Remember it was Qatar that was the designated headquarters for the Taliban, it was also Qatar that provided a ClubMed resort for the 5 former Gitmo detainees traded for Bowe Bergdahl.
Qatar also hosted the Muslim Brotherhood leadership until they quietly expelled but a few, but the faithfulness still remains.
So how could any businessman do business with Qatar with any conscience?
Obama Gives Qatar Undeserved A+ on Fighting Incitement
Hate Preachers on Qatar Campus: Obama Gives Qatar Undeserved A+ on Fighting Incitement
David Andrew Weinberg
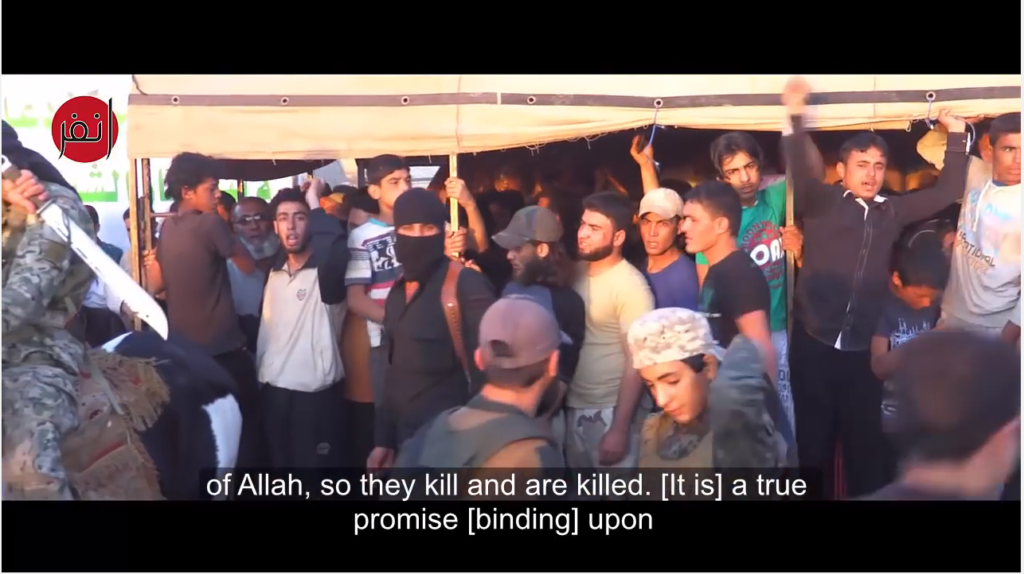
“Kill the infidels… Count them in number and do not spare one.” Blatant religious incitement of this sort feels like such a caricature of radical Islam that it borders on the implausible. Yet it is happening right under the noses of six prestigious American universities on their satellite campuses in Qatar.
Although this incitement violates a prominent pledge by Qatar’s government to the U.S. administration, President Obama gave Qatar’s Emir Tamim a free pass on the issue after they met in Riyadh on Thursday. Their one-on-one meeting was on the sidelines of a U.S.-Gulf summit, following which the President signed onto a joint communique that said America “commended” the Gulf states for their efforts to combat terrorism. Among these, it praised “actions by Gulf partners to counter ISIL’s hateful ideology and message, and more broadly to counter violent extremism.”
Yet there can be no more pivotal component to the Islamic State’s hateful ideology than its call to murder infidels. Thus, even if President Obama has chosen to give the Qatari regime an undeserved A+ report card on combating religious incitement, legislators who represent these public and private American schools must urgently speak out. Similarly, conscientious students, faculty, and other community members at these schools should spread the word and stand up in opposition to this dangerous new development on campus.
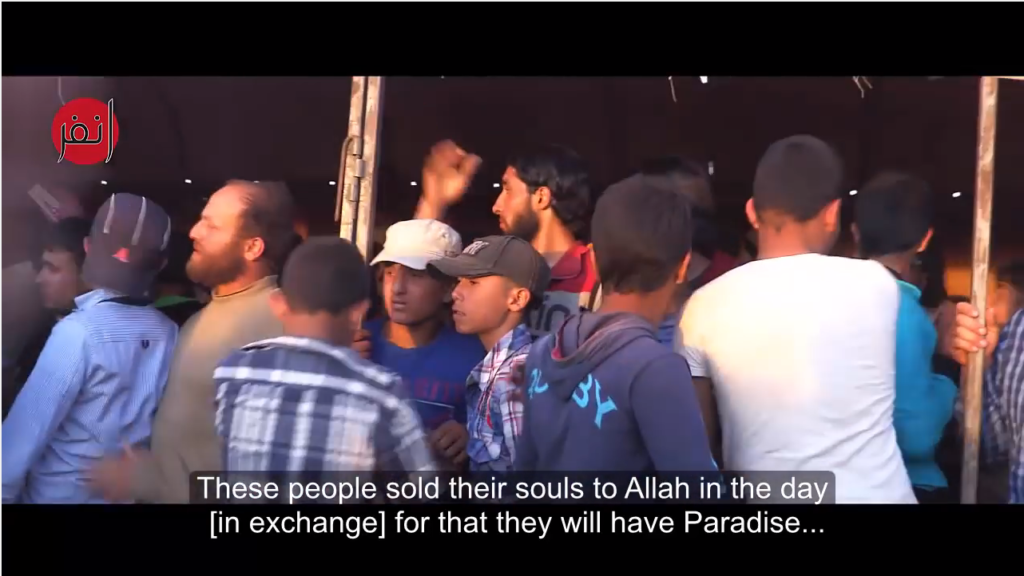
These particular hateful remarks about killing infidels were delivered on March 18th by preacher Mudassir Ahmed at the main mosque in Education City – a project of the quasi-governmental Qatar Foundation. The sprawling Education City campus, located not far from downtown Doha, is also home to satellite programs for Virginia Commonwealth, Cornell, Georgetown, Northwestern, Carnegie Mellon, and Texas A&M Universities. Since the mosque was inaugurated last year, the Foundation has promoted a slew of appearances there by speakers with records of religious incitement.
