Both sides here need to be quite careful with regards of Russian relationship accusations. The work by the FBI, Congress or even independent counsel could blow things wide open in DC. This is going to be a long slog and wont fade from the headlines anytime soon.
Both articles below demonstrate more Russian relationships in the West on the political sides. The Kremlin has a long game for intrusion and influence and Putin is so far quite successful with installing geopolitical chaos across the globe. He is a master at framing his leadership abilities as rational, calm, measured and legal. Not so much when performing deeper dives. This post is a long read but essentially required reading to fully grasp the scope of Russian relationships.
When it comes to investigations by Congress, outside counsel or by the FBI, it is going to be a long tedious process. This matter wont fade from the headlines anytime soon and details are going to be quite important.
By James S. Henry
Wilbur J. Ross, Jr., the billionaire investor who is one of Donald Trump’s closest advisors on trade and economics, has extensive Russian financial ties that the Senate should thoroughly explore before voting on his nomination as Commerce Secretary.
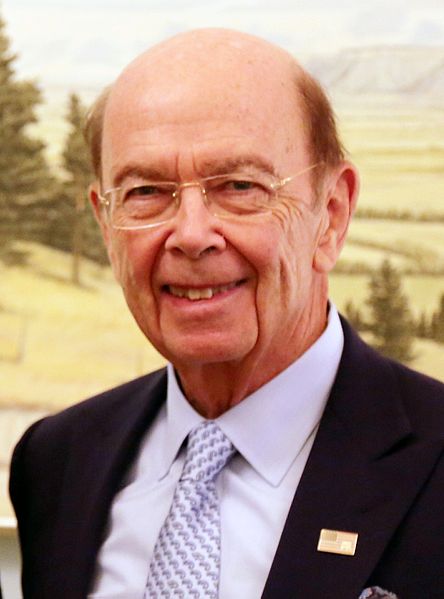

Businessman Wilbur Ross, nominated to be Secretary of Commerce, has extensive ties to Russian oligarchs and associates of Russian President Vladimir Putin.
INTRODUCTION
In the midst of the Trump Administration’s many other Russian entanglements,[1] it turns out that Wilbur J. Ross, Jr., the billionaire American investor who is one of Donald Trump’s closest advisors on trade and economics, has direct financial ties to several leading oligarchs from Russia and the Former Soviet Union or FSU.
The U.S. Senate should thoroughly investigate these ties before it votes on Ross’ nomination to be Commerce Secretary when it returns from recess next week.
Central to this inquiry is the question of Ross’s role as Vice Chair and a leading investor in the Bank of Cyprus, the largest bank in Cyprus, one of the key offshore havens for illicit Russian finance. Ross has been Vice Chairman of this bank and a major investor in it since 2014. His fellow bank co-chair evidently was appointed by none other than Vladimir Putin.
The Bank of Cyprus is just one of more than 100 direct and indirect investments that Ross listed on his U.S. Office of Government Ethics financial disclosure form last month. [2] He recently promised to resign as Vice Chairman of the Bank and disinvest from it within the next 90 days if his nomination is approved.[3]
Mere divestiture will not suffice here, even if it was immediate. Exiting a brothel in a hurry doesn’t explain what you were doing there in the first place.
Ross’ involvement in the Bank of Cyprus raises many questions about his judgment, but also about the Trump Administration’s seemingly endless direct and indirect connections with friends and associates of Vladimir Putin, who all 17 U.S. intelligence agencies say conspired to interfere in the November 2016 U.S. election on behalf of Donald Trump.
Whether or not these connections involve any criminality, these are the kind of relationships that most American business people would not tolerate for 30 seconds.
After all, as discussed below, since the 1990s Cyprus has served as one the top three offshore destinations for Russian and former Soviet Union flight capital, most of it motivated by tax dodging, kleptocracy, and money laundering.[4] As of 2013, just before the banking crisis, Russian deposits accounted for at least a third of all bank deposits in Cyprus. [5] As one leading newspaper put it, “Russian money is in fact at the heart of the island’s economy.”[6]
Nor is Ross’ Bank of Cyprus in particular –now probably at least half owned by Russians, as we‘ll see [7]—any stranger to money laundering,[8] tax dodging, or odious finance. With a market share of 30 percent, Bank of Cyprus has long been the market leader in Cypriot financial chicanery:[9]
- As of 2013, for example, more than 81 percent of the bank’s deposits were accounted for by 21,000 mainly foreign depositors, up to half of them Russians, who each had at least €100,000 on deposit.[10]
- By 2013, after a decade of rampant inflows of offshore capital and irresponsible lending, Bank of Cyprus alone had €11.5 billion of delinquent loans on its books – 60 percent of the country’s entire gross domestic product.[11] At that point, it required €11.3 billion of Emergency Liquidity Finance from the Central Bank of Cyprus to survive. [12]
- The top 20 Bank of Cyprus borrowers reportedly accounted for €3 billion of these non-performing loans. This is consistent with the patterns found in other recent credit booms—dodgy real estate projects, bust-out loans to insiders, and rampant control fraud. [13]
- In March 2015, it was discovered that 19 of the Cyprus Parliament’s 56 Members of Parliament, owed BOC €51.2mm, including 13 MPs whose non-performing loans totalled €35.3m.[14] The following month, the Parliament adopted a new pro-bank law to accelerate foreclosures. Evidently the revelations increased the pressures to act.[15]
- In a series of recent criminal trials in Nicosia, five former CEOs, Board Chairmen, and managers of Bank of Cyprus have been charged with a wide variety of financial misconduct pertaining to the pre-2013 period. The charges include conspiracy to defraud investors, forgery,[16] and market manipulation. [17] No one has yet been convicted.
