In Kentucky, funds available to the Archdiocese of Louisville, its parishes and other organizations grew from at least $153 million to $157 million during the fiscal year that ended in June, AP found. Those same offices and organizations received at least $17 million in paycheck money. “The Archdiocese’s operations have not been significantly impacted by the Covid-19 outbreak,” according to its financial statement.
In Illinois, the Archdiocese of Chicago had more than $1 billion in cash and investments in its headquarters and cemetery division as of May, while the faithful continued to donate “more than expected,” according to a review by the independent ratings agency Moody’s Investors Service. Chicago’s parishes, schools and ministries accumulated at least $77 million in paycheck protection funds.
Up the interstate from Charlotte in North Carolina, the Raleigh Diocese collected at least $11 million in aid. Yet during the fiscal year that ended in June, overall offerings were down just 5% and the assets available to the diocese, its parishes and schools increased by about $21 million to more than $170 million, AP found. In another measure of fiscal health, the diocese didn’t make an emergency draw on its $10 million line of credit.
Catholic leaders in dioceses including Charlotte, Chicago, Louisville and Raleigh said their parishes and schools, like many other businesses and nonprofits, suffered financially when they closed to slow the spread of the deadly coronavirus.
Some dioceses reported that their hardest-hit churches saw income drop by 40% or more before donations began to rebound months later, and schools took hits when fundraisers were canceled and families had trouble paying tuition. As revenues fell, dioceses said, wage cuts and a few dozen layoffs were necessary in some offices.
Catholic researchers at Georgetown University who surveyed the nation’s bishops last summer found such measures weren’t frequent. In comparison, a survey by the investment bank Goldman Sachs found 42% of small business owners had cut staff or salaries, and that 33% had spent their personal savings to stay open.
Church leaders have questioned why AP focused on their faith following a story last July, when New York Cardinal Timothy Dolan wrote that reporters “invented a story when none existed and sought to bash the Church.”
By using a special exemption that the church lobbied to include in the paycheck program, Catholic entities amassed at least $3 billion — roughly the same as the combined total of recipients from the other faiths that rounded out the top five, AP found. Baptist, Lutheran, Methodist and Jewish faith-based recipients also totaled at least $3 billion. Catholics account for about a fifth of the U.S. religious population while members of Protestant and Jewish denominations are nearly half, according to the Pew Research Center.
Catholic institutions also received many times more than other major nonprofits with charitable missions and national reach, such as the United Way, Goodwill Industries and Boys & Girls Clubs of America. Overall, Catholic recipients got roughly twice as much as 40 of the largest, most well-known charities in America combined, AP found.
The complete picture is certainly even more lopsided. So many Catholic entities received help that reporters could not identify them all, even after spending hundreds of hours hand-checking tens of thousands of records in federal data.
The Vatican referred questions about the paycheck program to the United States Conference of Catholic Bishops, which said it does not speak on behalf of dioceses.
Presented with AP’s findings, bishops conference spokeswoman Chieko Noguchi responded with a broad statement that the Paycheck Protection Program was “designed to protect the jobs of Americans from all walks of life, regardless of whether they work for for-profit or nonprofit employers, faith-based or secular.”
___
INTERNAL SKEPTICISM
The AP’s assessment of church finances is among the most comprehensive to date. It draws largely from audited financial statements posted online by the central offices of 112 of the country’s nearly 200 dioceses.
The church isn’t required to share its financials. As a result, the analysis doesn’t include cash, short-term assets and lines of credit held by some of the largest dioceses, including those serving New York City and other major metropolitan areas.
The analysis focused on available assets because federal officials cited those metrics when clarifying eligibility for the paycheck program. Therefore, the $10 billion AP identified doesn’t count important financial pillars of the U.S. church. Among those are its thousands of real estate properties and most of the funds that parishes and schools hold. Also excluded is the money — estimated at $9.5 billion in a 2019 study by the Delaware-based wealth management firm Wilmington Trust — held by charitable foundations created to help dioceses oversee donations.
In addition, dioceses can rely on a well-funded support system that includes help from wealthier dioceses, the bishops conference and other Catholic organizations. Canon law, the legal code the Vatican uses to govern the global church, notes that richer dioceses may assist poorer ones, and the AP found instances where they did.
In their financial statements, the 112 dioceses acknowledged having at least $4.5 billion in liquid or otherwise available assets. To reach its $10 billion total, AP also included funding that dioceses had opted to designate for special projects instead of general expenses; excess cash that parishes and their affiliates deposit with their diocese’s savings and loan; and lines of credit dioceses typically have with outside banks.
