So, all terror roads in the Middle East still lead to Tehran. At the direction of Tehran, Hezbollah, the Iranian militias and the Iranian Revolutionary Guard Corp operations is selection regions across the globe with wild abandon.
January 2018, in a question and answer session: Q: On Iran’s role in Iraq and Syria, do you believe that a land bridge exists between Iran and Syria through Iraq? And, if so, are you concerned about it? Is there anything the United States can do about it?
SEC. MATTIS: No, I don’t — I don’t think there’s a land bridge right now. There’s still enough rough times — you know, rough terrain, rough enemy units that haven’t been cleaned up, and all the usual cleanup going on, and — plus you’ve got the combination of where the people we’re fighting — advising and that sort of thing in Syria are abutting, in some cases, the Russian forces who are helping the regime, abutting the Turkish elements. There’s — I don’t think there’s a land bridge right now.
*** So, while the United States along with France and Britain delivered 105 missiles to take out three chemical weapons locations in Syria, other locations remain in addition to the Assad air assets. Russia, North Korea, and Tehran were all watching for weeks the actions of the West. Russia declares the most recent chemical weapons attack was at the hand of the White Helmets, then it was a ploy by Britain, then it was a CIA operation. Meanwhile, the chemical weapons inspection envoy arriving in Douma, the suburb of Damascus had to find cover after being fired upon.

That brings us back to domestic threats and the strategy as developed by the Trump administration in dealing with Iran and Russia, much less Iraq. Is there one other than the threat of exiting the JCPOA? Not so far it seems. The increasing threat? Satellite land bridges perhaps….from Latin America to covert cells across our homeland.
***
Iranian-backed militants are operating across the United States mostly unfettered, raising concerns in Congress and among regional experts that these “sleeper cell” agents are poised to launch a large-scale attack on the American homeland, according to testimony before lawmakers.
Iranian agents tied to the terror group Hezbollah have already been discovered in the United States plotting attacks, giving rise to fears that Tehran could order a strike inside America should tensions between the Trump administration and Islamic Republic reach a boiling point.
Intelligence officials and former White House officials confirmed to Congress on Tuesday that such an attack is not only plausible, but relatively easy for Iran to carry out at a time when the Trump administration is considering abandoning the landmark nuclear deal and reapplying sanctions on Tehran.
There is mounting evidence that Iran poses “a direct threat to the homeland,” according to Rep. Peter King (R., N.Y.), a member of the House Homeland Security Committee and chair of its subcommittee on counterterrorism and intelligence.
A chief concern is “Iranian support for Hezbollah, which is active in the Middle East, Latin America, and here in the U.S., where Hezbollah operatives have been arrested for activities conducted in our own country,” King said, referring the recent arrest of two individuals plotting terror attacks in New York City and Michigan.
“Both individuals received significant weapons training from Hezbollah,” King said. “It is clear Hezbollah has the will and capability.”
After more than a decade of receiving intelligence briefs, King said he has concluded that “Hezbollah is probably the most experienced and professional terrorist organization in the world,” even more so than ISIS and Al Qaeda.
Asked if Iran could use Hezbollah to conduct strikes on the United States, a panel of experts including intelligence officials and former White House insiders responded in the affirmative.
“They are as good or better at explosive devices than ISIS, they are better at assassinations and developing assassination cells,” said Michael Pregent, a former intelligence officer who worked to counter Iranian influence in the region. “They’re better at targeting, better at looking at things,” and they can outsource attacks to Hezbollah.
“Hezbollah is smart,” Pregent said. “They’re very good at keeping their communications secure, keeping their operational security secure, and, again, from a high profile attack perspective, they’d be good at improvised explosive devices.”
Others testifying before Congress agreed with this assessment.
“The answer is absolutely. We do face a threat,” said Emanuele Ottolenghi, a senior fellow at the Foundation for Defense of Democracies who has long tracked Iran’s militant efforts. “Their networks are present in the Untied States.”
Iran is believed to have an auxiliary fighting force or around 200,000 militants spread across the Middle East, according to Nader Uskowi, a onetime policy adviser to U.S. Central Command and current visiting fellow at the Washington Institute for Near East Policy.
At least 50 to 60 thousand of these militants are “battle tested” in Syria and elsewhere.
“It doesn’t take many of them to penetrate this country and be a major threat,” Uskowi said. “They can pose a major threat to our homeland.”
While Iran is currently more motivated to use its proxies such as Hezbollah regionally for attacks against Israel or U.S. forces, “those sleeper cells” positioned in the United States could be used to orchestrate an attack, according to Brian Katulis, a former member of the White House National Security Council under President Bill Clinton.
“The potential is there, but the movement’s center of focus is in the region,” said Katulis, a senior fellow at the Center for American Progress.
Among the most pressing threats to the U.S. homeland is Hezbollah’s deep penetration throughout Latin America, where it finances its terror activities by teaming up with drug cartels and crime syndicates.
“Iran’s proxy terror networks in Latin America are run by Tehran’s wholly owned Lebanese franchise Hezbollah,” according to Ottolenghi. “These networks are equal part crime and terror” and have the ability to provide funding and logistics to militant fighters.
“Their presence in Latin America must be viewed as a forward operating base against America’s interest in the region and the homeland itself,” he said.
These Hezbollah operatives exploit loopholes in the U.S. immigration system to enter America under the guise of legitimate business.
Operatives working for Hezbollah and Iran use the United States “as a staging ground for trade-based and real estate-based money laundering.” They “come in through the front door with a legitimate passport and a credible business cover story,” Ottolenghi said.
The matter is further complicated by Iran’s presence in Syria, where it has established not only operating bases, but also weapons factories that have fueled Hezbollah’s and Hamas’s war on Israel.
