Oh Hillary…do tell…
Marc Elias is a partner in the law firm Perkins and Coie. Beyond that he was the general counsel for the Hillary presidential campaign. Previously to that, he did the same for the John Kerry presidential campaign….sheesh….oh yeah…he did the same for Al Franken.
Keep a large supply of popcorn handy….week by week this has the makings of good theater. Opposition research on candidates is nothing new, but this creates a new definition to research, to Clinton and fraud.
What is remarkable is that the Hillary campaign and the DNC punked the intelligence agencies that spent months and huge investigative resources on tracking down people and facts in the dossier. Further, while parts of the dossier are accurate and others not at all, it also proves that someone had a direct point of contact with people inside the Kremlin.
Let that sink in….
Related reading: Fusion GPS partners plead Fifth before House Intel
According to The Hill, the FBI, “obtained an eyewitness account -backed by documents- indicating Russian nuclear officials had routed millions of dollars to the U.S. designed to benefit former President Bill Clinton’s charitable foundation… during the time Secretary of State Hillary Clinton served on a government body that provided a favorable decision to Moscow.”
***
Clinton campaign, DNC paid for research that led to Russia dossier
WaPo: The Hillary Clinton campaign and the Democratic National Committee helped fund research that resulted in a now-famous dossier containing allegations about President Trump’s connections to Russia and possible coordination between his campaign and the Kremlin, people familiar with the matter said. Marc E. Elias, a lawyer representing the Clinton campaign and the DNC, retained Fusion GPS, a Washington firm, to conduct the research.

Marc E. Elias of Perkins Coie represented the Clinton campaign and the Democratic National Committee. (Matt McClain/The Washington Post)
After that, Fusion GPS hired dossier author Christopher Steele, a former British intelligence officer with ties to the FBI and the U.S. intelligence community, according to those people, who spoke on the condition of anonymity.
Elias and his law firm, Perkins Coie, retained the firm in April 2016 on behalf of the Clinton campaign and the DNC. Before that agreement, Fusion GPS’s research into Trump was funded by a still unknown Republican client during the GOP primary.
The Clinton campaign and the DNC, through the law firm, continued to fund Fusion GPS’s research through the end of October 2016, days before Election Day.
Fusion GPS gave Steele’s reports and other research documents to Elias, the people familiar with the matter said. It is unclear how or how much of that information was shared with the campaign and DNC, and who in those organizations was aware of the roles of Fusion GPS and Steele. One person close to the matter said the campaign and the DNC were not informed of Fusion GPS’s role by the law firm. The dossier has become a lightning rod amid the intensifying investigations into the Trump campaign’s possible connections to Russia. Some congressional Republican leaders have spent months trying to discredit Fusion GPS and Steele, and tried to determine the identity of the Democrat or organization that paid for it. Trump tweeted as recently as Saturday that the Justice Department and FBI should “immediately release who paid for it.”
Elias and Fusion GPS declined to comment on the arrangement. Spokespersons for the Clinton campaign and the DNC had no immediate comment.
Some of the details are included in an Oct. 24 letter sent by Perkins Coie to a lawyer representing Fusion GPS, telling the research firm that it was released from a client-confidentiality obligation. The letter was prompted by a legal fight over a subpoena for Fusion GPS’s bank records.
People involved in the matter said that they would not disclose the dollar amounts paid to FusionGPS, but said that the campaign and the DNC shared the cost.
Steele previously worked in Russia for British intelligence. The dossier is a compilation of reports he prepared for Fusion. The dossier alleged that the Russian government collected compromising information about Trump and the Kremlin was engaged in an active effort to assist his campaign for president. Washington Post reporters Tom Hamburger and Rosalind S. Helderman explain the story behind a controversial dossier on President Trump. (Jason Aldag,Sarah Parnass/The Washington Post)U.S. intelligence agencies later released a public assessment which asserted that Russia intervened in the 2016 election to aid Trump. The FBI has been investigating whether any Trump associates helped the Russians in that effort.
[FBI once planned to pay former British spy who authored controversial Trump dossier]
Trump has adamantly denied the allegations in the dossier and has dismissed the FBI probe as a witch hunt.