Some church officials said AP was misreading their financial books and therefore overstating available assets. They insisted that money their bishop or his advisers had set aside for special projects couldn’t be repurposed during an emergency, although financial statements posted by multiple dioceses stated the opposite.
For its analysis, AP consulted experts in church finance and church law. One was the Rev. James Connell, an accountant for 15 years before joining the priesthood and becoming an administrator in the Milwaukee Archdiocese. Connell, also a canon lawyer who is now retired from his position with the archdiocese, said AP’s findings convinced him that Catholic entities did not need government aid — especially when thousands of small businesses were permanently closing.
“Was it want or need?” Connell asked. “Need must be present, not simply the want. Justice and love of neighbor must include the common good.”
Connell was not alone among the faithful concerned by the church’s pursuit of taxpayer money. Parishioners in several cities have questioned church leaders who received government money for Catholic schools they then closed.
Elsewhere, a pastor in a Western state told AP that he refused to apply even after diocesan officials repeatedly pressed him. He spoke on condition of anonymity because of his diocese’s policy against talking to reporters and concerns about possible retaliation.
The pastor had been saving, much like leaders of other parishes. When the pandemic hit, he used that money, trimmed expenses and told his diocese’s central finance office that he had no plans to seek the aid. Administrators followed up several times, the pastor said, with one high-ranking official questioning why he was “leaving free money on the table.”
The pastor said he felt a “sound moral conviction” that the money was meant more for shops and restaurants that, without it, might close forever.
As the weeks passed last spring, the pastor said his church managed just fine. Parishioners were so happy with new online Masses and his other outreach initiatives, he said, they boosted their contributions beyond 2019 levels.
“We didn’t need it,” the pastor said, “and intentionally wanted to leave the money for those small business owners who did.”
WEATHERING A DOWNTURN
Months after the pandemic first walloped the economy, the 112 dioceses that release financial statements began sharing updates. Among the 47 dioceses that have thus far, the pandemic’s impact was far from crippling.
The 47 dioceses that have posted financials for the fiscal year that ended in June had a median 6% increase in the amount of cash, short-term investments and other funds that they and their affiliates could use for unanticipated or general expenses, AP found. In all, 38 dioceses grew those resources, while nine reported declines.
Finances in Raleigh and 10 other dioceses that took government assistance were stable enough that they did not have to dip into millions they had available through outside lines of credit.
“This crisis has tested us,” Russell Elmayan, Raleigh’s chief financial officer, told the diocese’s magazine website in July, “but we are hopeful that the business acumen of our staff and lay counselors, together with the strategic financial reserves built over time, will help our parishes and schools continue to weather this unprecedented event.” Raleigh officials did not answer direct questions from AP.
The 47 dioceses acknowledged a smaller amount of readily available assets than AP counted, though by their own accounting that grew as well.
The improving financial outlook is due primarily to parishioners who found ways to continue donating and U.S. stock markets that were rebounding to new highs. But when the markets were first plunging, officials in several dioceses said, they had to stretch available assets because few experts were forecasting a rapid recovery.
In Louisville, Charlotte and other dioceses, church leaders said they offered loans or grants to needy parishes and schools, or offset the monthly charges they assess their parishes. In Raleigh, for example, the headquarters used $3 million it had set aside for liability insurance and also tapped its internal deposit and loan fund.
Church officials added that the pandemic’s full toll will probably be seen in a year or two, because some key sources of revenue are calculated based on income that parishes and schools generate.
“We believe that we will not know all of the long-term negative impacts on parish, school and archdiocesan finances for some time,” Louisville Archdiocese spokeswoman Cecelia Price wrote in response to questions.
At the nine dioceses that recorded declines in liquid or other short-term assets, the drops typically were less than 10%, and not always clearly tied to the pandemic.
The financial wherewithal of some larger dioceses is underscored by the fact that, like publicly traded companies, they can raise capital by selling bonds to investors.
One was Chicago, where analysts with the Moody’s ratings agency calculated that the $1 billion in cash and investments held by the archdiocese headquarters and cemeteries division could cover about 631 days of operating expenses.

Graphic shows excerpt from Moody’s Investors Service analysis of the Catholic Bishop of Chicago. (AP Illustration/Peter Hamlin)

Graphic shows excerpt from Moody’s Investors Service analysis of the Archdiocese of New Orleans. (AP Illustration/Peter Hamlin)
Church officials in Chicago asserted that those dollars were needed to cover substantial expenses while parishioner donations slumped. Without paycheck support, “parishes and schools would have been forced to cut many jobs, as the archdiocese, given its liabilities, could not have closed such a funding gap,” spokeswoman Paula Waters wrote.
