1:35 PM, EST Update:
The names of those who had Interpol red notices lifted by the State Department, the Department of Justice and the White House:
Mohammad Abbas Mohammadi, Kurosh Taherkhani, Sajjad Farhadi, Seyed Ahmad Abtahi, Gholamreza Mahmudi, Hamid Arabnezhad, Ali Mo’attar, Mohammad Ali She’rbaaf, Amin Ravan, Behruz Dowlatzadeh, Said Jamili, Jalal Salami, Matin Sadeghi, Alireza Mo’azami-Gudarzi.
***
Today, Barack Obama issued at least 3 pardons to Iranians in U.S. prisoners for violating Iran sanctions. Likely, there are other prisoners that will be part of a future swap in coming days.
Switzerland facilitated Iran-U.S. prisoner swap, Iran’s UN ambassador tells state TV.
Confirmed: Hamid Arabnejad, CEO of Mahan, which delivers weapons to Assad daily, to be taken off Interpol list as part of swap.
America does not do prisoner swaps, at least until Barack Obama, where it has become and epidemic. Further, we still don’t know the status of former DEA/FBI operative Robert Levinson who was last heard from in 2011 and was kidnapped on Kish Island, as the Iranians continue to say they never heard of him.
The State Department has dropped Interpol ‘red notices’ on several others, those names have not been formally announced but several included those involved in the AIMA bombing in Buenos Aries, Argentina.
August, 2015: BUENOS AIRES, Argentina (JTA) — An international arrest warrant for Iran’s former defense minister in the AMIA Jewish center bombing will not be lifted under the Iran nuclear deal, U.S. officials said.
Ahmad Vahidi is still being sought in connection with the deadly 1994 bombing of the Buenos Aires center and nothing will change under the agreement between Iran and the world powers reached last month, according to the State Department.
“Nothing in the recently concluded Joint Comprehensive Plan Of Action, or JCPOA, on Iran’s nuclear program has an impact on or removes the Red Notice for General Vahidi issued by Interpol, in relation to the 1994 bombing in Argentina,” the State Department said in a statement Friday, two days after Argentine Foreign Minister Hector Timerman asked Secretary of State John Kerry about Vahidi’s status in a letter. “And we continue to urge the international community and Argentine authorities to do whatever is necessary to hold the AMIA bombers accountable for that atrocity.
Along with Vahidi, Iran’s Revolutionary Guards Corps and its officials remain sanctioned in the United States because they were listed for reasons outside the scope of the agreement, the statement said.
Timerman’s letter also was sent to European Union foreign affairs chief Federica Mogherini.
The Wall Street Journal reported last week that “the E.U.’s planned delisting of Tehran’s former minister of defense, retired Brig. Gen. Ahmad Vahidi, is among a group of Iranian military officers, nuclear scientists and defense institutions set to be rehabilitated internationally in the wake of the nuclear accord.”
The State Department added in its response that “our secondary sanctions will also stay in force, which means that foreign banks and companies could be exposed to sanctions if they engage in transactions with these listed individuals.”
Since Vahidi is not listed under any nuclear-related activities, the State Department said, he will remain on the Interpol list for eight more years.
Timerman, who is Jewish, in February asked Kerry to include the AMIA attack in the negotiations with Iran, but the attack was not part of the talks.
March of 2015:
Interpol won’t lift warrants for 6 Iranians in AMIA bombing
Arrest orders to remain active despite Tehran’s participation in probe of 1994 terror attack
The above position of not lifting the red notices has been declared null and void by Barack Obama as of January 16, 2016 in the larger mission of additional prisoner swaps.
VIENNA (AP) — The latest developments as Iran and world powers prepare to implement a landmark deal reached last year to curb Iran’s nuclear activities in exchange for the lifting of international sanctions (all times local).
5:30 p.m.
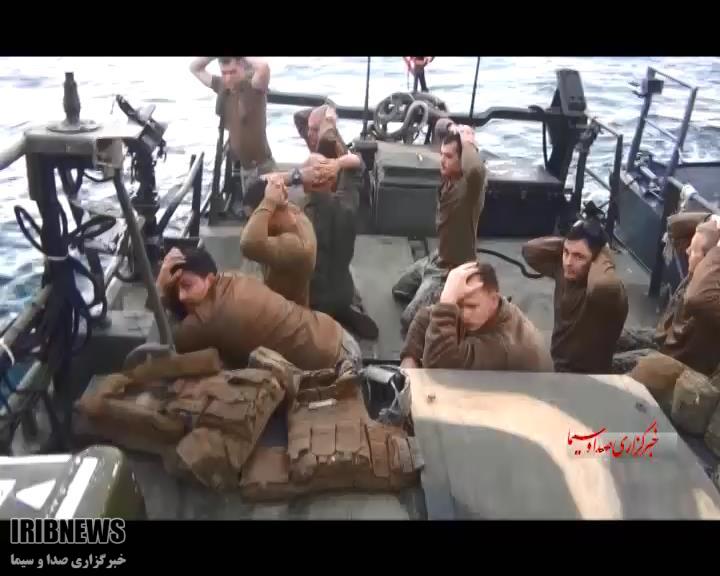
U.S. and Iranian officials say Iran is releasing four detained Iranian-Americans in exchange for seven Iranians held or charged in the United States.