The Foundation’s newspaper regularly encourages readers to “join the QF community for prayer” at the Education City Mosque and to “avail the services of the Education City buses to and from the mosque.” The Foundation’s Housing and Residence Life office reportedly emailed students to inform them that the mosque’s Friday sermons would be translated into English “to ensure that everyone is benefiting.” As for hate preacher Mudassir Ahmed in particular, the Foundation promoted his sermon in advance on social media, posting and reposting a flier with its logo as well as that of Qatar’s Ministry of Endowments and Islamic Affairs.
That sermon, however, was not the first time incitement was uttered from the Education City Mosque. Last November, less than a week before Michelle Obama visited Doha to address a conference at the Foundation, Saudi preacher Tareq al-Hawas used its pulpit to condemn “the aggressor Zionists,” urging God to “count them in number and kill them completely; do not spare one.” And just this month, a different preacher with a record of glorifying Hamas (including specifically its military wing) called at the campus’s mosque for God to “render victorious our brothers the mujahideen… in every place” and even to “guide their shooting.”
Such language should not have come as a surprise. Ahmed had delivered similar remarks in a 2013 sermon at Qatar’s state-controlled Grand Mosque, where another preacher called just last year for Allah to “destroy” Christians, Alawites, Shi’ites and Jews. Also in 2013, Hawas reportedly lamented on air that Hitler had not “finished off” the Jews, thus “relieving humanity” of them. And in spite of Hawas’s 2015 incitement at the Education City Mosque, he was just invited back, delivering additional militaristic remarks there on March 11th, just one week before Ahmed’s outrageous appearance.
In fact, every Friday preacher at the mosque this March has had a distinguished past record of religious incitement. Omar Abdelkafi, who addressed the mosque on March 25th, is an Egyptian fundamentalist who recently declared that the Charlie Hebdo murders in Paris were “the sequel to the comedy film of 9/11,” in which Muslims “played no part.” He also seems to have instructed pious Muslims not to shake hands with Christians or even walk on the same sidewalk.
And on March 4th, the Education City Mosque hosted Mohammed al-Arefe, a prominent hardliner from Saudi Arabia with more followers on Twitter than Beyoncé. In the past, Arefe has reportedly described Shi’ite Muslims as purveyors of “treachery” and “evil,” and in 2013 as “non-believers who must be killed” according to Human Rights Watch. He has allegedly offered tips on wife-beating, called Osama bin Laden a “sheikh,” and proclaimed that “one’s devotion to jihad for the sake of Allah and one’s will to shed blood, smash skulls, and chop off body parts… constitute an honor for the believer.”
This was not the first time any of these four preachers was permitted to deliver a guest sermon at the Education City Mosque. Nor are they its only speakers with a record of hate speech. When the facility was inaugurated a year ago, the Foundation misleadingly proclaimed that it reflected a “strong commitment” to pluralism.
Yet the mosque’s guest preacher for that very event was Saudi cleric Saleh al-Moghamsy, who had previously opined on Qatari TV that bin Laden died with more dignity than any Christian, Jew, Zoroastrian, apostate, or atheist simply by virtue of being a Muslim. Moghamsy has also asserted that God created women as an “ornament“ to men. Another guest preacher at the mosque has previously declared that “the dumbest girl is that who judges her beauty with the number of those who molest her. This poor idiot girl does no [sic] know that flies fall only on stinking things.”
[“Skyline of Doha at Night”; Source: Wikipedia]Freedom of speech is a touchstone of the American academy, and freedom of religion is a fundamental American value enshrined in the Bill of Rights. But that doesn’t mean these six U.S. universities should remain silent in the face of such blatant hate speech. President Obama missed a real opportunity to make clear that Qatar’s embrace of such hate preachers violates its 2014 pledge to aid the fight against the Islamic State by “repudiating their hateful ideology.” Even the Emir himself has embraced several such hate preachers in the past year. And providing prestigious platforms to those who advocate killing infidels would seem to be a rather blatant violation of that 2014 pledge.
Further, if these six American colleges turn a blind eye to the problem, they would convey the impression that they care more about Gulf petrodollars than creating a tolerant atmosphere for female students and religious minorities, for whom such incitement could pose even a physical danger on campus. The U.S. universities with programs in Qatar reportedly receive a combined $320 million a year from the Qatar Foundation to sustain their campuses in the energy-rich city state. Cornell alone reportedly receives an astonishing yearly outlay of $122 million.
Of course, such generous, recurring payments give school administrators a powerful incentive to remain silent about the revolving door of hate preachers at the Education City Mosque. But improving the selection of these guest preachers would actually make U.S.-Qatari education programming more sustainable by removing one of the biggest potential obstacles to continued cooperation.
Regardless, these schools may have no choice in the matter. Their students and faculty have already begun to raise concerns about systematic labor abuses in Qatar, as well as potential risks to academic inquiry in a nation that throws people in jail for insulting religion or the ruler.
There are many more people of good conscience in student government, campus groups, faculty bodies, and university boards who would be shocked to learn about the appalling promotion of hate speech inside Qatar’s glittering Education City. They can and should let their voices be heard.