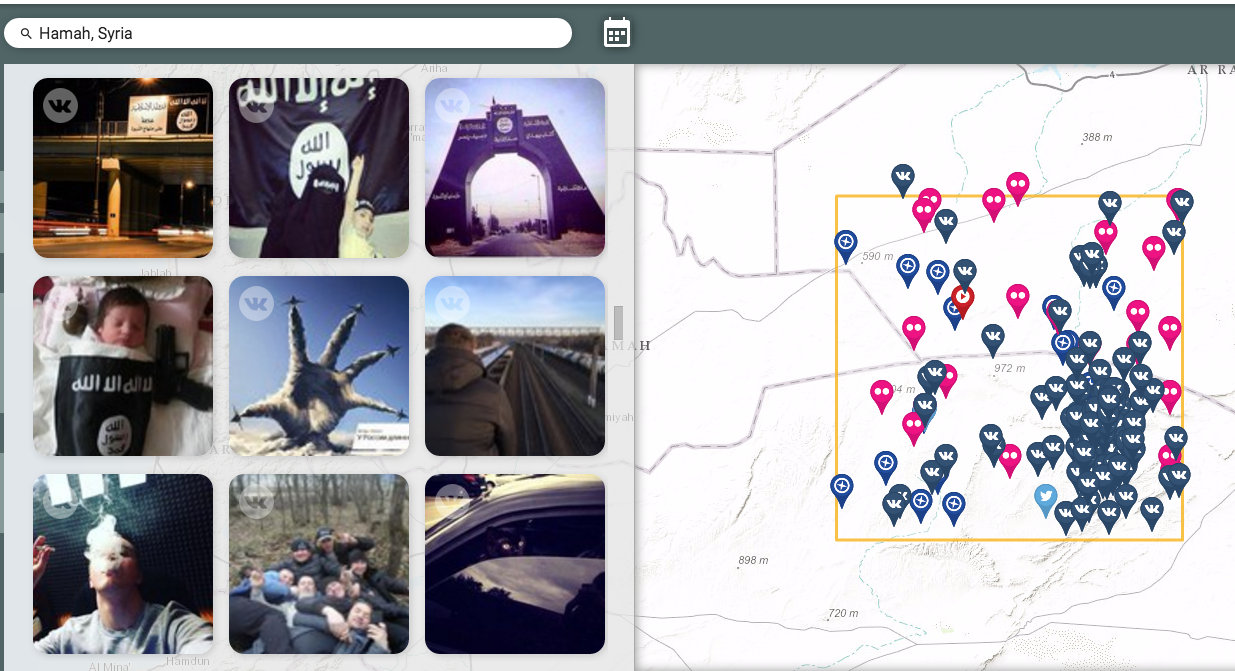
North Korea troops fighting in Syrian civil war, delegate says
Asaad Al-Zoubi said “fatally dangerous” North Korean soldiers are fighting on behalf of President Bashar al-Assad.
GENEVA, Switzerland, March 22 (UPI) — Two North Korean military units are fighting on behalf of President Bashar al-Assad in the Syria conflict.
Asaad Al-Zoubi, the head of the Syrian opposition’s High Negotiations Committee delegation, told Russian news agency TASS that North Koreans have committed troops to the civil war.
According to Al-Zoubi, the two units are called Chalma-1 and Chalma-2.
The Syrian delegate provided the information as he attended Syria peace talks at the United Nations European headquarters in Geneva.
Al-Zoubi added there are fighters from Iran and Afghanistan fighting on behalf of Assad.
Russia’s Sputnik International also confirmed the Syrian representative’s statement on North Korean soldiers in the Middle East, and quoted Al-Zoubi as saying the “North Korean troops are fatally dangerous” during an explanation of the presence of foreign troops in the Syrian civil war.
The civil war has continued for five years, and the opposition and the Assad regime are at odds regarding the details of a peace negotiation.
But Pyongyang maintains friendly ties with the dictatorship in Damascus, and Russia has supported Assad’s rule.
North Korea’s presence in the Middle East conflict is unprecedented, but the two countries have cultivated military ties for many years.
North Korea has been a staunch ally of the Syrian government of Bashar al-Assad, opposed by the Islamic State, and Pyongyang helped Syria build a nuclear facility destroyed by an Israeli air raid in 2007.
Last September Syria dedicated a park to former North Korean leader Kim Il Sung.
****** 2013:
38North: When Kim Jong Un assumed power two years ago, foreign observers predicted North Korea would cut its losses short and disengage from Syria in the wake of the overthrow of friendly regimes in Algeria, Egypt and Libya. But this proved to be wishful thinking. On the contrary, Kim Jong Un got off the fence and has joined the Assad government to actively fight against the anti-government rebels in Syria, many of whom are affiliated with Al-Qaeda. Indeed, the DPRK says it is its duty to help a legitimate sovereign government in the fight against international terrorism in Syria.