There are also disturbing reports of several recent high-profile money laundering cases in Cyprus.[18] There are also reports that attempts to clean up money laundering and improve financial transparency stalled, [19] and that as of 2016, “Geldwasching” may be back, not only in Cyrus as a whole, but also at the Bank of Cyprus. [20]
So this is the fundamental question:
How did a prospective U.S. Commerce Secretary come to play a lead role in what turns out to be one of the world’s leading haven banks for laundering Russian money, precisely at a time when the U.S. Government and the EU have been trying so hard to enforce economic sanctions against Russia and Putin’s wealthy allies?
Before the U.S. Senate approves Ross’s nomination, it is essential to get to the bottom of these curious relationships. Unfortunately, no one bothered to ask Ross even a single question about them, the Bank of Cyprus, or dirty Russian money at his January 18 confirmation hearing before the Senate Commerce Committee, where he received unanimous approval along with a ringing endorsement from his Florida Senator. [21]
In “TrumpLand,” however, as we have recently come to appreciate, that was eons ago. And there are now signs that the U.S. Senate may finally be waking up. [22]
THE ‘BANKRUPTCY KING’ SWOOPS IN
In July 2014, Ross became Vice Chairman of the Bank of Cyprus.[23] At that point the bank was in deep financial trouble, having nearly failed in 2013.
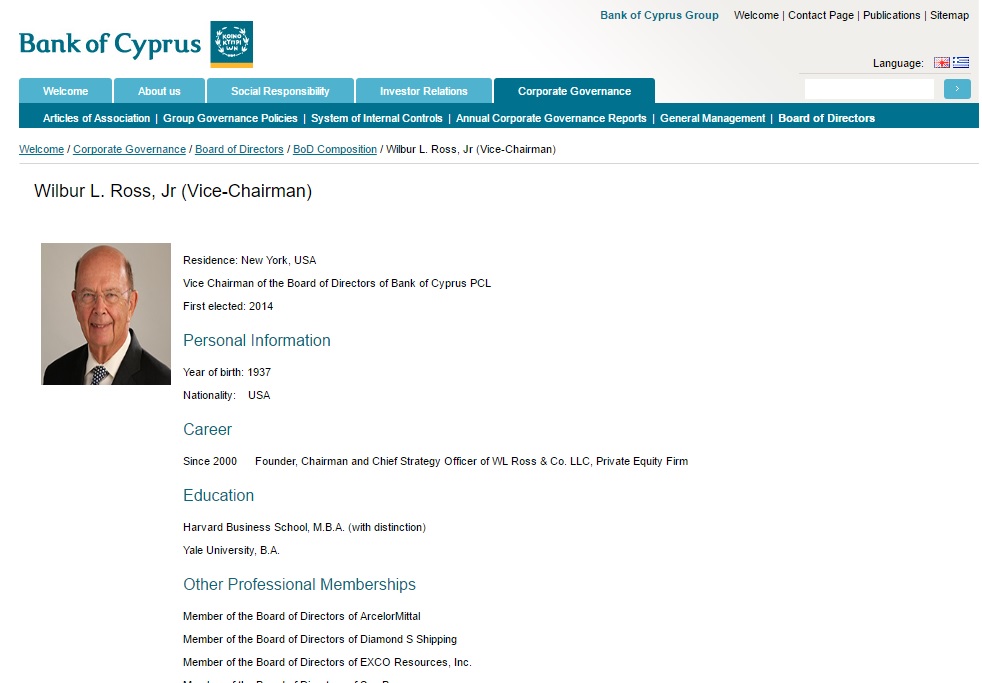
The Bank of Cyprus lists Wilbur Ross as an officer.
Ross, who specializes in buying troubled firms cheap and then reselling them, organized a group of U.S. and European-based investors to spend €1 billion (U.S. $1.3 billion then) to acquire 17 percent of the common stock of this deeply troubled bank, including Ross’ own 1.6 percent stake.[24]
Since then, Ross has played an active role in recruiting and nominating its senior management team, especially its board chairman, Josef Ackermann, the long-time former Chairman of Deutsche Bank—one of the few banks in the world that would make loans to Donald Trump.[25]
THE ROOTS OF THE CYPRUS CRISIS
To understand Ross’s role in Bank of Cyprus, we really have to start with what happened following the 1989 collapse of the Soviet Union, when state-owned enterprises and vast amounts of oil and gas reserves and mineral wealth were sold for a song to a new class of incredibly rich, politically well-connected oligarchs and their partners in the state security apparatus.
As we have recently explored elsewhere,[26] from the mid-1990s on, this massive reconcentration of wealth gave way to an extraordinary outflow of flight capital, and the proliferation of tax dodging and criminal enterprises.
Among the key beneficiaries of this economic crisis was Vladimir Putin, who rode it to power. But the tsunami of illicit Russian money also greatly benefited Donald Trump, who, as discussed in more detail in a previous article,[27] simply could not have financed his bankrupt business empire in the early 2000s without it.
Of course, Trump has reiterated time and again—most recently at his White House press conference on Feb. 17—that he has no business deals with Russia. Significantly, Trump said nothing about Russians, investors from other former Soviet Union states like the Ukraine or Kazakhstan, or ventures with Russians outside of Russia and the former Soviet Union.
