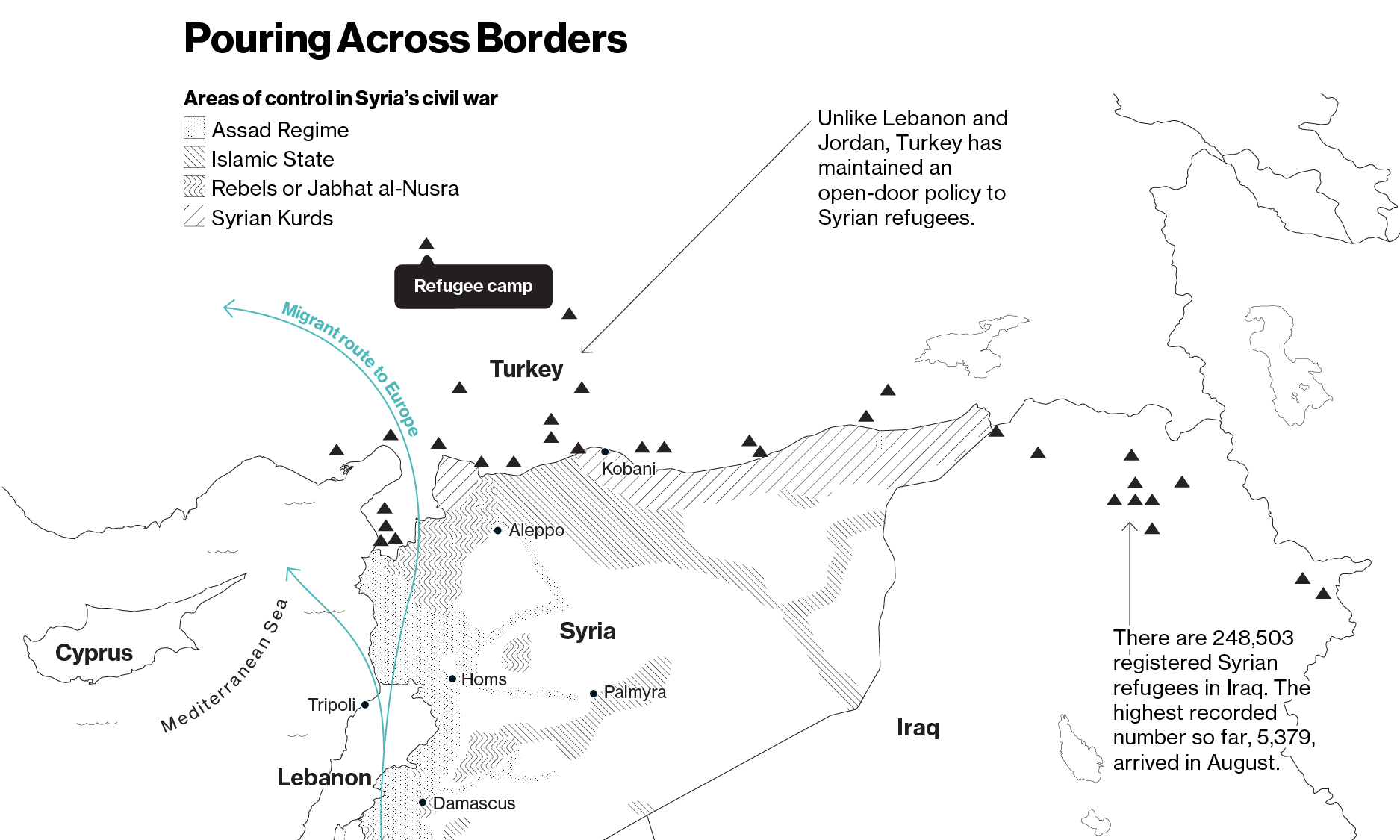
It boils down to Syria, the failed policy to control Bashir al Assad or remove him when the 5 year civil war has caused a global crisis. A country that once had a population of more than 20 million, today, an estimated 11 million Syrians are no longer in their home country. The crisis? The United Nations and member countries are out of money and resources to aid and provide humanitarian support for refugees any where they are located.
