The Justice Department today announced the dismantling of three terrorist financing cyber-enabled campaigns, involving the al-Qassam Brigades, Hamas’s military wing, al-Qaeda, and Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant (ISIS). This coordinated operation is detailed in three forfeiture complaints and a criminal complaint unsealed today in the District of Columbia. These actions represent the government’s largest-ever seizure of cryptocurrency in the terrorism context.
These three terror finance campaigns all relied on sophisticated cyber-tools, including the solicitation of cryptocurrency donations from around the world. The action demonstrates how different terrorist groups have similarly adapted their terror finance activities to the cyber age. Each group used cryptocurrency and social media to garner attention and raise funds for their terror campaigns. Pursuant to judicially-authorized warrants, U.S. authorities seized millions of dollars, over 300 cryptocurrency accounts, four websites, and four Facebook pages all related to the criminal enterprise.
Funds successfully forfeited with a connection to a state sponsor of terrorism may in whole or in part be directed to the United States Victims of State Sponsored Terrorism Fund (http://www.usvsst.com/) after the conclusion of the case.
“It should not surprise anyone that our enemies use modern technology, social media platforms and cryptocurrency to facilitate their evil and violent agendas,” said Attorney General William P. Barr. “The Department of Justice will employ all available resources to protect the lives and safety of the American public from terrorist groups. We will prosecute their money laundering, terrorist financing and violent illegal activities wherever we find them. And, as announced today, we will seize the funds and the instrumentalities that provide a lifeline for their operations whenever possible. I want to thank the investigators from the Internal Revenue Service, Department of Homeland Security, Federal Bureau of Investigation, and the prosecutors from the D.C. United States Attorney’s Office and National Security Division for their hard and innovative work in attacking the networks that allow these terrorists to recruit for and fund their dangerous actions.”
“Terrorist networks have adapted to technology, conducting complex financial transactions in the digital world, including through cryptocurrencies. IRS-CI special agents in the DC cybercrimes unit work diligently to unravel these financial networks,” said Secretary of the Treasury Steven T. Mnuchin. “Today’s actions demonstrate our ongoing commitment to holding malign actors accountable for their crimes.”
“The Department of Homeland Security was born after the September 11, 2001 terrorist attacks and, nearly 20 years later, we remain steadfast in executing our critical mission to safeguard the American people, our homeland, and our values,” said Acting Secretary of Homeland Security Chad F. Wolf. “Today’s announcement detailing these enforcement actions targeting foreign terrorist organizations is yet another example of the Department’s commitment to our mission. After launching investigations that identified suspected online payments being funneled to and in support of terrorist networks, Homeland Security Investigations skillfully leveraged their cyber, financial, and trade investigative expertise to disrupt and dismantle cyber-criminal networks that sought to fund acts of terrorism against the United States and our allies. Together with our federal law enforcement partners, the Department will utilize every resource available to ensure that our Homeland is and remains secure.”
“These important cases reflect the resolve of the D.C. United States Attorney’s Office to target and dismantle these sophisticated cyber-terrorism and money laundering actors across the globe,” stated Acting United States Attorney Michael R. Sherwin. “While these individuals believe they operate anonymously in the digital space, we have the skill and resolve to find, fix and prosecute these actors under the full extent of the law.”
“IRS-CI’s ability to trace funds used by terrorist groups to their source and dismantle these radical group’s communication and financial networks directly prevents them from wreaking havoc throughout the world,” said Don Fort, Chief, IRS Criminal Investigation. “Today the world is a safer place.”
“As the primary law enforcement agency charged with defeating terrorism, the FBI will continue to combat illicit terrorist financing regardless of platform or method employed by our adversaries,” said FBI Director Christopher Wray. “As demonstrated by this recent operation, the FBI remains committed to cutting off the financial lifeblood of these organizations that seek to harm Americans at home and abroad.”
“Homeland Security Investigations continues to demonstrate their investigative expertise with these enforcement actions,” said ICE Deputy Director and Senior Official Performing the Duties of the Director Matthew T. Albence. “Together with law enforcement partners, HSI has utilized their unique authorities to bring to justice those cyber-criminal networks who would do us harm.”
Al-Qassam Brigades Campaign
The first action involves the al-Qassam Brigades and its online cryptocurrency fundraising efforts. In the beginning of 2019, the al-Qassam Brigades posted a call on its social media page for bitcoin donations to fund its campaign of terror. The al-Qassam Brigades then moved this request to its official websites, alqassam.net, alqassam.ps, and qassam.ps.