In the past, even Trump has boasted repeatedly about raking in many millions from Russian oligarchs who bought luxury Trump apartments and joined his golf clubs. Nor has he denied that he was paid $13 million to hold the 2013 Miss Universe pageant in Moscow. His three oldest children also made 13 trips to Moscow over 18 months, in what the Trump Organization described at the time as business trips intended to recruit Russian investors.
Furthermore, as noted below, one Russian oligarch shelled out at least $95 million to Trump in one Florida real estate deal. [28] This allowed Trump to more than double his $41 million investment in that property in four years. [29] This profit were earned at a time, when by Trump’s own account, the U.S. real estate market was a “disaster”—so dead that he actually sued Deutsche Bank, his one remaining global creditor,[30] in a failed effort to avoid repaying a $40 million real estate loan.[31]
DESIGNER HAVEN
In Ross, we see an indirect beneficiary of the 1990s Russian debacle. More suspicious money inundated Cyprus, and especially the Bank of Cyprus, than could possibly be put to work in that island nation. Ultimately this created a lucrative opportunity for Ross, his investment group, and the wealthy Russian investors in the Bank.
The Bank of Cyprus is certainly no ordinary bank. At the time it nearly failed in March 2013, it was the largest financial institution in Cyprus, a tiny island country that is strategically located in the eastern Mediterranean and is one of the EU’s newest members.
According to money laundering experts, the Bank of Cyprus also has a long history of being up to its ears in Russian flight capital.[32] Indeed, Like Trump and Putin, Cyprus in general—and the Bank of Cyprus in particular—have been huge beneficiaries of Russia’s 1990s economic crisis and the extraordinary deluge of dirty money that it produced. Especially since Cyprus was admitted to the EU in 2004 and the Eurozone in 2008,[33] the island has captured the bronze medal, just behind more venerable havens like the Switzerland and the UK. And, as noted, the Bank of Cyprus was the market leader, as the island’s largest single financial institution, which for a time also had branches in Moscow, the Ukraine, Greece, and Rumania. [34]
Of course Russian flight capital might have landed in many places. The interesting thing about Cyprus’ unusual success in capturing it is that it was by design. Since the 1980s, the Cypriot tax system, tax treaties, financial regulations, company laws, and residency requirements have all been carefully engineered to attract offshore money, especially from the Russia/FSU region. This was done at the urging of the island’s influential bank lobby and its nearly 2,000 lawyers and accountants. The Central Bank of Cyprus did its part by turning a blind eye to money laundering, unless it clearly involved terrorism.
So the island soon developed quite a reputation. Today, Cyprus-based holding companies and banks account for a majority of the world’s direct investments into Russia and a significant share of all Russian capital outflows. And the Bank of Cyprus has led the way. [35]
Much of this direct foreign investment into Russia from Cyprus involves “round-tripping,” where funds are channeled through offshore companies and then rerouted back as if it were foreign capital. The financial secrecy and special tax treaty provisions offered by Cyprus insulated the owners from pesky annoyances like taxes, creditors, exchange controls, and restrictions on money laundering.
By the mid-2000s, many affluent Russians had also decided to move their “human capital” to Cyprus.Thousands bought real estate on the sunny, relatively democratic isle and started living there at least part time. Up to 50,000 Russians now reside in Cypriot enclaves like “Limassol-grad,” which features Russian language newspapers, radio stations, schools, restaurants, films, law firms, and ice-cold bottles of Baltika. [36] Especially after Cyprus was admitted to the EU (2004) and the Eurozone (2008), they expected bank deposits to be guaranteed by the ECB and that the Euro would be relatively sound. Those who could afford to invest €5 million in real estate ($6.5 million back then) could also get EU passports, [37] which allowed them to move freely around Europe. It was a uniquely Cypriot combination – Mediterranean relaxation and Russian riches.
MORE MONEY THAN LEGITIMATE USES FOR IT
Sadly for many Cypriots, all this loose incoming Russian loot—combined with lax Eurozone bank regulation and the Cyprus banks’ increasing confidence after 2008 that the ECB would bail them out, no matter how they misbehaved—led to a classic case of what economists now call “the finance curse.”
Eventually, the deluge of unregulated offshore deposits produced a gigantic financial bubble. Cyprus banks issued more than €160 billion of dodgy real estate loans and corporate loans and poured tens of €billions more into dodgy Greek bonds.
The result was a tandem debt crisis. Especially after the Greek debt crisis hit in 2011, Cyprus banks started to tremble. But no one wanted to slow lending and trigger a (much milder) recession, so they delayed facing reality as long as possible.
By 2013 the island’s two largest private banks, the Bank of Cyprus and Laiki, were on the verge of insolvency. Cypriot government debt soared to 125 percent of gross domestic product, as the overall economy and tax revenues tanked. By 2012-13, private bank loans exceeded 800 percent of GDP. Even today, while the public debt ratio still hovers around 100 percent,[38] an astounding 60 percent of Cyprus bank loans, or 150 percent of GDP, are classified as “non-performing” because they are not being paid back. For comparison, U.S. banks now class just 1.28 percent of their commercial loans as nonperforming.[39]
To this day, Cyprus is still paying a huge price for this boom-bust cycle and the failure to regulate its financial institutions. While it is no longer in the acute care ward, and the IMF has recently praised the island – in contrast to Greece!—for being able to pay off the emergency loans and terminate the bailout program,[40] Cyprus still suffers from the enormous private debt overhang. And that, in turn, has yielded slow growth, 15 percent unemployment, and a highly uncertain future—plus the pleasure of hosting 50,000 Russians.