Iran’s development of advanced ballistic missile and rocket technology—which has continued virtually unimpeded since the nuclear deal was enacted—has benefitted terror groups such as Hezbollah.
“Iran is increasing Hezbollah’s capability to target Israel with more advanced and precision guided rockets and missiles,” according to Pregent. “These missiles are being developed in Syria under the protection of Syrian and Russian air defense networks.”
In Iraq, Iranian forces “have access to U.S. funds and equipment in the Iraqi Ministry of Defense and Iraq’s Ministry of Interior,” Pregent said.
The Trump administration has offered tough talk on Iran, but failed to take adequate action to dismantle its terror networks across the Middle East, as well as in Latin American and the United States itself, according to CAP’s Katulis.
“The Trump administration has talked a good game and has had strong rhetoric, but I would categorize its approach vis-à-vis Iran as one of passive appeasement,” said Katulis. “We simply have not shown up in a meaningful way.”




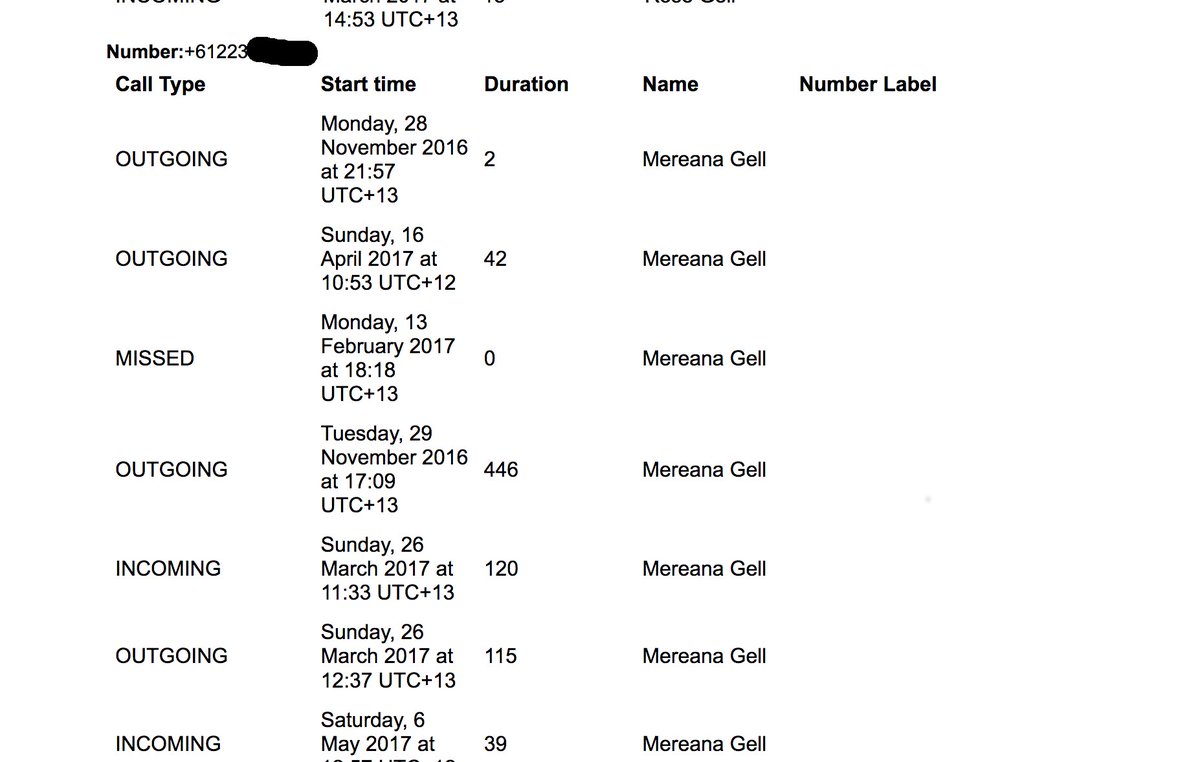
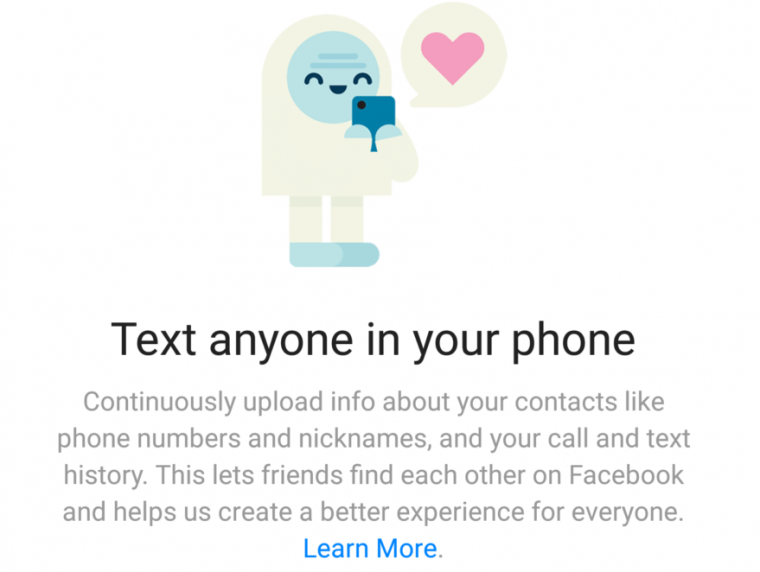 This screen in the Messenger application offers to conveniently track all your calls and messages. But Facebook was already doing this surreptitiously on some Android devices until October 2017, exploiting the way an older Android API handled permissions.
This screen in the Messenger application offers to conveniently track all your calls and messages. But Facebook was already doing this surreptitiously on some Android devices until October 2017, exploiting the way an older Android API handled permissions.