The United States as the historic world’s equalizer, failed to act in Syria for up to now 5 years….shameful as the consequences are worldwide and deaths are reported to be approaching 300,000 if not more.
The decision was made last month with no fanfare to break into the Doomsday inventory.
Arctic ‘Doomsday Vault’ opens to retrieve vital seeds for Syria
Deep in the side of a mountain in the Arctic archipelago is the Svalbard Global Seed Vault.
Known as the “Doomsday Vault,” this seed bank — operated by the Norwegian government and containing a seed of just about every known crop in the world — is meant to be humanity’s backup in the event of a catastrophe that devastates crops.
But it was not a natural disaster that has caused scientists to have to dip in and make the first significant withdrawal from the vault. Rather, it was the most preventable of man-made disasters — war.
The bloody conflict in Syria has left scientists at an important gene bank in Aleppo — where new strains of drought- and heat-resistant wheat have been developed over time — unable to continue their work in recent years.
Now, with no sign of conditions in Syria improving, scientists have begun recovering their critical inventory of seeds, sourced from around the Fertile Crescent and beyond, that have been in safekeeping beneath the Arctic ice.
The seeds are being planted at new facilities in Lebanon and Morocco, allowing scientists to resume the important research they’ve been doing for decades, away from the barrel bombs of Aleppo.
READ: Syrian war forces first ‘Doomsday Vault’ withdrawal
An important storehouse in the Fertile Crescent
The gene bank in Aleppo, run by the International Center for Agricultural Research in the Dry Areas, is one of the most important in the world and includes more than 135,000 varieties of wheat, fava bean, lentil and chickpea crops, as well as the world’s most valuable barley collection.
“These are land races that were inherited from our grand-grandparents, most of them are unfortunately extinct now,” ICARDA Director General Mahmoud El-Solh said. “And this is where the cradle of agriculture (was)10,000 years ago. In this part of the world, many of the important crops were domesticated from the wild to cultivation.”
ICARDA representative Thanos Tsivelikas, who is overseeing the withdrawal from the vault, describes the operation as “a rescue mission; these seeds cannot be replaced.”
The ICARDA Aleppo center had sent nearly 80% of the seeds and samples to the Global Seed Vault as a backup by 2012, with its last deposit being in 2014.
And now, Solh and his ICARDA team have the challenge of keeping and reproducing one of humanity’s most important collections of food crop genetic lines.
Moved to neighboring Lebanon
Relocated to Lebanon, Solh opens the door to a vault on the Agricultural Research and Educational Center of the American University of Beirut campus in the Bekaa Valley. This is where the seeds ICARDA received back from Svalbard are housed.
Solh carefully shakes out a few wisps of what looks like wheat from a brown envelope. It is the plant from which the wheat we eat today originated 10 millennia ago.
“This is a source of desirable traits including drought tolerance, including heat tolerance, including resistance to disease and so forth. So this had lived through natural selection for over hundreds of years,” he said.
A 10-minute drive away and just across the mountain range from Syria, a new vault is being built by ICARDA.
To begin replenishing the stock, there are greenhouses nearby where the seeds will be planted, grown and reproduced. Once restocked, the seeds will once again become available for researchers and other seed vaults.
A parallel project is being set up in Morocco to ensure that humanity always has access to this irreplaceable cache of genetic material.
“Two-thirds of material is coming from dry areas which … are adapted to very harsh environments and have desirable traits” for drought, heat, cold, salinity and pests, Solh said.
Researchers are looking at ways to improve food crops with existing and extinct-in-nature genetic lines that are more adapted to the challenges that may lie ahead with global warming.
The answers could very well be in these specific seeds harvested from a specific moment in time. “This variety could help us adapt to climate change,” Solh said, holding up a small fava bean.
“You know that climate change is a reality and climate change is changing the whole environment in terms of more drought, hotter environments and even new diseases.”
ICARDA and others know that the past could very well contain the key to our future, though no one thought they would see such a mass withdrawal in their lifetime.