For Wilbur Ross and his fellow private vulture capitalists, this Russian-flight induced crisis presented an irresistible investment opportunity. (Exactly who introduced Wilbur’s group to the island is an interesting question that the Senate should explore.)
The bank’s management and board spent the first year after the March 2013 crisis staving off bankruptcy with the help of €10 billion in ECB and IMF emergency assistance—including €6.5 billion for the Bank of Cyprus alone. In 2014 it decided to raise new capital. In July 2014, in exchange for €1 billion, Ross and his group were able to acquire 17 percent of the bank’s stock, the largest single ownership block, plus the Vice Chairmanship and significant management influence.[41]
The only trouble was that Ross and his group could not afford to be too discriminating about who their co-investors were. To this day, as noted, not only is Bank of Cyprus at least half owned by Russian investors, but several of the largest ones are “super-garchs” who have business and personal histories that are, to be polite, colorful.
Nor could Wilbur’s investment group afford to be too particular about the uses these co-investors made of the bank, or the fact that Bank of Cyprus’s new business model – apart from financial chicanery and more MP loans–requires an awful lot of hard work trying to collect money they don’t have from thousands of recalcitrant borrowers.
THE BANK AND THE OLIGARCHS
Under the terms of Cyprus’ 2013 agreement with the ECB and the IMF, to qualify for for their €10 billion bailout—fully €7.3 billion of which went to bail out the Bank of Cyprus and other private banks[42]—the country was compelled to agree to “bail-in” “large depositors” – those with over €100,000 on deposit.
In return for seizing 47.5 percent of their deposits, 21,000 of depositors – and especially a core group of about 560 – initially received 81.5 percent percent of the bank’s stock. When the Ross group arrived this was slashed. The Bank’s financial disclosures don’t permit us to say precisely how this ownership is distributed. But at least a third to fifty percent accrued to wealthy Russians who received stock in proportion their confiscated deposits.[43] In addition, our three leading identified Russian ‘garchs also ended up owning at least 14.3 percent of the bank.[44]
Another 9.6 percent of Bank of Cyprus shares is managed on behalf of Laiki’s former customers – many of whom were also Russian depositors—by Bank of Cyprus management, without direct board representation.[45] All told, as discussed in this footnote, even after the Ross group’s entry, at least 40 to 50 percent of the Bank of Cyprus’s voting power is now Russian-controlled.[46]
As for the largest Russian shareholders, we are only able to identify those who now own at least at least 3 percent of Bank of Cyprus’s shares. But even this subset includes several well-known oligarchs. All three maintain important connections to Russia, they all are on reasonably good terms with President Putin, and at least one is no stranger to Donald Trump.
As of now, Ross maintains a joint Co-Chairmanship in Bank of Cyprus with Maksim Goldman, who represents Lamesa Holding S.A. , a part of the Renova Group, an aluminum and oil conglomerate that is majority-owned by Vekselberg.
As of 2014, Lamesa’s stake in the Bank was 5.5 percent; in 2015 it was increased to 6.2 percent with the purchase of the 0.7 percent stake from Strzhalkovsky. In January 2017, it increased again to 9.3 percent, making Renova Group the bank’s largest single shareholder.

Russian-born, UCLA-educated Maksim Goldman (This photo appears on the Bank of Cyprus website.)
Together with his long-time business partner Leo Blavatnik, Vekselberg is a major aluminum and oil industries investor through Renova Group, their corporate umbrella group. He also reportedly owns the world’s largest collection of Faberge eggs, and a yacht, the Odessa II, that is valued at $150 million.
Vekselberg is the 7th wealthiest Russian, according to the Russian edition of Forbes magazine.[65] He is reportedly also on reasonably good terms with President Putin. In fact, he reportedly delighted the “new Tsar” by spending millions to buy up the Faberge eggs and return them to a special museum he has created for them in Moscow. Vekselberg has denied reports of some tension between him and Putin.[66] There have been some recent reports of tensions in the relationship, but VV has denied it. [67]
Here are a few questions that Senators should ask Ross in public hearings about Viktor Vekelsberg:
- When, where and under what circumstances have you ever met or communicated with Viktor Vekelsberg or his business partners? How frequently do you communicate directly or through Maksim Goldman or anyone else associated with Renova Group?
- What business dealings, if any, have you had directly or indirectly with Vekelsberg and his various business enterprises? With his partner Len Blavatnik, directly or indirectly? What role has he and his family played in the bank? Do other members of his family do business with the Bank? Do other members of his affiliated companies do business with the Bank or with other investors in the Bank? To your knowledge, has he or his business partners done any business with the Trump Organization?
- What has been Renova’s role at the Bank of Cyprus? How does Vekelsberg use the bank, as a depositor, investor or borrower? What loans or advances were extended to him or at his direction to others? Has Vekelsberg brought any new clients to the bank? If so, who?
- What can you tell us about business dealings between Vekelsberg and others associated with the Bank of Cyprus and Renova Group and Donald Trump, his organization and his family?