Careful reading of the DPRK Foreign Ministry’s latest tepid and contorted denial[1] of the persistent rumors that Pyongyang supplies weapons to Syria or flies pilots in anti-rebel air raids suggests that North Korean arms and military advisors may indeed be engaged on the battlefields of the Syrian civil war but not necessarily in the exact manner alleged by the rebels and Western media. Pyongyang is known for its penchant to split hairs: it knows the facts, and even if the rumors come close to the reality, but do not exactly match it, Pyongyang will hit back hard. The fact that it hasn’t suggests that indeed there is fire where there is smoke.
Why Did Kim Jong Un Come to Assad’s Rescue?
In 2013, North Korea’s young leader stepped up military support for his country’s long-time strategic partner, the Assad regime, in the nationwide civil war against the radical Sunni rebels backed by the Western liberal democracies in alliance with conservative Gulf monarchies. Why is North Korea fighting for Assad?
The well-entrenched Kim family came to the rescue of the faltering Assad family, exporting its trademark anti-American “revolutionary spirit of the offensive,” for four reasons. First, birds of a feather flock together. Both countries are former Soviet client states that lost their patron after the collapse of the USSR in the early 1990s. The collapse resulted in the loss of the strategic support that the Soviets had provided them, forcing Pyongyang and Damascus to abandon the dream of “strategic parity” with Seoul and Tel Aviv, respectively, and to adopt a new formula of “strategic deterrence,” vis-a-vis the ROK and Israel, as well as their allies and like-minded countries. In that context, both face an acute security dilemma in their respective neighborhood since they are also divided countries fighting to force out foreign troops that occupy what they believe are their homelands, namely the U.S. forces in the southern half of the Korean peninsula and Israeli troops in the Golan Heights. Finally, both have also been branded as “rogue states” and are isolated in the international community. The United States considers them as “states sponsoring international terrorism” and engaged in “nuclear proliferation” and, therefore, has imposed broad-ranging political and economic sanctions on both countries.
In that context, Pyongyang and Damascus have similar worldviews as part of the anti-US, anti-imperialist united front. Supreme People’s Assembly (SPA) Chairman Choe Tae Bok once said: “The unity of our two peoples fighting in the same trench against the common enemy is everlasting, though Syria and Korea are geographically far away from each other. Our bilateral relations of friendship and cooperation will grow stronger and stronger.”[2] When the DPRK’s nominal head of state Kim Yong Nam met with the Syrian Prime Minister Wael Nader Al Halqi in Tehran in August 2013, the latter said that “Syria regards the DPRK as a military power with tremendous military force and a country of comrades-in-arms struggling against the common enemy.”[3]
This close political relationship is reflected in a number of ways. Neither country has been willing to normalize relations with the other’s enemies. The DPRK rejected Israeli overtures in the early 1990s[4] seeking to establish diplomatic relations,[5] despite Israeli promises to pay considerable compensation (up to USD 500 million) if Pyongyang were to abandon Syria and terminate its missile sales to the Middle East.[6] Similarly, Syria rejected past ROK attempts to normalize relations, unlike the former Soviet Union and China, despite its growing trade and investment links with Seoul.[7] Pyongyang and Damascus also support each other in the United Nations and other international organizations. For example, upon cues from Damascus, Pyongyang denounces US proposals for the Middle East peace process, Lebanon situation, Palestinian problem, and Arab-Israeli settlement.[8] In turn, Syria supports the DPRK’s positions in various talks on denuclearization of the Korean peninsula and inter-Korea reconciliation.[9]
State-to-state and party-to-party ties are well developed and based on extensive institutional links and personal affinities. Since the beginning of this year alone, Kim Jong Un has exchanged personal letters with Bashar Al-Assad on ten different occasions—more than with any other foreign leader, including Chinese. Many senior DPRK leaders have either visited Syria over the past two decades or worked closely with its government.[10] For instance, Kim Yong Nam traveled to Syria as President of the SPA Presidium in July 2002 and June 2000, and as Foreign Minister in July 1992. Former KPA Chief of General Staff hardline general Kim Kyok Sik served as North Korea’s military liaison to Syria in the tumultuous 1970s, coordinating the North’s military assistance to the Assad regime during the October 1973 Arab-Israeli War and post-war rehabilitation of Syrian armed forces in the mid-1970s. He also managed North Korean military sales and military construction projects there for almost a decade. As a result, many North Korean leaders have some personal knowledge of Syria and its leaders, as well as a good understanding of Pyongyang’s stakes in its relationship with Damascus.
