That’s it? On second thought, keep him employed to cough up the goods on Project Cassandra. More on that below. As an aside, in late December, Jeff Sessions ordered a complete review of Project Cassandra.
FNC: A Justice Department official demoted late last year for concealing his meetings with the men behind the anti-Trump “dossier” has been stripped of yet another title, Fox News has learned.
Bruce Ohr is no longer head of the Organized Crime Drug Enforcement Task Force.
Separately, sources familiar with the discussions tell Fox News that the Justice Department is expected to comply with demands from the House Intelligence Committee to provide Ohr for an interview. He is scheduled to visit the committee on Jan. 17, sources said.
Fox News first reported in December that Ohr had been demoted from the position of associate deputy attorney general, after it was revealed he had conducted undisclosed meetings with dossier author Christopher Steele and Glenn Simpson of Fusion GPS, the opposition research firm that produced the salacious document.
Fox News also reported that his wife Nellie Ohr worked for Fusion GPS, specifically on research related to the dossier.
At the time of his demotion, DOJ officials told Fox News that Bruce Ohr had been “wearing two hats,” and would fall back to his other title and portfolio – as head of OCDETF.
Now, Ohr has been stripped of that role as well; former deputy director Thomas Padden is now acting director. It is unclear where Ohr has landed, only that he is still an employee with the Department of Justice.
One DOJ insider joked that Ohr might end up in “one of those offices without a phone.”
Fox News has also confirmed that Bruce Ohr, as the head of OCDETF, was directly involved with Project Cassandra, the interagency investigation spearheaded by the DEA that tracked a massive international drug and money laundering scheme allegedly run by Hezbollah.
The project recently was the subject of a critical and lengthy Politico report looking at how the Obama administration may have hampered the investigation. Those closest to Project Cassandra, including Derek Maltz, the now-retired supervisory DEA agent who was a major player in the operation, claim the project and its potential prosecutions were sidelined by senior Obama administration officials who didn’t want to upset Iran in the lead-up to the historic nuclear deal with Tehran in 2015.
Attorney General Jeff Sessions has promised to look into what happened with the investigation.
He said in a statement last month: “While I am hopeful that there were no barriers constructed by the last admission to allowing DEA agents to fully bring all appropriate cases under Project Cassandra, this is a significant issue for the protection of Americans. We will review these matters and give full support to investigations of violent drug trafficking organizations.”
Sources close to the attorney general told Fox News that he was recently made aware of Ohr’s role in Project Cassandra and that Sessions is personally involved in the review and frequently asks for updates.
 photo
photo
The 76 page criminal complaint for Project Cassandra is here.
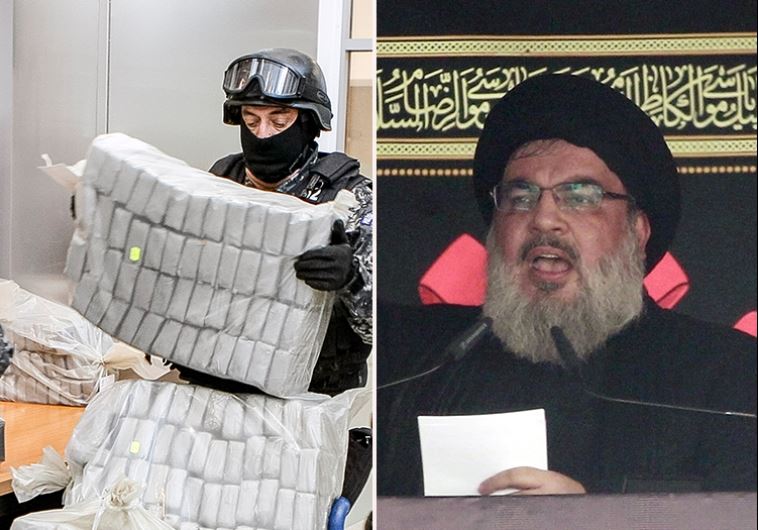
Hezbollah Business Affairs Component 85 tons of cocaine was sold to Los Zetas one of the most violent Mexican cartels. Bruce Ohr was head of the teams assigned to Project Cassandra.
The United States Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA) (2016) announced significant enforcement activity including arrests targeting Lebanese Hizballah’s External Security Organization Business Affairs Component (BAC), which is involved in international criminal activities such as drug trafficking and drug proceed money laundering. These proceeds are used to purchase weapons for Hizballah for its activities in Syria. This ongoing investigation spans the globe and involves numerous international law enforcement agencies in seven countries, and once again highlights the dangerous global nexus between drug trafficking and terrorism.
