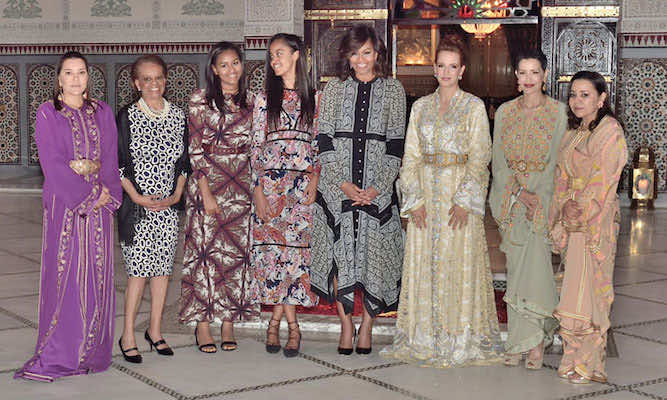
While there is the matter of Hillary and Bill with the Morocco thing, we cannot dismiss lil miss Michelle Obama and her relationship with the King as noted in the summer of 2016.
Using vague words, twisting sentences and altering priority of facts is all part of damage control within the Hillary inner circle.
When it comes to the Hillary event with this Morocco King, wow even the press operating on a tip or two gets places on a spinning wheel. The Clinton Foundation and it seems the Hillary inner circle as well as the State Department certainly placed their attention on the King. Why:
Aides publicly downplayed Clinton’s role, while privately doing damage control and working to keep foreign money.
A portrait of Moroccan King Mohamed VI is on display as then-Secretary of State Hillary Clinton meets with Foreign Minister Saad Eddine Othmani in Rabat, Morocco, in 2012 on her whistle-stop diplomatic tour. | AP Photo
Politico: Hillary Clinton’s top advisers downplayed her involvement in arranging a lavish Clinton Foundation conference in Marrakech last year, but behind the scenes they acknowledged her pivotal role and worked to minimize fallout from it.
After media inquiries about the role of Clinton and the king of Morocco in setting the stage for the conference, Clinton confidants, including her husband, Bill, scrambled to craft a new foreign contribution policy that looked tougher but still let them accept the Moroccan cash, according to hacked emails released by WikiLeaks.
The picture that emerges from the emails — as well as from interviews with a half dozen people familiar with the foundation’s inner workings and other contemporary reporting — shows Clintons’ confidants becoming acutely sensitive to criticism of the foundation’s foreign fundraising around the time Clinton was preparing to launch her presidential campaign.
The Moroccan saga also provides a window into the Clinton teams’ internal decision-making process on thorny ethics issues, as well as the occasionally less-than-forthcoming manner in which they deal with scrutiny.
It’s an approach that is familiar to longtime Clinton watchers and one that will be tested immediately if Clinton emerges victorious on Tuesday in her closer-than-expected race against Republican Donald Trump. Congressional Republicans have vowed to launch a series of investigations from Day One of a Clinton presidency, possibly starting even before she’s sworn in, including into whether she accorded special treatment during her time as secretary of state to donors who wrote huge checks to support her family’s foundation, its meetings, operations or endowment.
When it comes to Morocco, there’s no evidence that Clinton provided special treatment to the royal family or companies in which it’s invested as a result of their donations to her family’s foundation.
But there is evidence that Clinton’s aides sought to downplay a long and lucrative relationship between her family and that of Moroccan King Mohammed VI, even as her aides were trying to bring in a huge sum of cash through the monarch. And human rights watchdogs contend that the relationship played a role in the Clinton State Department — and the Clinton Foundation — turning a blind eye toward abuses by authorities in the Moroccan-occupied territory of Western Sahara.
Clinton’s own State Department advisers in 2011 flagged human rights concerns and the Western Sahara push for self-governance as among the “issues of sensitivity with Morocco when it comes to the Western Sahara,” according to an email released this year by the State Department in response to Freedom of Information Act litigation.
The Marrakech meeting of the foundation’s Clinton Global Initiative (or CGI) promised to increase attention on this thorny relationship, given that it was scheduled for early May 2015 — less than a month after Clinton would announce her candidacy. The timing sparked a vigorous debate among Clinton’s aides about whether she should go, which was revealed by emails hacked from the Gmail account of Clinton campaign Chairman John Podesta and disseminated starting last month by WikiLeaks.
Clinton’s right-hand aide, Huma Abedin, argued forcefully that her boss was obligated to attend the CGI conference because “her presence was a condition for the Moroccans to proceed so there is no going back on this.”
Buttressing Abedin’s argument, the Morocco meeting was included in a 2014 internal foundation memo released by WikiLeaks about “Secretary Clinton’s Foundation work.”
After a bit of pushback from other aides questioning the wisdom of Clinton’s attendance, Abedin in a January 2015 email made the financial case for Clinton going to Marrakech, suggesting that she had helped arrange a massive contribution for the foundation from the king of Morocco.
Referring to Clinton by her initials “HRC,” Abedin wrote that the meeting “was HRC’s idea, our office approached the Moroccans and they 100 percent believe they are doing this at her request. The King has personally committed approx $12 million both for the endowment and to support the meeting. It will break a lot of china to back out now when we had so many opportunities to do it in the past few months. She created this mess and she knows it.”
On the other side of the debate was Robby Mook, who would go on to become Clinton’s campaign manager. He argued that Clinton needed to back away from her commitment to attend the CGI meeting in Marrakech, as well as other foundation events and paid speeches, while also distancing herself from the foundation, as a whole.