Fusion GPS’s work researching Trump began during the Republican presidential primaries, when the GOP donor paid for the firm to investigate the real estate tycoon’s background.
Fusion GPS did not start off looking at Trump’s Russia ties, but quickly realized that those relationships were extensive, according to the people familiar with the matter. When the Republican donor stopped paying for the research, Elias, acting on behalf of the Clinton campaign and the DNC, agreed to pay for the work to continue. The Democrats paid for research, including by Fusion GPS, because of concerns that little was known about Trump and his business interests, according to the people familiar with the matter.
These people said that it is standard practice for political campaigns to use law firms to hire outside researchers to ensure their work is protected by attorney-client and work-product privileges.
The Clinton campaign paid Perkins Coie $5.6 million in legal fees from June 2015 to December 2016, according to campaign finance records, and the DNC paid the firm $3.6 million in “legal and compliance consulting’’ since Nov. 2015 — though it’s impossible to tell from the filings how much of that work was for other legal matters and how much of it related to Fusion GPS.
At no point, these people said, did the Clinton campaign or the DNC direct Steele’s activities. They described him as a Fusion GPS subcontractor.
Some of Steele’s allegations began circulating in Washington in the summer of 2016 as the FBI launched its counterintelligence investigation into possible connections between Trump associates and the Kremlin. Around that time, Steele shared some of his findings with the FBI.
After the election, the FBI agreed to pay Steele to continue gathering intelligence about Trump and Russia, but the bureau pulled out of the arrangement after Steele was publicly identified in news reports. The dossier was published by BuzzFeed News in January. Fusion GPS has said in court filings that it did not give BuzzFeed the document.
Officials have said that the FBI has confirmed some of the information in the dossier. Other details, including the most sensational accusations, have yet to be verified and may never be.
Current and former U.S. intelligence officials said that Steele was respected by the FBI and the State Department for earlier work he performed on a global corruption probe.
In early January, then-FBI Director James B. Comey presented a two-page summary of Steele’s dossier to President Barack Obama and President-elect Trump.
In May, Trump fired Comey, which led to the appointment of Robert S. Mueller III as special counsel investigating the Trump-Russia matter.
Congressional Republicans have tried to force Fusion GPS to identify the Democrat or group behind Steele’s work, but the firm has said that it would not do so, citing confidentiality agreements with its clients. Last week, Fusion GPS executives invoked their constitutional right not to answer questions from the House Intelligence Committee. The firm’s founder, Glenn Simpson, had previously given a 10-hour interview to the Senate Judiciary Committee.
Over objections from Democrats, the Republican leader of the House Intelligence Committee, Rep. Devin Nunes (Calif.), subpoenaed Fusion GPS’s bank records to try to identify the mystery client.
Fusion GPS has been fighting the release of its bank records. A judge on Tuesday extended a deadline for Fusion GPS’s bank to respond to the subpoena until Friday while the company attempts to negotiate a resolution with Nunes.



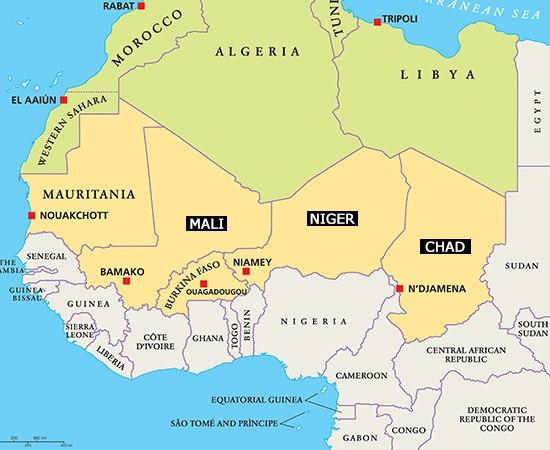
 McCain and Graham both stated they were unaware of the operations in Niger, much less the other countries located in West Africa. The United States has an estimated 7000 troops operating in about 50 countries in Africa. Militant Islam has no boundaries globally.
McCain and Graham both stated they were unaware of the operations in Niger, much less the other countries located in West Africa. The United States has an estimated 7000 troops operating in about 50 countries in Africa. Militant Islam has no boundaries globally.