- Were you aware that Vekselberg’s long time business partner is Len Blavatnik? Were you aware that on October 25 2016, AI ALTEP Holdings Inc., a company reportedly based in New York City and owned directly or indirectly by Vekselberg’s business partner Len Blavatnik, made a $1 million contribution to Senator Mitch McConnell’s “Senate Leadership Fund?”[68]
Dmitry Rybolovlev: Reportedly owned the largest stake in the Bank of Cyprus as of 2010 (9.7%); bought Donald Trump’s Palm Beach house in 2008 for $95 million, at the time the most expensive property in the U.S., more than doubling what Trump paid four years earlier; his personal jet’s flight pattern shows an odd coincidence of airports with Trump’s appearances on the fall campaign trail. (See the discussion below.)

Dmitry Rybolovlev
Wilbur Ross also has a direct link through the Bank of Cyprus to a third leading Russian oligarch who, as of 2010, was the bank’s largest single investor and appears to still own a significant position in the Bank.
This is Dmitry Rybolovlev, a 50-year old Russian once known as the country’s “potash king.” During the “Wild West” days of Russian privatization back in the mid-1990s, “Rybo” had acquired a two-thirds stake in a critical fertilizer company, Uralkali, which eventually supplied up to 30 percent of global potash sales.[69] Beginning in June 2010, however, shortly before Rybolovlev invested €233 million in the Bank of Cyprus, he rather wisely started to dispose of his 66% stake in UralKali, completing the divestiture in 2011.[70] Since then potash prices have slumped, so in hindsight, this was an adroit move.
Even after an expensive divorce, in recent years Rybolovlev’s net worth has variously estimated at $5 to $13.8 billion, depending on the year and source, with $7.8 billion being the most popular guesstimate. [71] According to published reports, he has a very impressive €500 million art collection, although some of it was recently the subject of nasty litigation concerning provenance. [72] He has also reportedly acquired xCitbank CEO Sandy Weill’s $88 million penthouse in New York,[73] a $20 million mansion in Hawaii that used to belong to the actor Will Smith,[74] a waterfront property in Palm Beach that he purchased from Donald Trump,(see below), two luxury villas in Gstaad, two personal jets that are reportedly worth over $100 million, including a private Airbus A319 (see below), [75] a mansion on the Rue de l’Elysée in Paris that overlooks the Presidential Palace, the entire island of Scorpios, a $68 million 67-meter yacht, and the football club in Monaco.[76]
If this fellow had invented fertilizer, it is hard to believe that this collection of toys and lucre or his collection of invoices from divorce attorneys would be any more elaborate.
In addition to just being yet another fabulously rich Russian natural resources billionaire — for our purposes Rybolovlev is interesting for at least three other reasons.
First, as noted, in 2010 Rybolovlev bought 9.7% of the Bank of Cyprus, becoming at that point by far its largest single investor. By 2013, just before the crash, he had reportedly increased that to 9.9 percent. Even after the 2013 crash and refinancing that produced a “haircut” for existing Bank of Cyprus investors, he appears to have retained at least a 3.3% stake. Although this stake is larger than Ross’s 1.6 percent, Rybolovlev does not have a seat on the board of directors. [77]
Second, like many other hypertense members of the Russian elite, since the early 2000s Rybolovlev has been on of a crusade to diversify his wealth internationally. The potash mines were hard to relocate physically, so he sold off some his stake in it, and has focused since 2007 on purchasing foreign properties, joining the Russian émigré flood abroad.
In particular, in addition to all the other foreign properties described earlier, in June 2008 he purchased a Palm Beach waterfront property from Donald Trump for $95 million plus a sales commission, one that Trump had reportedly purchased himself in July 2004 for just $41 million.[78] The unusual nature of this transaction is only underscored by the fact that the property had been valued at just $59.8 million on Palm Beach County’s tax rolls as of 2013. Eight years later, in 2016, Rybolovlev had the 60,000 square foot mansion that Trump built torn down, subdivided the property in three, and sold off a 2.74-acre plot for $34 million – nearly $3 million per acre less than he had paid for it.[79]
This price gain is also especially interesting because in mid-2008, Trump was complaining loudly the American real estate market was “dead” and that many of his projects were cratering. Indeed, as we noted earlier, that same year he fought tooth and nail to avoid repaying a $40 million real estate loan to Deutsche Bank.
Now precisely at that crucial point in mid-2008, just as the Great Recession was unfolding, this extraordinary $50 million Russian cash injection into Donald Trump’s balance sheet may well have saved him from personal bankruptcy. On top of his six other corporate bankruptcies, that one, in turn, might well have been the beginning of the end for Donald Trump’s political ambitions.
Third, according to flight logs from FlightRadar24 and PlaneFinder, as well as photos of planes on the ground taken from Jetphotos.co and amateur photos taken at airports by amateur Twitter journalists, an Airbus A319-133X(CJ) with the registration M-KATE that very much appears to belong to Dmitry Rybolovlev appears to have followed some very unusual flight patterns during the fall 2016 American presidential campaign.
When Rybolovlev still owned his potash company, he reportedly maintained an Airbus A319 that was outfitted for personal use. This plane, with the registration M-KATE, is registered to Sophar Property Limited, a British Virgin Islands company.[80] While this company was originally registered to UralKali, the potash company that he disposed of by 2011, apparently Rybo, as he is known, enjoyed this plane and another, a Falcon, so much that he retained ownership or at least use rights to the two planes, this Airbus and, a Falcon jet. The Airbus A319’s registration is reportedly named after one of his two daughters, Ekaterina. [81]
For our purposes, the intriguing thing is that this plane, normally based in Moscow and Switzerland, can be tracked. According the flight logs available from FlightRadar24, it made numerous flights all over the U.S. from August 2016 through November 2016, the peak season for the U.S. 2016 Presidential campaign – of course right at the moment when Moscow was supposedly trying to jack the election on Trump’s behalf.
