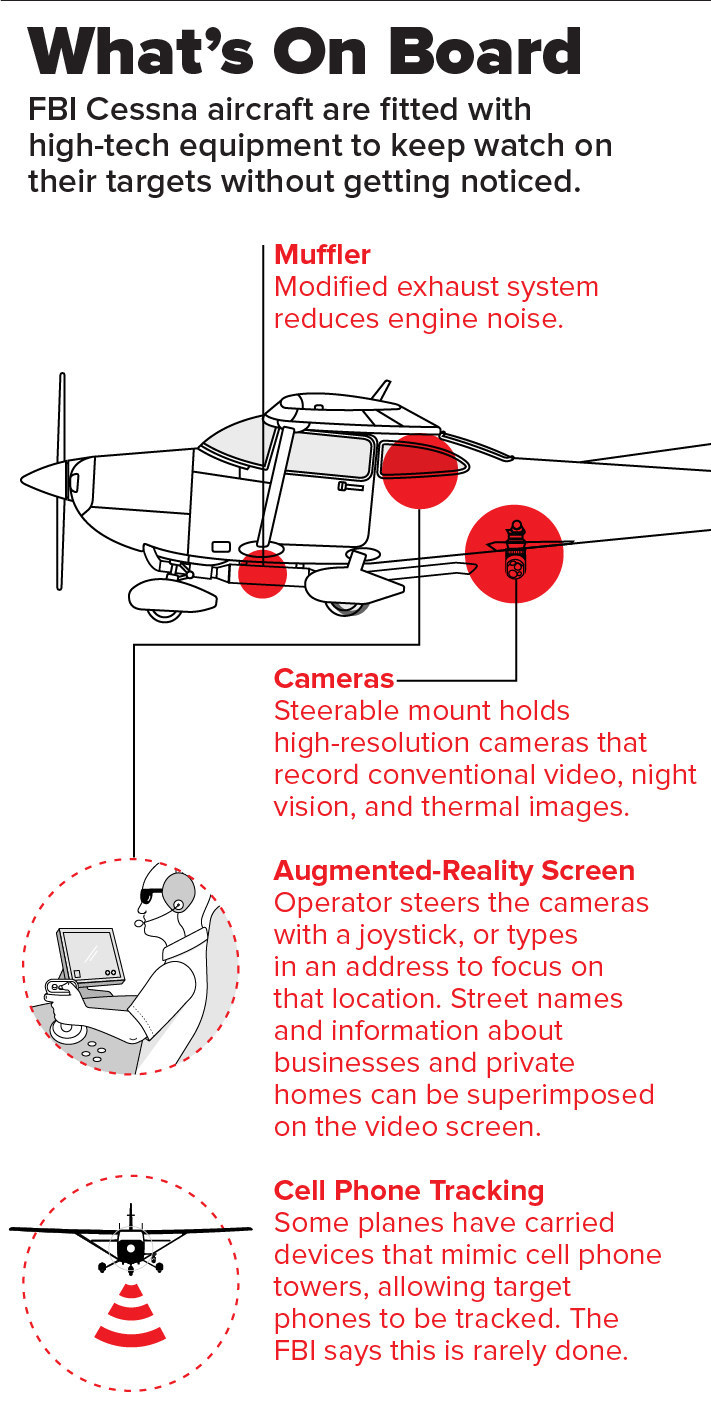
BuzzFeed: Each weekday, dozens of U.S. government aircraft take to the skies and slowly circle over American cities. Piloted by agents of the FBI and the Department of Homeland Security (DHS), the planes are fitted with high-resolution video cameras, often working with “augmented reality” software that can superimpose onto the video images everything from street and business names to the owners of individual homes. At least a few planes have carried devices that can track the cell phones of people below. Most of the aircraft are small, flying a mile or so above ground, and many use exhaust mufflers to mute their engines — making them hard to detect by the people they’re spying on.
The government’s airborne surveillance has received little public scrutiny — until now. BuzzFeed News has assembled an unprecedented picture of the operation’s scale and sweep by analyzing aircraft location data collected by the flight-tracking website Flightradar24 from mid-August to the end of December last year, identifying about 200 federal aircraft. Day after day, dozens of these planes circled above cities across the nation.
Some graphics and images are interactive, click here to access.
Day after day, dozens of these planes circled above cities across the nation.
The FBI and the DHS would not discuss the reasons for individual flights but told BuzzFeed News that their planes are not conducting mass surveillance.
The DHS said that its aircraft were involved with securing the nation’s borders, as well as targeting drug smuggling and human trafficking, and may also be used to support investigations by the FBI and other law enforcement agencies. The FBI said that its planes are only used to target suspects in specific investigations of serious crimes, pointing to a statement issued in June 2015, after reporters and lawmakers started asking questions about FBI surveillance flights.