Moody’s noted in its May report that while giving was down, federal aid had compensated for that and helped leave the archdiocese “well positioned to weather this revenue loss over the next several months.” Among the reasons for the optimism: “a unique credit strength” that under church law allows the archbishop to tax parish revenue virtually at will.
In a separate Moody’s report on New Orleans, which filed for bankruptcy in May while facing multiple clergy abuse lawsuits, the ratings agency wrote in July that the archdiocese did so while having “significant financial reserves, with spendable cash and investments of over $160 million.”
Moody’s said the archdiocese’s “very good” liquid assets would let it operate 336 days without additional income. Those assets prompted clergy abuse victims to ask a federal judge to dismiss the bankruptcy filing, arguing the archdiocese’s primary reason for seeking the legal protection was to minimize payouts to them.
The archdiocese, along with its parishes and schools, collected more than $26 million in paycheck money. New Orleans Archdiocesan officials didn’t respond to written questions.
PURSUING AID
Without special treatment, the Catholic Church would not have received nearly so much under the Paycheck Protection Program.
After Congress let nonprofits and religious organizations participate in the first place, Catholic officials lobbied the Trump Administration for a second break. Religious organizations were freed from the so-called affiliation rule that typically disqualifies applicants with more than 500 workers.
Without that break, many dioceses would have missed out because — between their head offices, parishes, schools and other affiliates — their employee count would exceed the limit.
Among those lobbying, federal records show, was the Los Angeles Archdiocese. Parishes, schools and ministries there collected at least $80 million in paycheck aid, at a time when the headquarters reported $658 million in available funds heading into the fiscal year when the coronavirus arrived.
Catholic officials in the U.S. needed the special exception for at least two reasons.
Church law says dioceses, parishes and schools are affiliated, something the Los Angeles Archdiocese acknowledged “proved to be an obstacle” to receiving funds because its parishes operate “under the authority of the diocesan bishop.” Dioceses, parishes, schools and other Catholic entities also routinely assert to the Internal Revenue Service that they are affiliated so they can maintain their federal income tax exemption.
While some Catholic officials insisted their affiliates are separate and financially independent, AP found many instances of borrowing and spending among them when dioceses were faced with prior cash crunches. In Philadelphia, for example, the archdiocese received at least $18 million from three affiliates, including a seminary, to fund a compensation program for clergy sex abuse survivors, according to 2019 financial statements.
Cardinals and bishops have broad authority over parishes and the pastors who run them. Church law requires parishes to submit annual financial reports and bishops may require parishes to deposit surplus money with internal banks administered by the diocese.
“The parishioners cannot hire or fire the pastor; that is for the bishop to do,” said Connell, the priest, former accountant and canon lawyer. “Each parish functions as a wholly owned subsidiary or division of a larger corporation, the diocese.”
Bishops acknowledged a concerted effort to tap paycheck funds in a survey by Catholic researchers at Georgetown University. When asked what they had done to address the pandemic’s financial fallout, 95% said their central offices helped parishes apply for paycheck and other aid — the leading response. That topped encouraging parishioners to donate electronically.
After Congress approved the paycheck program, three high-ranking officials in New Hampshire’s Manchester Diocese sent an urgent memo to parishes, schools and affiliated organizations urging them to refrain from layoffs or furloughs until completing their applications. “We are all in this together,” the memo read, adding that diocesan officials were working expeditiously to provide “step by step instructions.”
Paycheck Protection Program funds came through low-interest bank loans, worth up to $10 million each, that the federal government would forgive so long as recipients used the money to cover about two months of wages and operating expenses.
After an initial $659 billion last spring, Congress added another $284 billion in December. With the renewal came new requirements intended to ensure that funds go to businesses that lost money due to the pandemic. Lawmakers also downsized the headcount for applicants to 300 or fewer employees.
A QUESTION OF NEED
In other federal small business loan programs, government help is treated as a last resort.
Applicants must show they couldn’t get credit elsewhere. And those with enough available funds must pay more of their own way to reduce taxpayer subsidies.
Congress didn’t include these tests in the Paycheck Protection Program. To speed approvals, lenders weren’t required to do their usual screening and instead relied on applicants’ self-certifications of need.
The looser standards helped create a run on the first $349 billion in paycheck funding. Small business owners complained that they were shut out, yet dozens of companies healthy enough to be traded on stock exchanges scored quick approval.
As blowback built in April, Treasury Secretary Steven Mnuchin warned at a news briefing that there would be “severe consequences” for applicants who improperly tapped the program.
“We want to make sure this money is available to small businesses that need it, people who have invested their entire life savings,” Mnuchin said. Program guidelines evolved to stress that participants with access to significant cash probably could not get the assistance “in good faith.”