The major diplomatic breakthrough was announced Saturday as the implementation of a landmark nuclear deal appeared imminent.
U.S. officials say the four Americans, including Washington Post reporter Jason Rezaian, former Marine Amir Hekmati and pastor Saeed Abidini, were to be flown from Iran to Switzerland on a Swiss plane and then brought to a U.S. military base in Landstuhl, Germany, for medical treatment.
In return, the U.S. will either pardon or drop charges against seven Iranians — six of whom are dual citizens — accused or convicted of violating U.S. sanctions. The U.S. will also drop Interpol “red notices” — essentially arrest warrants — on a handful of Iranian fugitives it has sought.
___
5:10 p.m.
There are conflicting reports about the identities of the four prisoners released by Iran.
Iranian state TV on Saturday announced that four prisoners holding dual Iranian-American citizenship were released, without elaborating. The announcement fueled speculation that Jason Rezaian, the jailed Washington Post bureau chief, was among them.
An official close to Iran’s judiciary told The Associated Press that the prisoners included Rezaian, former U.S. Marine Amir Hekmati and pastor Saeed Abedini. The official spoke on condition of anonymity because he was not authorized to speak to the media.
It was unclear who the fourth person was. Iranian state TV later reported it was Siamak Namazi, the son of a politician from the era of the shah, while the official IRNA news agency said it was Nosratollah Khosravi. The accounts could not be reconciled immediately.
— Ali Akbar Dareini in Tehran, Iran
4 p.m
A source close to Iran’s judiciary is telling The Associated Press that four Iranian-Americans have been freed from prison in Iran: Washington Post bureau chief Jason Rezaian as well as Amir Hekmati, Saeed Abedini and Siamak Namazi.
The source, who spoke on condition of anonymity because he was not authorized to speak to the media, said the four were freed Saturday in exchange for the release of seven Iranians held in U.S. prisons. He didn’t name the Iranians but said the seven have already arrived in Tehran.
He says “authorities at the top had agreed to free the four Iranian-Americans only after the Iranian prisoners land in Tehran.”
— Ali Akbar Dareini in Tehran
3:45 p.m.
A source close to Iran’s judiciary is confirming to The Associated Press that jailed Washington Post bureau chief Jason Rezaian is one of four dual-national prisoners freed today by Iran’s government.
Iranian state television announced the release of the four prisoners on Saturday but gave no names.
The source spoke on condition of anonymity since he was not authorized to publicly speak to the media.
— Ali Akbar Dareini in Tehran
3:30 p.m.
Iranian state television says the government has freed four dual-nationality prisoners.
The report Saturday did not identify the prisoners but it comes amid speculation that jailed Washington Post bureau chief Jason Rezaian, a dual Iran-U.S. citizen convicted of espionage in a closed-door trial in 2015, could be among them.
The report by the semi-official ISNA news agency quotes a statement from the Tehran prosecutor’s office as saying the inmates were freed “within the framework of exchanging prisoners,” without elaborating.
The U.S. would not immediately confirm the Iranian report. But the family of one of the U.S prisoners received unofficial word from Iran that their relative was being released today, according to a person close to that family.
___
11:20 a.m.
The EU’s top diplomat has met with Iran’s foreign minister for talks on implementing the nuclear deal between Tehran and six world powers, as the U.N. atomic agency works on a report certifying that Iran has met its commitments under the accord.
U.S. Secretary of State John Kerry will join Federica Mogherini of the European Union and Iranian Foreign Minister Mohammad Javad Zarif in Vienna, the headquarters of the U.N’s International Atomic Energy Agency, later Saturday.
IAEA certification that Iran is honoring its obligations would trigger sanctions relief for Iran worth an estimated $100 billion.
Under the July 14 deal between Iran and six world powers, Tehran Iran agreed to crimp programs it could use to make nuclear weapons in return for an end to international nuclear-related sanctions
Iran says it has no interest in such arms.
___
11:15 a.m.
Iranian hard-liners are accusing moderate President Hassan Rouhani of “burying” the country’s nuclear program as Tehran and world powers are on the verge of implementing a historic nuclear accord.
Under the front-page headline “Nuclear Burial,” Hard-line daily Vatan-e-Emrooz on Saturday criticized the removal of the core of Iran’s only heavy water reactor, which was filled in with cement earlier this week as one of the final steps under the agreement.
The Javan daily says filling in the reactor is “hurting national pride.”
It says the Iranian people hope that the “bitterness of filling the Arak reactor with cement will be accompanied with the sweetness of filling their table,” referring to the lifting of crippling international sanctions.