“It should come as no surprise that the FBI uses planes to follow terrorists, spies, and serious criminals,” said FBI Deputy Director Mark Giuliano, in that statement. “We have an obligation to follow those people who want to hurt our country and its citizens, and we will continue to do so.”
But most of these government planes took the weekends off. The BuzzFeed News analysis found that surveillance flight time dropped more than 70% on Saturdays, Sundays, and federal holidays.
“The fact that they are mostly not flying on weekends suggests these are relatively run-of-the-mill investigations,” Nathan Freed Wessler, an attorney with the American Civil Liberties Union’s (ACLU) Project on Speech, Privacy, and Technology, told BuzzFeed News.
The government’s aerial surveillance programs deserve scrutiny by the Supreme Court, said Adam Bates, a policy analyst with the Cato Institute, a libertarian think tank in Washington, D.C. “It’s very difficult to know, because these are very secretive programs, exactly what information they’re collecting and what they’re doing with it,” Bates told BuzzFeed News.


The BuzzFeed News analysis also revealed how the government responded to the mass shooting last December in San Bernardino, California.
Surveillance flight time dropped more than 70% on Saturdays, Sundays, and federal holidays.
In the weeks leading up to the deadliest terrorist attack on U.S. soil since 9/11, nearby neighborhoods in and around Los Angeles were watched intensively by FBI aircraft. But San Bernardino itself was apparently ignored: Our data shows no FBI surveillance flights over the city.
That changed abruptly after the attack on the morning of Dec. 2. Within 90 minutes, two planes — one an FBI Cessna, the other a DHS Pilatus PC-12 surveillance aircraft — were circling the scene. Later that afternoon, the FBI plane flew around the home of the two shooters, Syed Rizwan Farook and Tashfeen Malik.
Farook attended the nearby Dar Al Uloom Al-Islamiyah of America mosque. And starting Dec. 3, FBI planes traced circles with the mosque near their center. Three different FBI planes flew around the mosque, some circling for more than three hours at a time. There were flights on each day in the week after the attack — except for Saturday and Sunday.
The FBI told BuzzFeed News that it cannot launch investigations based on race, ethnicity, or religion — surveillance means that individual criminal suspects are being watched, not groups of people.
But Shakeel Syed, executive director of the Islamic Shura Council of Southern California, an umbrella organization representing the region’s mosques and Islamic centers, told BuzzFeed News that he is alarmed that the FBI’s knee-jerk reaction to the San Bernardino massacre seems to have been to send its planes to watch the Dar Al Uloom mosque.
“That is extremely troubling, and reconfirms the fears that we continue to talk about,” Syed said. “I don’t know that they have ever done surveillance of churches or synagogues when people of those traditions have committed acts of criminality.”
In the months before the San Bernardino attack, some of the government’s surveillance planes circled over other neighborhoods with large Muslim populations. In the San Francisco Bay Area, for instance, there was a clear circle above Little Kabul in Fremont, home to the largest concentration of ethnic Afghans in the nation. The main concentrations of surveillance in Minneapolis, meanwhile, were above an area known as Little Mogadishu for its large Somali population.
But these neighborhoods did not come under heightened aerial scrutiny after the terrorist mayhem in Paris on Nov. 13, nor after San Bernardino. And on Thanksgiving Day, less than two weeks after the Paris attacks, with the nation under a State Department–issued global terrorism alert, federal surveillance planes almost entirely stopped flying, only to resume once the holiday was over.
The BuzzFeed News analysis almost certainly underestimates the scope of surveillance by federal aircraft. Some two dozen planes operated by the FBI and more than 130 registered to the DHS never appeared on Flightradar24, suggesting that some surveillance planes may be hidden from public view on plane-tracking websites. (See here for details on the BuzzFeed News analysis.)
FBI planes have also on occasion been used to support local law enforcement. In April 2015, after riots broke out in Baltimore following the death of Freddie Gray in police custody, FBI planes were sent to monitor the situation, documents obtained by the ACLU show. FBI Director James Comey told Congress that the agency’s aircraft also flew over Ferguson, Missouri, in the summer of 2014, after a local police officer shot Michael Brown.