Mnuchin’s Treasury Department said it would audit loans exceeding $2 million, although federal officials have not said whether they would hold religious organizations and other nonprofits to the same standard of need as businesses.

Graphic shows excerpt from a U.S. Department of the Treasury Paycheck Protection Program FAQ document. (AP Illustration/Peter Hamlin)
The headquarters and major departments for more than 40 dioceses received more than $2 million. Every diocese that responded to questions said it would seek to have the government cover the loans, rather than repay the funds.
One diocese receiving a loan over $2 million was Boston. According to the archdiocese’s website, its central ministries office received about $3 million, while its parishes and schools collected about $32 million more.
The archdiocese — along with its parishes, schools and cemeteries — had roughly $200 million in available funds in June 2019, according to its audited financial report. When that fiscal year ended several months into the pandemic, available funds had increased to roughly $233 million.
Nevertheless, spokesman Terrence Donilon cited “ongoing economic pressure” in saying the archdiocese will seek forgiveness for last year’s loans and will apply for additional, new funds during the current round.
Beyond its growing available funds, the archdiocese and its affiliates benefit from other sources of funding. The archdiocese’s “Inspiring Hope” campaign, announced in January, has raised at least $150 million.
And one of its supporting charities — the Catholic Schools Foundation, where Cardinal Sean O’Malley is board chairman — counted more than $33 million in cash and other funds that could be “used for general operations” as of the beginning of the 2020 fiscal year, according to its financial statement.
Despite these resources, the archdiocese closed a half-dozen schools in May and June, often citing revenue losses due to the pandemic. Paycheck protection data show four of those schools collectively were approved for more than $700,000.
The shuttered schools included St. Francis of Assisi in Braintree, a middle-class enclave 10 miles south of Boston, which received $210,000. Parents said they felt blindsided by the closure, announced in June as classes ended.
“It’s like a punch to the gut because that was such a home for so many people for so long,” said Kate Nedelman Herbst, the mother of two children who attended the elementary school.
Along with more than 2,000 other school supporters, Herbst signed a written protest to O’Malley that noted the archdiocese’s robust finances. After O’Malley didn’t reply, parents appealed to the Vatican, this time underscoring the collection of Paycheck Protection Program money.
“It is very hard to reconcile the large sums of money raised by the archdiocese in recent years with this wholesale destruction of the church’s educational infrastructure,” parents wrote.
In December, the Vatican turned down their request to overrule O’Malley. Spokesman Donilon said the decision to close the school “is not being reconsidered.”




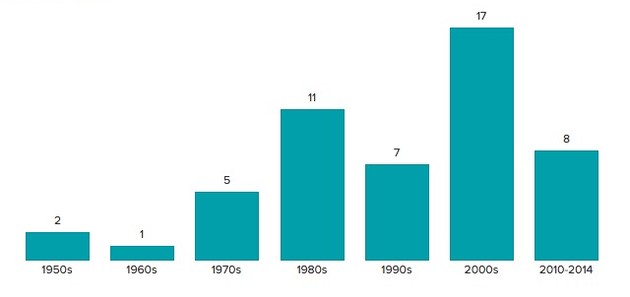
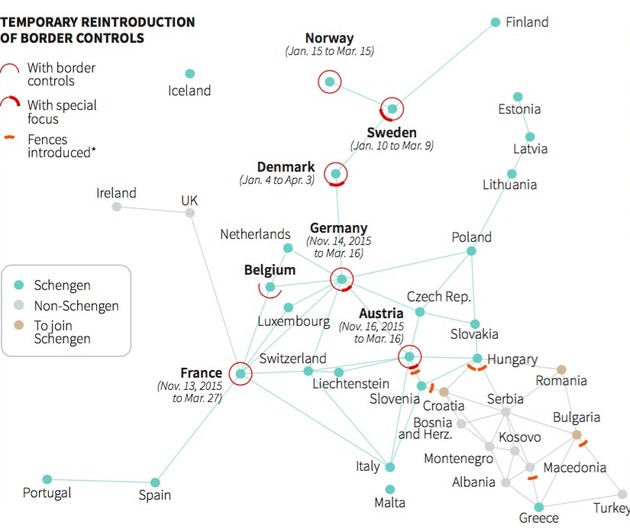 “Talking about walls or no walls is not the right discussion,” Ramo added. He would rather the discussion be about how gatekeeping should work, including questions like “what kind of immigration do we want to encourage and how do we want to structure that process.”
“Talking about walls or no walls is not the right discussion,” Ramo added. He would rather the discussion be about how gatekeeping should work, including questions like “what kind of immigration do we want to encourage and how do we want to structure that process.”