“We really need to shut Morocco and these paid speeches down,” Mook emailed Podesta in February 2015. A few days later, he emailed Podesta and Abedin a Wall Street Journal article about ethical questions arising from an increase in foreign donations to the Clinton Foundation. The article did not mention the Morocco meeting or its funding, but Mook, alluding to Clinton’s impending campaign launch, asserted “This is why Morocco would be such a problem — more of this the first week she’s out selling her story.”
The following week, Mook in a memo to Podesta, Abedin and ex-Clinton State Department chief of staff Cheryl Mills flagged what he called “Foundation vulnerability points.” While he did not expressly single out the Marrakech CGI meeting, it would seem to have triggered several of the vulnerabilities he listed, including “Money from foreign governments” and “Overseas events with foreign leaders or government,” as well as “lavish/high-end hotels for events” and Clinton “attending Foundation events.”
After the vulnerability memo, the WikiLeaks email trail on the Morocco meeting fell silent.
That changed on April 7 — just five days before Clinton would announce her candidacy. POLITICO, acting on a tip about the role of Clinton and the king in arranging the conference and a $1 million sponsorship from a Moroccan-government-owned phosphate company active in Western Sahara called OCP, emailed a foundation spokesman with a number of questions. Did Clinton plan to follow through on her commitment to attend the conference and would the foundation continue holding overseas conferences during a then-imminent Clinton presidential campaign, POLITICO asked.
The spokesman immediately forwarded the email to top aides to the Clintons. Within minutes, Bill Clinton’s chief of staff Tina Flournoy sent an email with the subject line “Morocco” to Podesta and Mills. “We have press calls on their contributions,” she wrote.
The spokesman responded to POLITICO’s inquiry saying “it’s unlikely that Secretary will attend,” but requesting not to be named in the resulting story revealing OCP’s $1 million sponsorship.
The anonymous spokesman did not answer follow-up questions about the king’s role in arranging the donations.
In fact, the spokesman tried to cast doubt on reporting that Clinton and the king discussed the possibility of a foundation meeting in Morocco, and that Abedin was involved in “subsequent high-level planning conversations.”
Later, when asked to explain the discrepancy between their initial answers and Abedin’s characterization in the WikiLeaks emails, Brian Cookstra, a different foundation spokesman, bristled. “It sounds like you are suggesting we misled you which is a serious accusation, and it’s not accurate,” Cookstra said. “We stand by our original answers on this,” he said, explaining, “we have no record of” Clinton and the king “discussing this personally.”
However, emails released by the State Department suggest a personal relationship between Clinton and the king, showing Clinton and her staff arranging conversations with the king and other Moroccans. But Cookstra said “Discussions handled by her office may have been exploratory — they were before the meeting was set or the location was finalized, and do not constitute the kind ‘high-level planning conversations’ the CGI staff undertake for every meeting.”
The anonymous spokesman in the days before Clinton’s announcement also ignored POLITICO’s questions about whether the foundation would continue accepting foreign donations and holding overseas events during her campaign.
Instead, the WikiLeaks email show that Clintons’ aides began a debate about crafting a new policy that would bar the foundation from holding overseas conferences or accepting foreign donations during Clinton’s presidential campaign — with a couple notable exceptions.
“CGI will no longer conduct CGI-International events nor accept any funding from foreign government hosts of such events after the already-scheduled events in May (CGI-Morocco) and June (CGI-Greece) of 2015,” read a draft of a document containing several “Foundation Policies Adjustments.” The draft, which was emailed to top Clinton aides seven hours after POLITICO’s initial inquiry and was among the documents included in the Podesta Gmail hack, also indicated that Hillary Clinton would resign from the foundation’s board and “will no longer be available to fundraise for the Foundation’s programs and activities.”
Among the first questions about the draft came from CGI chief Bob Harrison, who emailed the group, “What about the Morocco money?”
“Morocco money exception is included in there,” responded foundation executive Maura Pally.
Ultimately, Hillary Clinton did not attend the CGI conference in Marrakech, sending her husband and daughter in her stead.
The king was traveling during the CGI conference and did not attend, but POLITICO revealed that he loaned one of his palaces to Bill and Chelsea Clinton to stay in during their time in Marrakech. The conference included a mix of plenary sessions in which corporations pledged to spend millions on humanitarian causes — including expanding access to clean water access and education in the Middle East and Africa — and an extravagant Moroccan feast with a hookah lounge and a nine-piece band playing traditional Moroccan Gnawa music at a five-star resort on the outskirts of Marrakech.
Cookstra said the king did not donate any money to the foundation and never has, despite once having been listed on a donor roll as having pledged as much as $500,000 to help build Bill Clinton’s presidential library (the foundation says the donation never came through).
Officials at the Moroccan Embassy in Washington did not respond when asked whether the king had originally committed the $12 million referenced in Abedin’s email. They also didn’t answer questions about the role of Clinton or the king in initiating the meeting or whether the king expected Clinton to attend the meeting, and skipped it himself because she did.
The Clinton Foundation did not respond to questions about whether the conference was Hillary Clinton’s idea, whether the king had committed $12 million or why Clinton’s aides weren’t more forthcoming originally when asked about the roles of Hillary Clinton, Huma Abedin and the king in initiating the meeting.
“We’ve addressed what you’ve asked,” Cookstra said.
Josh Gerstein contributed to this report.


 More from
More from