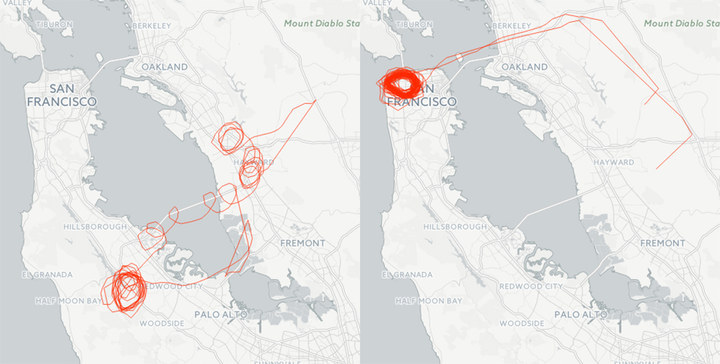
Responding to the BuzzFeed News analysis, FBI spokesman Christopher Allen said that planes may circle over cities while waiting for a suspect to emerge from a building. In some cases, the BuzzFeed News analysis showed that FBI aircraft indeed seemed to be following a vehicle from place to place, pausing to circle at each stop. Other flights, however, circled a single location for several hours, and then returned to their airfields.
Left image shows plane likely following a suspect; right shows repeated circling
As to the big drop-off in flights on the weekends, Allen told BuzzFeed News that the agency’s surveillance depends on the needs of individual investigations.
“If we need it, it’s going to happen,” Allen said. The targets of surveillance may simply be less active on the weekends, he said. And because traffic is lighter, he added, it’s easier for the FBI to follow suspects on the ground instead of by air.
That explanation did not convince James Wedick, a former FBI agent based near Sacramento, California.
“That’s painful,” Wedick told BuzzFeed News. He suspects that the weekend dip reflects the controversial practice of using undercover agents and informants to entice suspects into joining fake terrorist plots devised by the FBI. “The FBI today is better able to control investigations, enabling agents to orchestrate events when more resources were available,” Wedick said.

US Customs and Border Patrol

US Customs and Border Patrol

Courtesy William Larkins
Left: Two DHS aircraft patrol the U.S. border; Center: DHS helicopter, with cameras beneath the cockpit door; Right: Cessna 208, operated by an FBI front company
In June of last year, the Associated Press reported that it had linked more than 50 planes, mostly small Cessna Skylane 182 aircraft, to 13 fake companies created as fronts for the FBI. Also using Flightradar24, AP reporters tracked more than 100 flights in 11 states over the course of a month.
BuzzFeed News extended the list of FBI front companies, drawing from other sources that have investigated the agency’s airborne operations. We then looked for planes registered to these front companies in data provided by Flightradar24. (Its data comes from radio signals broadcast by transponders that reveal planes’ locations and identifying information, picked up by receivers on the ground that are hosted by volunteers across the country.)
We detected nearly 100 FBI fixed-wing planes, mostly small Cessnas, plus about a dozen helicopters. Collectively, they made more than 1,950 flights over our four-month-plus observation period. The aircraft frequently circled or hovered around specific locations, often for several hours in the daytime over urban areas.
We also tracked more than 90 aircraft, about two-thirds of them helicopters, that were registered to the DHS, which is responsible for border protection, customs, and immigration. Not surprisingly, these planes were especially active around border towns such as McAllen, Texas, which faces the Mexican city of Reynosa across the Rio Grande.
But the DHS’s airborne operations also extended far into the U.S. interior. And over some cities, notably Los Angeles, its aircraft seemed to circle around particular locations, behaving like those in the FBI’s fleet.

The DHS would not comment on flights over specific cities, but confirmed that its planes regularly support other law enforcement agencies, including the FBI.
DHS spokesman Carlos Lazo told BuzzFeed News by email that its planes are mainly used to combat the illegal drug trade, human trafficking, and violent crime. In 2015, he said, DHS aerial surveillance missions supported investigations that “resulted in 706 arrests including violent criminals and sex traffickers, the seizure of more than 10,000 lbs of cocaine, 342 lbs of heroin, more than 1,000 lbs of methamphetamine, 350 weapons, and $24 million in cash.”
BuzzFeed News
Regulations require that a plane’s owners submit documents to the Federal Aviation Administration describing modifications that might affect a plane’s airworthiness, and BuzzFeed News obtained this paperwork for about 130 of the planes identified in our analysis — giving a strong sense of what the aircraft are capable of.
Many FBI Cessnas, for example, are fitted with exhaust mufflers to reduce engine noise. FBI and DHS aircraft carry sophisticated camera systems in steerable mounts that can provide conventional video, night vision, and infrared thermal imaging. These include Talon devices, manufactured by FLIR Systems of Wilsonville, Oregon. The company’s website boasts that these devices “deliver high-resolution imagery day or night.”
On FBI planes, cameras are typically paired with augmented reality systems, which superimpose a variety of information over the video, and can embed the feed from a camera into a wider scene built up from stored satellite images.