Second, in addition to being birds of a feather, geopolitical considerations also push Pyongyang to assist Damascus. As a strategic partner of both Syria and Iran, North Korea may have been contracted by Iran to defend their mutual ally in Damascus. It is also plausible that there may be some DPRK-Syria-Russia connections in the area of military-technical cooperation, probably, in the development of Syrian air defense capabilities. Pyongyang takes full advantage of all-out Russian and Iranian support for Damascus “to defend the frontline of the joint anti-American and anti-imperialist struggle” on the Syrian battlefield without fear of being depicted as a pariah or having to pay diplomatic or political price for its actions.
Third, North Korea’s intervention in Syria’s civil war is aimed at stopping the “hostile forces” and “colored revolutions” they export at the far-flung gates to ensure they will never reach North Korea’s shores. Kim Jong Un allegedly discussed how his government might be able to help the Assad regime fight back against the rebels with a visiting Syrian government delegation on July 24, 2013, when he was accompanied by party secretaries Kim Ki Nam (ideology) and Kim Yang Gon (South Korea), and first vice-foreign minister Kim Gye Gwan, the regime’s heavyweights known for their concern about the possible impact of the Arab Spring on the North.[11] The North’s official mouthpiece, Rodong Sinmun, often discusses “the reactionary ideology and culture of imperialists that can be as effective as military capability in realizing their hegemonic ambition,” stressing that “the youth is the main target of the imperialists’ offensive” because “young people played a large role in bringing about “Egyptian-style change,” “Libyan-style victory,” and “Syrian calamity.”

Kim Jong Un holds talks with the high-ranking visiting delegation of Syrian Arab Republic in Pyongyang, on July 24, 2013. (Photo: Rodong Sinmun, July 25, 2013)
Pyongyang may also seek to divert Washington’s attention and resources away from the Korean peninsula by waging a proxy war against the United States and its allies in Syria. The North Korean leadership is not ignorant or naive. It does understand that if the US gets sucked into another war in the Middle East during “sequestration,” not only will it undermine the short-to-mid-term credibility of its defense commitment to South Korea, but it will also buy time for Pyongyang to further build up its own nuclear arsenal and advance its war preparations against the South.
Fourth, while not a military alliance based on legally binding mutual defense obligations, North Korea and Syria have a long history of extensive bilateral military-to-military ties based on their close political relationship. These ties include:
- Fraternal assistance in several Middle Eastern wars: Since Israel joined the UN coalition troops fighting in the Korean War, the DPRK government has never considered it inappropriate or unwise to send troops to aid the Syrian government in the Arab-Israeli wars in the Middle East. For instance, the DPRK sent 25 pilots to Syria to defend the air space over Damascus during the Arab-Israeli war of 1967.[12] In 1970, the DPRK dispatched 200 tank crewmen, 53 pilots, and 140 missile technicians to Syria. During the October 1973 Arab-Israeli War, the DPRK dispatched 30 pilots to Egypt and Syria, who provided training for Syrian pilots to fight against Israel.[13] Moreover, the North Korean Air Force pilots themselves flew the Soviet-made Egyptian and Syrian airplanes during some key air battles. In 1975 and 1976, Pyongyang sent 75 Air Force instructors and 40 MIG pilots to Damascus, respectively. In 1982, during the Lebanese civil war, the DPRK government dispatched SOF (special operations forces) servicemen to Syria to provide training for guerrilla operations, some killed by the Israeli military. In 1984-1986 and 1990, 50 and 30 North Korean military instructors were sent to Syria, respectively.
- Military Education and Training: In the mid-1980s, Kim Jong Il approved the request of the Syrian government for its military officers’ to be educated and trained at DPRK military educational institutions at the expense of North Korea. Since then, the North Korean military has been training Syrian military officers at the Kim Il Sung Military University (an analogue of US National Defense University). Officers at the colonel rank usually participate in the one-year high-level officers’ course. Syrian officers at the captain rank are also admitted to the four-year course. They are taught military strategy, operational art, and military tactics, including guerrilla operations. Kim Jong Il is said to have followed with interest the successful careers of the Syrian general officers who graduated from the university.
- Foreign military sales: Beginning in the late 1970s through the 1980s, the DPRK supplied Syria with various conventional weapons such as rifles, guns, mortars, ammunition, bombs, armored vehicles, anti-tank missiles, radars, and even military uniforms. In particular, in 1978, the DPRK sold 300 recoilless guns to Syria. In 1982, when the civil war broke out in Syria, the Syrian military killed 20,000 civilians by firing “BM-11, 122mm MLRS (Multiple Launch Rocket System),” the weapon system imported from the DPRK. The Israel military snatched the notorious “BM-11” from Syria during the Lebanon war in 1982, killing 25 KPA soldiers who serviced it. In 1992, Pyongyang shipped 20 tons of bombs to Damascus.