Moreover, in at least three cases, Airbus A319M-KATE showed up at very same airports, where candidate Trump was – in the North Carolina cities of Charlotte and Concord and in Las Vegas, for example. Indeed, in the case of Charlotte, local photographers took pictures of M-KATE and the Trump campaign jet at the very same airport on November 3, 2016. During a presidential campaign close aides often arrive before and after the candidate, times that overlap with the Rybolovlev jet in several cities.[82]
Local photographers took pictures of M-KATE and Trump’s Boeing 757 the Trump campaign jet at the same airport on November 3, 2016.
Indeed, earlier this month — on Friday, Feb. 10 2017 — Rybolovlev‘s Airbus A319 M-KATE flew all the way from Switzerland to Miami. That airport is near where the White House said that the president was partying with hedge fund mogul Steven Schwartzman in Palm Beach on Saturday night. Rybolovlev’s jet returned to Switzerland on February 12, flight records show.
There were also M-KATE flights to Westhampton, New York and Los Angeles in early August 2016 and October-November, 2016, but the intersections with Trump’s travels are less clear. Why would Rybolovlev’s plane scurry back and forth from Moscow to odd destinations like Charlotte and Concord, as well as to Las Vegas, New York, Burbank, and Miami, to arrive there precisely when Trump was there? The obvious question: was Rybolovlev a Putin emissary?
These flight patterns that were first noted by observant ‘Twitter journalists” like @Observer14 and @AceInCharlotte back on Nov. 3, 2016, just as they were occurring. [83]
But what could Rybolovlev possibly have been carrying that couldn’t have been ported more efficiently and discretely by other methods? Furthermore, are we sure that relations between Putin and Rybolovev are all that good? After all, in 2008, Igor Sechin, Putin’s Deputy Prime Minister at the time — and now the Executive Chairman of the fabled Rosneft, the world’s largest publicly-traded oil producer — reportedly threatened to prosecute Dmitry Rybolovlev’s potash company over a mine disaster, exposing it to huge fines.[84] Soon after this threat, Rybolovlev’s potash company, UralKali, reportedly paid $250 million of “voluntary” compensation to the government. After that Rybolovlevalso accelerated his efforts to diversify abroad. The Financial Times does say that relations between Putin and Rybolovlev are now fine. [85] But this pattern also fits the standard Putin stratagem whereby oligarchs are pressured into becoming semi-feudal servants of the de facto modern Tsar.
In any case, these flights remain a genuine enigma. We do yet not have any eyewitness reports or photos that show that Rybolovlev was actually on the planes or actually met with Trump or any of his staff. But these coincidences, combined with everything else we know about Rybolovlev’s connections to Trump and Ross, certainly deserves further scrutiny.
This prompts still more questions for Wilbur Ross, this time regarding Dmitry Rybolovlev:
- How long have you known Dmitry Rybolovlev? How much of the Bank of Cyprus does he currently own? What role has he and his family played in the bank? Do other members of his family do business with the Bank? Do other members of his affiliated companies do business with the Bank or with other investors in the Bank? What contacts have you or associates had with Dmitry Rybolovlev?
- What attention did you and your team pay to Rybolovlev because of his 3.3 % (and at one time nearly 10%) stake in the Bank of Cyprus? What due diligence did you or your associates perform regarding Rybolovlev and Trump? What did you find?
- When and how did you learn of the lucrative deal Trump made with Rybolovlev in 2008 to sell his Florida property at a huge profit? As a long-time Trump friend and associate, were you involved in that deal? Did you meet Rybolovlev at the time? To your knowledge, has Donald Trump had any other business dealings with Rybolovlev or his associates?
- Have you or your businesses done any business with Rybolovlev or entities associated with him?
- When and when if ever, have you or your team met or communicated by telephone mail, email or through intermediaries with Rybolovlev? Are you aware of any occasions where Dmitry Rybolovlev may have met with Donald Trump or other members of his staff? Were you present at any occasions in the last year in the U.S. or elsewhere where Dmitry was present? How do you account for the unusual flight patterns listed above? Do you know who recently bought one-third of Rybolovlev’s Palm Beach property? Did you attend the Schwartzman party in Palm Beach on February 11? Was Dmitry there? Did you meet Donald Trump or other members of his staff that weekend? If so, what was discussed?
Josef Ackermann: Chairman of the Board, The Bank of Cyprus since 2014; former Chairman of Deutsche Bank (2002-12) during period when it engaged in a wide range of corporate misbehavior, including laundering $10 billion of Russian money, incurred fines that nearly bankrupted the bank, which is the largest single lender to the Trump Organization; “Friend of Vlad” who reportedly knows Putin well.
When Wilbur Ross became Vice Chairman of The Bank of Cyprus in July 2014, one of his first acts was to nominate Josef Ackermann, who had headed Deutsche Bank from 2002 to 2012, to become Bank of Cyprus’s new board chairman. He assumed that role in November 2014 and still holds it. Even back in July 2014, it was difficult to make Ackermann’s decade running Deutsche Bank look like an achievement, to say the least. Since then, it has become even clearer that he presided over a period of spectacular chicanery at Germany’s largest bank. Given this, his nomination by Ross to head the Bank of Cyprus in 2014 seems peculiar, to say the least.