This promotional video from Churchill Navigation of Boulder, Colorado, whose systems are installed on FBI surveillance aircraft, explains some of their capabilities.
Over the past few years, news organizations and advocacy groups have also accumulated evidence that some government surveillance planes can carry equipment to track cell phones on the ground.
Federal and local law enforcement agencies are known to use devices called cell-site simulators that mimic cell phone towers, emitting powerful signals that trick people’s phones into connecting to them as if they were the real thing. Sometimes called “Stingrays” for the brand name of one popular model, these devices read the unique identification codes of the cell phones that connect to them, and so can be used to track people — even if they are indoors, in dense crowds, or otherwise hidden from view.
Official records indicate that both the DHS and the FBI can connect to cell phones from the air. Documents obtained by Chris Soghoian, principal technologist with the ACLU’s Project on Speech, Privacy, and Technology, show that in 2010 the DHS spent almost $190,000 under a contract that included the purchase of cell-site simulators and an “airborne flight kit” for a Stingray device — consisting of “specialized antennas, antenna mounts, cables and power connections.” The contract also covered training for up to four DHS Immigration and Customs Enforcement agents to be instructed on how to operate Stingrays from an aircraft.
Other government spending records, reviewed by BuzzFeed News, show that in 2008 the FBI purchased a Stingray airborne kit for $55,000.
And in March, the San Francisco–based Electronic Frontier Foundation (EFF) released a series of documents, obtained through a Freedom of Information lawsuit, in which FBI officials discussed the use of cell-site simulators from aircraft. The documents reveal that the agency was unsure how many times the devices had been used, when pressed for information by the Senate judiciary committee.
“I cannot say for certain that the mission numbers are 100% accurate,” one official wrote, noting that so far, five flights involving Stingrays had been identified.
The FBI told BuzzFeed News that cell-site simulators are used very rarely, and only to track suspects. Calls are not intercepted, and personal data is not captured, Allen said.
The DHS declined to comment on how often it used the devices from the air, but Lazo, the department’s spokesman, said the technology provides “invaluable assistance” in hunting down criminal suspects. “Cell-site simulators used by DHS are not used to collect the contents of any communication, including any data contained on the phone itself,” he added.
BuzzFeed News
Still, tracking the movements of specific criminal suspects may entail connecting to the phones of thousands of people who just happen to be nearby. And although government policies say that information about nontarget phones should be quickly discarded, privacy advocates remain concerned about cell-site simulators, which may not require a warrant in emergency situations.
“In our opinion, any time Stingrays or the like are used, they need to have a warrant based on probable cause,” Nate Cardozo, senior staff attorney with the EFF, told BuzzFeed News.
One of the most sensitive questions surrounding the government’s surveillance flights is whether Muslims are being disproportionately targeted.
Even before San Bernardino, Republican presidential frontrunner Donald Trump was calling for surveillance of certain mosques. And in the wake of the bombings in Brussels in March, rival Ted Cruz said that surveillance in Muslim neighborhoods should be intensified.
BuzzFeed News mapped mosques and Islamic centers throughout the nation, as detailed in a database maintained by the Hartford Institute for Religion Research in Connecticut. Some mosques were at the center of the circles traced by FBI planes, but BuzzFeed News could see no clear pattern indicating widespread surveillance of mosques.
Privacy advocates argue that all of the flights should be subjected to greater official scrutiny, to ensure that a balance is being struck between effective law enforcement and privacy.
“When people think of surveillance, they think of the NSA, or of specific people being tracked, or mosques being infiltrated,” Ramzi Kassem, a law professor at the City University of New York, told BuzzFeed News. “They aren’t necessarily thinking about planes circling overhead of American cities and doing god knows what. It’s important for people to be aware.”


 FILE – In this April 30, 2001 file photo taken in Pieniezno, Poland, graffiti reading “Murderer”, “Shame” and others is seen on the memorial to Soviet General Ivan Chernyakhovsky, who is considered a symbol of the imposition of communism in Poland, but a national hero in Russia. Russian authorities are threatening serious consequences over the gradual dismantling of the monument that started on Thursday, Sept.17, 2015. (AP Photo/Wojtek Jakubowski) POLAND OUT
FILE – In this April 30, 2001 file photo taken in Pieniezno, Poland, graffiti reading “Murderer”, “Shame” and others is seen on the memorial to Soviet General Ivan Chernyakhovsky, who is considered a symbol of the imposition of communism in Poland, but a national hero in Russia. Russian authorities are threatening serious consequences over the gradual dismantling of the monument that started on Thursday, Sept.17, 2015. (AP Photo/Wojtek Jakubowski) POLAND OUT