This effort is part of DEA’s Project Cassandra, which targets a global Hizballah network responsible for the movement of large quantities of cocaine in the United States and Europe. This global network, referred to by law enforcement as the Lebanese Hizballah External Security Organization Business Affairs Component (BAC), was founded by deceased Hizballah Senior Leader Imad Mughniyah and currently operates under the control of Abdallah Safieddine and recent U.S.-designated Specially Designated Global Terrorist (SDGT) Adham Tabaja. Members of the Hizballah BAC have established business relationships with South American drug cartels, such as La Oficina de Envigado, responsible for supplying large quantities of cocaine to the European and United States drug markets. Further, the Hizballah BAC continues to launder significant drug proceeds as part of a trade based money laundering scheme known as the Black Market Peso Exchange.
“These drug trafficking and money laundering schemes utilized by the Business Affairs Component provide a revenue and weapons stream for an international terrorist organization responsible for devastating terror attacks around the world,” said DEA Acting Deputy Administrator Jack Riley. “DEA and our international partners are relentless in our commitment to disrupt any attempt by terrorists and terrorist organizations to leverage the drug trade against our nations. DEA and our partners will continue to dismantle networks who exploit the nexus between drugs and terror using all available law enforcement mechanisms.”
Beginning in February 2015, based on DEA investigative leads, European authorities initiated an operation targeting the network’s criminal activities in that region. Since then, law enforcement authorities, closely supported by DEA, have uncovered an intricate network of money couriers who collect and transport millions of euros in drug proceeds from Europe to the Middle East. The currency is then paid in Colombia to drug traffickers using the Hawala disbursement system. A large portion of the drug proceeds was found to transit through Lebanon, and a significant percentage of these proceeds are benefitting terrorist organizations, namely Hizballah.
This investigation is a result of leads developed during the investigation into the Lebanese Canadian Bank.
The combination of aggressive international law enforcement investigations and Treasury’s ongoing sanctions (see below) pressure shows the scope of the global commitment to diminish the ability of Hizballah and its financial supporters to move funds worldwide.
Enforcement Action
With DEA and Customs and Border Protection (CBP) working closely with foreign counterparts in France, Germany, Italy and Belgium, authorities arrested top leaders of the European cell of this Lebanese Hizballah External Security Organization BAC last week. The most significant arrest was of the U.S.-designated SDGT Mohamad Noureddine, a Lebanese money launderer who has worked directly with Hizballah’s financial apparatus to transfer Hizballah funds via his Lebanon-based company Trade Point International S.A.R.L. and maintained direct ties to Hizballah commercial and terrorist elements in both Lebanon and Iraq.
The CPB National Targeting Center partnered with DEA and international counterparts such as Europol in this investigation. CBP’s continued cooperation with the DEA , and European law enforcement counterparts is a vital component in dismantling complex global drug trafficking and money laundering networks as well as enhancing the security of the United States border.
U.S. Treasury Sanctions
Separately, the U.S. Department of the Treasury announced sanctions last week targeted Hizballah’s financial support network by designating Hizballah-affiliated money launderers Noureddine and Hamdi Zaher El Dine, as well as Trade Point International S.A.R.L, a company owned or controlled by Noureddine, pursuant to Executive Order 13224. This order targets terrorists and those providing support to terrorists or acts of terrorism. Noureddine and El Dine were designated for providing financial services to or in support of Hizballah, a Specially Designated Global Terrorist. Trade Point International S.A.R.L. was designated for being owned or controlled by Noureddine. As a result of Treasury’s action, all assets of the designated individuals or entities that are located in the United States or in the possession or control of U.S. persons are frozen, and U.S. persons are generally prohibited from engaging in transactions with them.
As part of its designation, Adam J. Szubin, Acting Under Secretary for Terrorism and Financial Intelligence, stated that, “Hizballah needs individuals like Mohamad Noureddine and Hamdi Zaher El Dine to launder criminal proceeds for use in terrorism and political destabilization. We will continue to target this vulnerability, and expose and disrupt such enablers of terrorism wherever we find them.”
Participating offices and agencies:
DEA Philadelphia, DEA Miami, DEA Newark, DEA New York, DEA Special Operations Division, DEA Bilateral Investigative Unit, DEA country offices in Europe, as well as Bogota and Cartagena
U.S. Customs and Border Protection
U.S. Treasury Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN)
U.S. Treasury Office of Foreign Assets Control (OFAC)
EUROPOL
EUROJUST