One possible explanation is that Wilbur Ross is a long-time financial ally of Donald Trump, dating back to an effort to restructure his casinos in 1990. From 2002 to 2012, under Ackerman, Deutsche Bank had become Trump’s largest bank creditor by far, with more than $650 million of loans to the Trump Organization and even more to other Trump partnerships, as of 2008. [86] Trump’s 2016 financial disclosures show that out of $650 million owed by him and his organization, $364 million was owed to Deutsche Bank.[87]
Meanwhile, ever since Trump failed to repay more than $900 million of bank loans in the early 1990s, other major U.S. and European banks had largely rejected him. He did not help his own cause by bragging in print that he had borrowed from the banks knowing full well that he would never repay.
To this day, why Deutsche Bank has continued lending to Trump and his organization remains a mystery.
Indeed, according to recent press reports, Deutsche Bank has recently been looking into allegations that the Russian Government may have guaranteed some of the bank’s more generous loans to Trump during the Ackerman period, either directly, or through offshore banks and companies. [88]
This would resemble a similar approach that was used by Putin in France. In 2014 he helped secure €11 million for Marine Le Pen’s cash-starved National Front from the “First Czech-Russian Bank,” a Moscow-based bank, as a reward for her support for Russia’s March 2014 invasion of Crimea and other Putin policies. [89]
In any case, as noted, during Ackermann’s tenure at Deutsche Bank, Deutsche Bank had indulged in an incredible range of financial misconduct, from sanctions-busting, interest rate rigging, and mortgage fraud to facilitating tax dodging, illicit trading, illegal foreclosures, rigging energy markets, and money laundering.[90] By no means were any of these full-blooded “white collar crimes” that were prosecuted to conviction and sentence; in most cases, they were disposed of by settlements and, at worst, deferred prosecution agreements. But in many ways that is the point – leniency may explain why they kept recurring.
Since 2010 all this misconduct has finally caught up with the bank, if not its former senior executive. Although no one has gone to jail, Deutsche Bank has already had to pay nearly $20 billion in fines and settlement costs.
Those already booked include a recent $7.2 billion U.S. Justice Department settlement for issuing fraudulent mortgage-backed securities in the 2008 financial crisis – the largest penalty of its kind to date. [91] This was also coupled with a $5.3 billion fine against Ackermann’s previous employer, Credit Suisse, for the same exact kind of toxic RMBSs. [92] Another case led to a $650 million fine for laundering $10 billion of Russian money, by way of Deutsche Bank’s offices in Moscow, New York, and Cyprus.
All these penalties were announced in January 2017. They all pertain to behavior that took root on Ackermann’s watch. As a New York State financial regulator remarked when he announced the Russian money-laundering fine for Deutsche Bank in January, “This Russian mirror-trading scheme occurred while the bank was on clear notice of serious and widespread compliance issues dating back a decade.” [93]
Since 2016, all this misbehavior has finally caught up with Deutsche Bank’s stock price. DB’s stock price has sharply underperformed other bank stocks because of the billions of litigation expense and penalties, to a large extent for offenses that originated during the Ackerman years. This, in turn, has led to huge job cuts, and even some serious concerns about whether Germany’s largest bank may soon require a bailout of its own. [94]
Meanwhile, Ackermann has moved on, bonuses and all, despite recent demands from shareholders to claw them back.
As the saying goes, however, “A shoemaker does not just make one shoe.” There are some reports from investigative journalists that Cyprus is still up to its old tricks, albeit on a smaller scale. As a German ZDF TV investigative program concluded last year after succeeding in laundering €15 million through the Bank of Cyprus and other Cyprus banks, “Money laundering in Cyprus is still possible.” [95] If so, the mere force of competitive pressures mean that Bank of Cyprus cannot stay far behind.
This is especially irritating to money laundering experts. After all, one of the key conditions for the €7.3 billion bailout that Cyprus received from the ECB and IMF in 2013-2016 was that Cyprus banks would commit to much tougher programs for monitoring compliance with “anti-money laundering” rules and statutes. As Ackermann acknowledged in a June 2016 interview, however, “There may still be individual cases…Money laundering had been the business model of Cyprus, and it is a difficult struggle.” [96]
Evidently, it is not a struggle for everyone. In addition to becoming Chairman of the Board of the Bank of Cyprus, Ackerman has also joined the board of directors of Viktor Vekselberg’s Renova Group. This is consistent with the fact that Ackermann also reportedly enjoys a long-standing, warm relationship with Vladimir Putin. While at Deutsche Bank, he met with Putin and other senior Russian officials frequently, served on Russia’s Foreign Investment Advisory Council and its “consultative committee” to form an “International Financial Center” in Moscow, and strongly endorsed Putin’s peculiar idea of a “free trade zone” between Russia and the EU.[97] In Putin’s own words, “It would take ages to describe everything that Deutsche Bank is doing in Russia.” [98]
Indeed I fear that it may.
So we also have a few more questions that Senators should ask Ross, under oath, in public hearings, with respect to Josef Ackermann:
- How long have you known Josef Ackerman? What loans or other business dealings have you had with Credit Suisse or Deutsche Bank? Do you have a private banking relationship with Deutsche Bank? With Credit Suisse?
