And counting…including the newly launched conservative open free speech social media site Parler.
HONG KONG (Reuters) – Apple removed 39,000 game apps on its China store Thursday, the biggest removal ever in a single day, as it set year-end as deadline for all game publishers to obtain a license.
The takedowns come amid a crackdown on unlicensed games by Chinese authorities.
Including the 39,000 games, Apple removed more than 46,000 apps in total from its store on Thursday. Games affected by the sweep included Ubisoft title Assassin’s Creed Identity and NBA 2K20, according to research firm Qimai.
Qimai also said only 74 of the top 1,500 paid games on Apple store survived the purge.
Apple did not immediately respond to a request for comment.
Apple initially gave game publishers an end-of-June deadline to submit a government-issued licence number enabling users to make in-app purchases in the world’s biggest games market.
Apple later extended the deadline to Dec. 31. Cases still pending.
China’s Android app stores have long complied with regulations on licenses. It is not clear why Apple is enforcing them more strictly this year.
Analysts said the move was no surprise as Apple continues to close loopholes to fall in line with China’s content regulators, and would not directly affect Apple’s bottom line as much as previous removals.
“However, this major pivot to only accepting paid games that have a game license, coupled with China’s extremely low number of foreign game licenses approved this year, will probably lead more game developers to switch to an ad-supported model for their Chinese versions,” said Todd Kuhns, marketing manager for AppInChina, a firm that helps overseas companies distribute their apps.
In December, shares of Apple (NASDAQ:AAPL) were down a bit after the company removed thousands of paid game apps from its China App Store. Meanwhile, Disney (NYSE:DIS) stock rose after the company reportedly plans a price increase for its ESPN+ streaming service.
The Wall Street Journal reported last week that tech giant Apple planned to remove thousands of game apps from its App Store in China due to government pressure. Apple reportedly warned Chinese developers earlier this month that paid gaming apps were at risk of removal.
China requires paid video games to be licensed before being released, a policy that has been in effect for the past four years. However, app developers have been able to get around that rule on Apple’s platform. Apple began closing the loophole this year, the Journal reports.
On Thursday, Apple followed through by removing 39,000 game apps from its China App Store, according to Reuters. These include popular titles like Assassin’s Creed Identity and NBA 2K20. Just 74 of the top 1,500 paid game apps on the China App Store are still available, according to research firm Qimai.
The license requirement applies to paid games and games with in-app purchases, so the move by Apple could push more developers to opt for an ad-supported model. Apple takes a cut from sales of apps and in-app content, so such a shift would hurt Apples sales in China. source
*** Expect more stock price decline given the recent anti-trust cases in the legal pipeline against Apple and other big tech corporations. Apple and Google both take a cut of the revenue of the apps on their respective stores.
***
The factory in China where Apple products, specifically iPhones, undergo final assembly has approximately 230,000 workers. In the US, there are only 83 cities that have the same population as this factory’s number of employees. Meaning the number of possible workers in the US is not enough to cover Apple’s needs.
In China, an estimated quarter of their workforce lives in company-owned dormitories. These barracks are located on factory property. Many people are living and working at the factory. Such jobs are in high demand in China, and they can hire many people overnight. These examples prove that the measure, speed, and efficiency of Chinese manufacturing surpass anything the US is presently capable of. (read slave labor)

Apple is a willing partner in the China 2025 plan. You will then understand the China policy of President Trump and Secretary of State, Mike Pompeo.
Continue reading…you need to understand the past implications and those when Biden takes office.
When the US and ultimately the rest of the Western world began to engage China, resulting in China finally being allowed into the World Trade Organization in the early 2000s, no one really expected the outcomes we see today.
There is no simple disengagement path, given the scope of economic and legal entanglements. This isn’t a “trade” we can simply walk away from.
But it is also one that, if allowed to continue in its current form, could lead to a loss of personal freedom for Western civilization. It really is that much of an existential question.
Doing nothing isn’t an especially good option because, like it or not, the world is becoming something quite different than we expected just a few years ago—not just technologically, but geopolitically and socially.
China and the West
Let’s begin with how we got here.
My generation came of age during the Cold War. China was a huge, impoverished odd duck in those years. In the late 1970s, China began slowly opening to the West. Change unfolded gradually but by the 1990s, serious people wanted to bring China into the modern world, and China wanted to join it.
Understand that China’s total GDP in 1980 was under $90 billion in current dollars. Today, it is over $12 trillion. The world has never seen such enormous economic growth in such a short time.
Meanwhile, the Soviet Union collapsed and the internet was born. The US, as sole superpower, saw opportunities everywhere. American businesses shifted production to lower-cost countries. Thus came the incredible extension of globalization.
We in the Western world thought (somewhat arrogantly, in hindsight) everyone else wanted to be like us. It made sense. Our ideas, freedom, and technology had won both World War II and the Cold War that followed it. Obviously, our ways were best.
But that wasn’t obvious to people elsewhere, most notably China. Leaders in Beijing may have admired our accomplishments, but not enough to abandon Communism.
They merely adapted and rebranded it. We perceived a bigger change than there actually was. Today’s Chinese communists are nowhere near Mao’s kind of communism. Xi calls it “Socialism with a Chinese character.” It appears to be a dynamic capitalistic market, but is also a totalitarian, top-down structure with rigid rules and social restrictions.