- Weapons of Mass Destruction and Delivery Systems: There is evidence to suggest that North Korea provided technical assistance to Syria in acquiring key nuclear-related technologies in China and Europe as well as in constructing a covert nuclear reactor at Al Kibar that was bombed by the Israeli Air Force in 2007. On ballistic missiles, cooperation began in the late 1980s, with the North selling Scud-C transporter-erector-launchers (TELs) and cluster warheads to Syria, helping to construct two missile assembly plants in Hama and an electronic missile launch control facility near Aleppo and providing special training for Syrian missile technicians in North Korea. Aside from strengthening the self-defense potential of one of its anti-imperialist, anti-US allies, the North has earned good money doing it.[14] On chemical weapons, there is only limited evidence of cooperation, including the interception of DPRK ships heading for Syria carrying cargos that might be useful in defending against chemical attacks. There has also been speculation that the explosion on July 20, 2007, at a facility near the city of Halab was the result of an attempt by North Korean scientists working with Syrian officials to load a chemical warhead onto one of the North Korean missiles, likely the No-dong 1 model. On biological weapons, there is information about bilateral cooperation between the Ministries of Public Health, pharmaceutical companies, and university biotech research labs but little on weapons cooperation. Still, some observers have asserted that “Syria has a biological weapons research and development program, and it is seeking professional assistance from China and North Korea in this area.”[15]
The Syrian conflict provides the North Korean military with an opportunity to gain valuable “real world” experience. Reportedly, North Korean advisors provide technical assistance to Syria’s defense industry, especially factories southeast of Aleppo, in addition to engineering and construction assistance in repairing and rehabilitating destroyed military infrastructure. The KPA is also involved in operational planning and supervision of artillery warfare as demonstrated by the battle for Qusair.[16] The North Korean military advisors are probably involved in planning and execution of the air and air defense operations of the Syrian army as well as collecting battlefield intelligence on the combat use and performance of Western arms, especially those that can potentially be used in the Korean battlefield. Finally, the Syrian civil war offers the North Korean military planners the first-hand look at the combat tactics of anti-regime rebels trained and guided by the US and its allies. And for good measure, there is no doubt that North Korean military advisors are also tasked with erasing any traces of Pyongyang’s past assistance to Assad’s programs to build weapons of mass destruction just in case he does lose power.
The Bottom Line
Given the history of DPRK-Syrian relations, despite what the North might say in public, it would be surprising if the North had not dispatched a small contingent of military advisors and instructors to aid the brotherly Assad regime in its fight against the anti-government rebels. Although that assistance is probably limited and does not have the potential to fundamentally change the course of the civil war, North Korean military expertise can affect the outcomes of local tactical battles, adding to the winning momentum of the Assad forces. Moreover, North Korea’s involvement in Syria may be an indicator that the Kim regime discounts the likelihood of any possible breakthrough in relations with either Washington or Seoul in the near future and views the risk that its national policy goals will be adversely affected by increasing support for the Assad regime as manageable.
Pyongyang’s involvement in Syria characterizes Kim Jong Un more as a steady hand and traditional alliance manager than an erratic wanderer and opportunistic risk-taker. Although he is playing with fire in the shifting sands of far-flung lands like Syria, but he is simply staying the course set forth by his grandfather and upheld by his father, demonstrating continuity in North Korea’s foreign policy. Moreover, potential material and reputational rewards far outweigh possible security or diplomatic risks, especially if Kim’s bet on Assad’s eventual victory proves to be correct. The DPRK’s decision to cast its lot with Damascus may upset wealthy Gulf monarchies—like Kuwait and Qatar—sponsoring the anti-Assad rebel groups and cause them to rethink their employment of North Korean labor and services in construction and irrigation system development projects and their provision of low-interest funds for some of Pyongyang’s infrastructure projects.[17] On the other hand, it may help Pyongyang earn much greater financial or in-kind compensation from other states concerned, including Iran, Russia, and others, and develop new diplomatic clout in the Middle East if Assad eventually wins. Pyongyang’s support for Syria may provoke Jihadist elements to strike back, but it is more likely that the KPA will gain valuable combat experience against the new age enemy—irregular anti-government militia fighting in a suburban setting. Finally, North Korea’s support for Syria may provide new fodder for others to further demonize Pyongyang but it also offers the North a chance to stand by a long-time ally in need, to show its resolve to fight for state sovereignty and territorial integrity on the world stage, and to prove with deeds it is fighting against Al Qaeda and international terrorism, even when it might be more expedient to do otherwise.