In its al-Naba newspaper, #\ISIS reported on the Brussels attacks: “The Islamic State Shakes Crusader Europe Again”
Third bomb ‘failed to explode’
A regional governor has said that the third bomb found in the airport, which has now been destroyed, malfunctioned.
“Three bombs were brought into the building, of which one failed to explode,” Lodewijk De Witte, the governor of Flemish Brabant province, told a press conference at the airport, adding that it was later destroyed in a controlled explosion.
*****
Belgium police are seeking the public’s help in finding Najim Laachraoui, a Syrian-trained fighter they say assisted alleged Paris attacker Salah Abdeslam. Belgium is also tracking a person designated as a key suspect in the Brussels airport attack. These two included in the manhunt may be one in the same and a name of interest is Soufiane Kayal. There’s a new suspect: Najim Laachraoui — who may have been group’s bomb-maker. His DNA was found on the explosives used in the gun and suicide attacks in Paris. His whereabouts are unknown, and prosecutors admitted they aren’t close to solving the puzzle. Yet another named suspect is believed to be known as Amine Choukri, who spent time in Syria.
Choukri also reportedly used a forged Syrian passport under the assumed name of Monir Ahmed Alaaj, in order to travel across Europe to reach Belgium.
*****
House to house searches are going on now in Brussels.
In part from Time: Molenbeek’s first deputy mayor Ahmed al-Khannouss told TIME local officials had the names of 85 residents who they believe have fought with jihadist groups in Syria and Iraq since 2012, and returned to Europe. “We need to figure out who is dangerous and who is not,” al-Khannouss said. On Monday Belgian officials named two accomplices of Abdeslam who were still on the run, plus a third who was killed in a shootout with police last Tuesday, in a separate part of Brussels.
In recent interviews with TIME, some intelligence experts said they feared that Europe could face further coordinated attacks like Paris, which killed 130 people and for which ISIS claimed responsibility. “What we expect is a multicity, multitarget attack at the same moment, and it will have terrible consequences,” Claude Moniquet, a retired agent for France’s external intelligence service DGSE, who now runs a private intelligence company in Brussels, told TIME in a recent interview.
Officials have centered their scrutiny on those who have been battle-trained abroad, and who might be under instructions to return to Europe to fight at home; several of the Paris attackers had returned from ISIS training in Syria, and had hatched the Paris plot from a rear base in Molenbeek.
But in recent days, E.U. leaders have warned that the number of people who could potentially wage terror appears larger than they previously estimated.
While police celebrated Abdeslam’s capture last Friday, their relief was tempered by the fact that a web of supporters and accomplices had apparently helped hide him for months—a group that still remains at large. “This is not over,” French President François Hollande told a press conference in Brussels on Friday night, adding that there the “wide, extensive” network of jihadists was bigger than French and Belgian investigators had believed in the immediate aftermath of the Paris attacks more than four months ago.
Belgian Foreign Minister Didier Reynders told a public panel discussion in Brussels on Monday that police had uncovered “many weapons, heavy weapons” during police raids last week that culminated in Abdeslam’s arrest. He said at least 30 jihadists remained at large in the city, and that Abdeslam had told interrogators in custody that he had been “ready to resume something in Brussels,” after apparently backing out at the last minute from his plan to blow himself up during the Paris attacks.
But despite Belgium’s maximum terror-alert level, tracking down the remnants of the jihadist network will not be easy—in part because the outlines of the network are becoming more and more blurred. Since the Charlie Hebdo attacks in Paris in January, 2015, intelligence experts have warned that jihadists have tapped into Mafia-type organized crime, with highly sophisticated smuggling operations, for logistics support like transporting people, issuing fake identity papers or selling weapons. “Where there is money to be made, there is always a business opportunity for organized crime,” says Yan St-Pierre, CEO and counter-intelligence advisor for the Modern Security Consulting Group, a private intelligence company in Berlin. “If they sell weapons to terrorists or someone else, it makes no difference, and often they are in the position to have access to smuggling,” he told TIME on Tuesday.
The mingling of two entirely separate worlds—organized crime and violent Islamic extremism—has hugely complicated the task of tracking down suspects. “This makes the situation extremely difficult for intelligence, because it is two different networks with two different logics,” Moniquet said by phone on Saturday. “And there is a clannish mentality, where if a friend comes and says ‘help me,’ you will do it without question.”
The deep budget cuts during Europe’s economic recession this decade presents another major challenge in dismantling terror networks, according to St-Pierre. He says E.U. governments are increasingly relying on high-tech surveillance methods, which are less costly than hiring people who can monitor every possible terror suspect. “Because of the cuts over the last five or six years, there are less and less people involved” in surveilling terror suspects, St-Pierre says. “They have to play catch-up, so it creates massive problems. The terrorists have adapted.”
****
The Brussels bombers are thought to have used an explosive nicknamed “Mother of Satan” that was also used in the July 7 at tacks in London in 2005.
Acetone peroxide can be made from household items like hair bleach and nail polish remover, and has been used in numerous previous terrorist bombs and suicide attacks.
Terrorists particularly like it because it does not contain nitrogen, and therefore can pass through security screening devices that rely on a nitrogenous presence to detect explosives.
The deadly substance – which forms highly unstable crystals – was also used in the suicide vests worn by the men involved in the Paris terror attacks in November.
One of the men who allegedly made the vests – named by Belgian police last week as Najim Laachraoui – is still on the run, and is regarded as a likely suspect in the Brussels bombings.

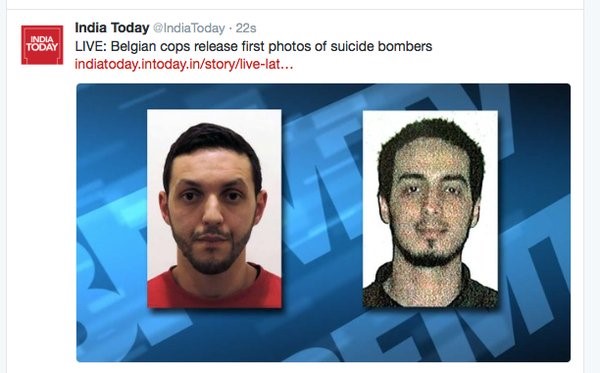
 From airport security camera.
From airport security camera.