The al-Qassam Brigades boasted that bitcoin donations were untraceable and would be used for violent causes. Their websites offered video instruction on how to anonymously make donations, in part by using unique bitcoin addresses generated for each individual donor.
However, such donations were not anonymous. Working together, IRS, HSI, and FBI agents tracked and seized all 150 cryptocurrency accounts that laundered funds to and from the al-Qassam Brigades’ accounts. Simultaneously, law enforcement executed criminal search warrants relating to United States-based subjects who donated to the terrorist campaign.
With judicial authorization, law enforcement seized the infrastructure of the al-Qassam Brigades websites and subsequently covertly operated alqassam.net. During that covert operation, the website received funds from persons seeking to provide material support to the terrorist organization, however, they instead donated the funds bitcoin wallets controlled by the United States.
The United States Attorney’s Office for the District of Columbia also unsealed criminal charges for two Turkish individuals, Mehmet Akti and Hüsamettin Karataş, who acted as related money launderers while operating an unlicensed money transmitting business.
Al-Qaeda Campaign
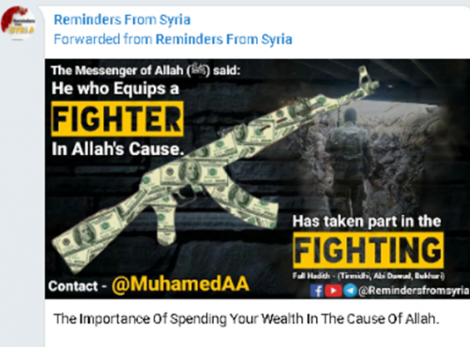
The second cyber-enabled terror finance campaign involves a scheme by al-Qaeda and affiliated terrorist groups, largely based out of Syria. As the forfeiture complaint details, these terrorist organizations operated a bitcoin money laundering network using Telegram channels and other social media platforms to solicit cryptocurrency donations to further their terrorist goals. In some instances, they purported to act as charities when, in fact, they were openly and explicitly soliciting funds for violent terrorist attacks. For example, one post from a charity sought donations to equip terrorists in Syria with weapons:
Undercover HSI agents communicated with the administrator of Reminder for Syria, a related charity that was seeking to finance terrorism via bitcoin donations. The administrator stated that he hoped for the destruction of the United States, discussed the price for funding surface-to air missles, and warned about possible criminal consequences from carrying out a jihad in the United States.
Posts from another Syrian charity similarly explicitly referenced weapons and extremist activities:
Al-Qaeda and the affiliated terrorist groups together created these posts and used complicated obfuscation techniques, uncovered by law enforcement, to layer their transactions so to conceal their actions. Today’s complaint seeks forfeiture of the 155 virtual currency assets tied to this terrorist campaign.
ISIS Campaign
The final complaint combines the Department’s initiatives of combatting COVID-19 related fraud with combatting terrorism financing. The complaint highlights a scheme by Murat Cakar, an ISIS facilitator who is responsible for managing select ISIS hacking operations, to sell fake personal protective equipment via FaceMaskCenter.com (displayed below)
The website claimed to sell FDA approved N95 respirator masks, when in fact the items were not FDA approved. Site administrators claimed to have near unlimited supplies of the masks, in spite of such items being officially-designated as scarce. The site administrators offered to sell these items to customers across the globe, including a customer in the United States who sought to purchase N95 masks and other protective equipment for hospitals, nursing homes, and fire departments.
The unsealed forfeiture complaint seized Cakar’s website as well as four related Facebook pages used to facilitate the scheme. With this third action, the United States has averted the further victimization of those seeking COVID-19 protective gear, and disrupted the continued funding of ISIS.
The claims made in these three complaints are only allegations and do not constitute a determination of liability. The burden to prove forfeitability in a civil forfeiture proceeding is upon the government. Further, charges contained in criminal complaint are merely allegations, and the defendants are presumed innocent unless and until proven guilty beyond a reasonable doubt in a court of law.
IRS-CI Cyber Crimes Unit (Washington, D.C.), HSI’s Philadelphia Office, and FBI’s Washington D.C., New York, and Los Angeles field offices are investigating the case. Assistant U.S Attorneys Jessi Camille Brooks and Zia M. Faruqui, and National Security Division Trial Attorneys Danielle Rosborough and Alexandra Hughes are litigating the case, with assistance from Paralegal Specialists Brian Rickers and Bria Cunningham, and Legal Assistant Jessica McCormick. Additional assistance has been provided by Chainalysis and Excygent.