So here we are, our economy now hardwired with an autocratic regime that has no interest in becoming like us.
China’s Hundred-Year Marathon
In The Hundred-Year Marathon, Michael Pillsbury marshals a lot of evidence showing the Chinese government has a detailed strategy to overtake the US as the world’s dominant power.
They want to do this by 2049, the centennial of China’s Communist revolution.
The strategy has been well documented in Chinese literature, published and sanctioned by organizations of the People’s Liberation Army, for well over 50 years.
And just as we have hawks and moderates on China within the US, there are hawks and moderates within China about how to engage the West. Unfortunately, the hawks are ascendant, embodied most clearly in Xi Jinping.
Xi’s vision of the Chinese Communist Party controlling the state and eventually influencing and even controlling the rest of the world is clear. These are not merely words for the consumption of the masses. They are instructions to party members.
Grand dreams of world domination are part and parcel of communist ideologies, going all the way back to Karl Marx. For the Chinese, this blends with the country’s own long history.
It isn’t always clear to Western minds whether they actually believe the rhetoric or simply use it to keep the peasantry in line. Pillsbury says Xi Jinping really sees this as China’s destiny, and himself as the leader who will deliver it.
To that end, according to Pillsbury, the Chinese manipulated Western politicians and business leaders into thinking China was evolving toward democracy and capitalism. In fact, the intent was to acquire our capital, technology, and other resources for use in China’s own modernization.
It worked, too.
Over the last 20–30 years, we have equipped the Chinese with almost everything they need to match us, technologically and otherwise. Hundreds of billions of Western dollars have been spent developing China and its state-owned businesses.
Sometimes this happened voluntarily, as companies gave away trade secrets in the (often futile) hope it would let them access China’s huge market. Other times it was outright theft. In either case, this was no accident but part of a long-term plan.
Pillsbury (who, by the way, advises the White House including the president himself) thinks the clash is intensifying because President Trump’s China skepticism is disrupting the Chinese plan. They see his talk of restoring America’s greatness as an affront to their own dreams.
In any case, we have reached a crossroads. What do we do about China now?
Targeted Response
In crafting a response, the first step is to define the problem correctly and specifically. We hear a lot about China cheating on trade deals and taking jobs from Americans. That’s not entirely wrong, but it’s also not the main challenge.
I believe in free trade. I think David Ricardo was right about comparative advantage: Every nation is better off if all specialize in whatever they do best.
However, free trade doesn’t mean nations need to arm their potential adversaries. Nowadays, military superiority is less about factories and shipyards than high-tech weapons and cyberwarfare. Much of our “peaceful” technology is easily weaponized.
This means our response has to be narrowly targeted at specific companies and products. Broad-based tariffs are the opposite of what we should be doing. Ditto for capital controls.
They are blunt instruments that may feel good to swing, but they hurt the wrong people and may not accomplish what we want.
We should not be using the blunt tool of tariffs to fight a trade deficit that is actually necessary. The Chinese are not paying our tariffs; US consumers are.
Importing t-shirts and sneakers from China doesn’t threaten our national security. Let that kind of trade continue unmolested and work instead on protecting our advantages in quantum computing, artificial intelligence, autonomous drones, and so on.
The Trump administration appears to (finally) be getting this. They are clearly seeking ways to pull back the various tariffs and ramping up other efforts.






/https://static.texastribune.org/media/files/174cf0beea0e357d19c00fe69593f659/Los_Alamos_TT.jpg) Los Alamos
Los Alamos
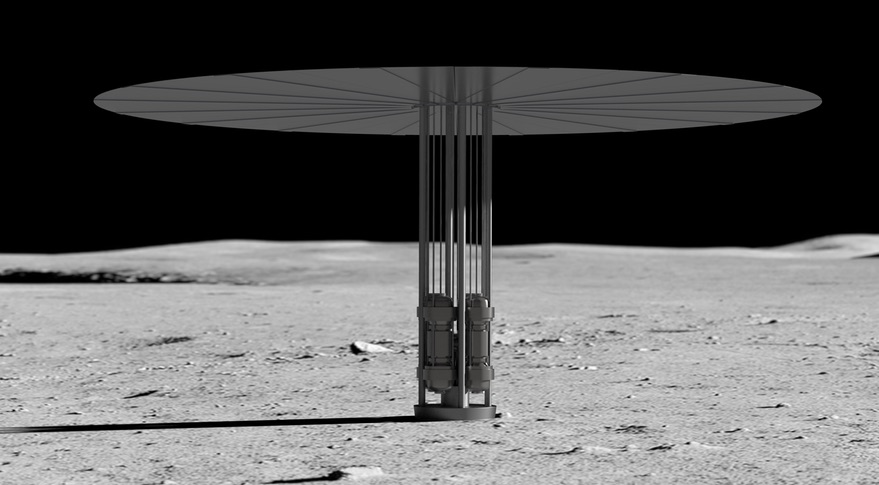 An illustration of a Kilopower nuclear reactor on the moon. Development of surface nuclear power technologies is a key element of the roadmap included in Space Policy Directive 6. Credit: NASA
An illustration of a Kilopower nuclear reactor on the moon. Development of surface nuclear power technologies is a key element of the roadmap included in Space Policy Directive 6. Credit: NASA