- Are you aware of Deutsche Bank’s history with respect to Donald Trump? To your knowledge, does Josef Ackerman know Donald Trump? To your knowledge, was he involved in the lending relationship between Deutsche Bank and the Trump Organization or between the private banking side of Deutsche Bank and Donald Trump or is family? Was this a factor in your decision to hire him?
- What due diligence did you do with respect to Josef Ackermann? What questions did you ask Ackermann about his connections to Trump, Putin and Russian oligarchs? Are you aware that Josef Ackerman has a very cordial relationship with Vladimir Putin? Was that a factor in your decision to nominate him? Does Vladimir Putin ever any banking relationships with The Bank of Cyprus?
- Given Ackerman’s track record, and in light of your own reputation for bank turn-around management, why did you hire Josef Ackerman to be Chairman of the Board of The Bank of Cyprus? How confident should its shareholders be in his leadership?
WILBUR ROSS – SUMMARY
At 79, Wilbur Ross’s energy level and sheer capacity to take on new challenges are impressive. If approved, he would be by far the oldest U.S. Commerce Secretary ever. But his nomination is actually not that surprising.
To begin with, Ross’ relationship with Trump goes back at least to the early 1990s, when he helped to finance one of Trump’s first Atlantic City casino deals. [99] Ross has also been one of the most generous donors to Trump’s 2016 campaign. And he is widely reported to be one Trump’s most trusted advisors—in so far as Trump listens to anything other than the voices in his head.
Ross fits right in with the ruling financier elite, way more easily than the President. Of course, Trump campaigned against all these folks when he was courting the lumpen proletariat back in the fall, but when he realized for the first time on Election Eve that he might actually have to govern, he immediately began to invite the hard-working Ivy elite in to do a reverse takeover.
Most important, while Ross’ investment funds have had trouble raising money lately, reportedly out of concern about his age, [100] he does provide Trump with a certain degree of respectability in the investment community. While Trump falsely claims a degree from the Wharton School (he actually attended Penn’s undergraduate real estate economics program), Ross has a degree from Yale and earned a Harvard MBA.[101] While Trump has no record of public or community service of any kind, Ross serves on the boards of a dozen prominent non-profits, including the Japan Society (Chair), Brookings, and the Dean’s Advisory Board at the Harvard Business School.[102] He also holds seats on the boards of 70 for-profit firms, including 7 banks and 19 offshore haven companies.
The January 15 “Ethics Agreement” Ross signed with federal Office of Government Ethics promises that he will divest up to 80 of these investments within 90 to 180 days and that he will resign from most of his board seats as well. [103]
Unfortunately, however, this does not put an end to potential conflicts of interest, especially in the Ross case.
First, from the standpoint of potential conflicts, as the Wall Street Journal recently reported, Ross still insists on retaining tens of millions of dollars in investments in non-transparent offshore entities. [104]
These include a major co-investment with the Chinese government, a stake in a shipping company that will probably be subject to Commerce Department regulations, and a Cayman Islands “fund of funds” whose underlying assets and co-investors are completely invisible — for all we know they include “friends of Putin.” Ross hasn’t been asked. [105]
Second, the proposed terms of disinvestment are pretty slack. Three months is an eternity on Wall Street – plenty of time to alter their value if Ross were so inclined.
Third, there are no limits on Ross’ partners’ investments in the Bank of Cyprus or any other enterprises. They might decide to reward him in Heaven for favors done now,
Fourth, Ross is not required to unwind his extensive loan portfolio, including the very large sums that he and his group owe to big banks like JP Morgan. These banks may well be within the range of various federal government regulations that official actions by Ross could impact.
Fifth, If Mr. Ross were so inclined, an endless variety of murky dis-invest and buy-back deals might be constructed to offset his formal disinvestments. This is the essence of the problem with trying to enforce conflict of interest rules against extremely rich business people who have built up global networks of other rich business people over decades. Favors are discretely provided and reciprocated. Just ask Vladimir Putin.
Just for the sake of argument, however, let’s assume for the moment that Wilbur is too long in the tooth to take advantage of such loopholes or be motivated by selfish considerations. Let’s also stipulate that he really does believe that what he is serving the public good, as he sees it.
Even then, there is still another valid concern— the most important. From this angle, classic “conflicts of interest” analysis and Ross’s pledges to discontinue his investments and board seats both miss the point.
For just as with the President, the stench of dodgy associations lingers on. In other words, even if Ross divested everything down to his garters, there would still be this annoying puzzle:
Why, at the ripe old age of 77, way back in 2014, did Wilbur Ross step in with a lot of his and his associates’ money to save this feral bank in Cyprus? Why did he pursue all these associations with dodgy Russian “investors,” including “close associates of Putin?”
Before it confirms Mr. Wilbur Ross, the U.S. Senate needs to conduct a full investigation and demand public testimony to help us understand this glaring puzzle.
(For full citations and footnotes, click here, see bottom)
















 Then we have the gullible Prime Minister of Canada, Justin Trudeau who has invited Middle Eastern migrants, asylees and refugees in a welcome to Canada. Yet the intelligence and security authorities in Canada have a different position.
Then we have the gullible Prime Minister of Canada, Justin Trudeau who has invited Middle Eastern migrants, asylees and refugees in a welcome to Canada. Yet the intelligence and security authorities in Canada have a different position.