Iran’s Foreign Minister Mohammad Javad Zarif earlier said that the imminent release of a U.N. compliance report would trigger “Implementation Day,” with Iran receiving billions in sanctions relief in return for limiting its nuclear activities.
___
10:40 a.m.
Iran’s foreign minister says an imminent compliance report by the U.N. nuclear agency will trigger the implementation of the historic nuclear accord reached with world powers last year, bringing a “good day” for Iran.
Mohammad Javad Zarif says the report will mark “Implementation Day,” when world powers provide Iran with billions of dollars in sanctions relief in exchange for it curbing its nuclear program.
Speaking in Vienna on Saturday, where he was to meet with U.S. Secretary of State John Kerry and top EU diplomat Federica Mogherini, Zarif called for greater cooperation to fight the “terrorism and extremism” that has engulfed the Middle East. His comments were broadcast on state TV.
******
WaPo: The full story of Jason Rezaian: On July 22, 2014, Iranian authorities crashed into the Tehran home of Washington Post Iran correspondent Jason Rezaian and arrested him and his wife, Yeganeh Salehi, also a journalist. Rezaian was taken to Iran’s infamous Evin Prison, where he was put in solitary confinement for months, without a word of explanation to his family or to the outside world. Salehi, an Iranian citizen, was released on bail last fall.
Iran has said it will release Post correspondent Jason Rezaian, according to Iranian media.
Along with Rezaian, three other detained Americans are being released in a swap for seven people imprisoned or charged by the United States.
Rezaian’s incarceration was the longest, by far, for a Western journalist in Iran since the 1979 revolution that brought Ayatollah Ruhollah Khomeini to power.
Throughout his captivity, the 39-year-old California native has been subjected to grueling interrogations and repeated deprivations, forced to stay for weeks in a bare cell without a mattress or even a toilet, family members said after they were allowed to speak with him.
Rezaian has been periodically deprived of medicine for his high blood pressure, family members said, and his physical condition has deteriorated, with dramatic weight loss, back pain and chronic eye and groin infections.
Top U.S. officials, including President Obama and Secretary of State John F. Kerry, have repeatedly demanded Rezaian’s release, echoing similar calls by other Western governments, human rights groups and Washington Post leadership, which has asserted the correspondent’s innocence.
July 25, 2014 : Iran confirms that Rezaian has been detained.
July 29, 2014: Wendy Sherman, undersecretary of state for political affairs, tells the Senate Foreign Relations Committee that the United States formally called for the immediate release of Rezaian, his wife and two other U.S. citizens detained the same night.
Aug. 6, 2014 : Iran’s deputy foreign minister, Hassan Ghashghavi, says the detention is “an internal matter” and says the country does not acknowledge Rezaian’s U.S. citizenship.
Aug. 20, 2014:A photojournalist who worked with Rezaian and Salehi and also was detained is released on bail.
Sept. 17, 2014: In an interview with NPR, Iranian Foreign Minister Mohammad Javad Zarif says Rezaian is “facing interrogation in Iran for what he has done as an Iranian citizen” but declines to name any crime. He says Iran’s judiciary “has no obligation to explain to the United States why it is detaining one of [Iran’s own] citizens.”
Douglas Jehl, The Post’s foreign editor, responds in a statement that Rezaian and his wife are “fully accredited journalists, and we remain mystified by their detention and deeply concerned about their welfare.”
Ali Rezaian, Jason’s older brother, says in a statement: “Neither I nor my mother have been permitted any communication with Jason. We remain concerned about their health and implore the Iranian authorities to release them in compliance with Iran’s existing laws and constitution.”
Oct. 5, 2014: Ali Rezaian says Salehi was released on bail during the previous week and was permitted one visit with her husband.
Dec. 6, 2014: After nearly five months of detention, Rezaian is charged after a 10-hour court proceeding that is closed to the public. He is denied legal representation and is accompanied by a government-appointed Farsi translator. He is denied bail.
Dec. 11, 2014: Mary Rezaian appears on video and pleads for her son’s release.
Jason Rezaian’s wife, Yeganeh Salehi, and his mother, Mary Rezaian, in Tehran on July 13 after the Washington Post correspondent’s third hearing at the Revolutionary Court. They were not allowed to attend the closed-door session, and Jason Rezaian’s attorney was barred from publicly discussing the proceedings. (Vahid Salemi/AP)Jan. 14, 2015: Jason Rezaian’s case is transferred to a branch of the Revolutionary Court, which is closely aligned with Iranian intelligence services.
Feb. 1, 2015:Judge Abolghassem Salavati is picked to preside over the trial, according to the International Campaign for Human Rights in Iran. He is one of six judges who are leading a crackdown on journalists and political activists in Iran, according to human rights groups. He formally charges Rezaian, then prohibits his chosen attorney from representing him.
Feb. 8, 2015: At a Munich Security Conference session, Washington Post columnist David Ignatius asks Zarif, the Iranian foreign minister, about Rezaian. “I hope that he will be cleared of the charges in a court of law,” Zarif answers, “and that will be a good day for me.”
Much more to his story is found here.