The special forces backed by attack helicopters fought their way into the town of Bartella, where IS militants unleashed at least nine suicide truck bombs. Lt. Gen. Talib Shaghati said the special forces retook Bartella, about 15 kilometers (nine miles) from the edge of Mosul. But Iraqi forces were facing stiff resistance inside the town shortly before he spoke.
The U.S. trained special forces are Iraq’s most highly trained and least sectarian fighters, and will lead the charge into Mosul.
Kurdish peshmerga forces also announced a “large-scale operation,” and peshmerga forces stationed on mountains northeast of Mosul descended from their positions and charged toward the front line. Military operations also appeared to be underway in the town of Bashiqa, northeast of Mosul, which was pounded by airstrikes and peshmerga mortars the day before. More here.
****
Stripes: WASHINGTON— A U.S. servicemember died Thursday after being wounded by an improvised explosive device in northern Iraq, according to a statement by the military’s Combined Joint Task Force Inherent Resolve.
A U.S. Army M109A6 Paladin conducts a fire mission at Qayyarah West, Iraq, in support of the Iraqi security forces’ push toward Mosul, Oct. 17, 2016. Christopher Brecht/U.S. Army
The command did not identify the servicemember or immediately provide any additional information about the death, which coincides with a joint U.S. operation to retake the city of Mosul from the Islamic State group. As many as 200 special operators were embedded with Iraqi and Kurdish units this week moving to the front lines of the battle, the Pentagon has said.
A total of about 4,800 troops are in Iraq assisting in the mission to liberate Mosul and its roughly 1 million inhabitants. The death announcement comes a day after two Americans – one a U.S. servicemember – were killed in Afghanistan in an apparent insider attack.
Earlier this week, the Pentagon said the embedded U.S. forces in northern Iraq were advancing to the last secure areas on the outskirts of Mosul as Iraqi and Kurdish forces wage a long-awaited offensive that could continue for weeks or months.
Iraq has about 18,000 troops moving on the city and the Kurdish peshmerga forces number about 10,000, according to Pentagon estimates.
Many U.S. troops were providing air support including nighttime raids by Apache helicopters, artillery bombardment, intelligence and forward air controllers who relay target information from Iraqi forces, according to the joint task force.
A Pentagon spokesman said troops were all operating behind the front lines of the conflict, which is the biggest offensive against the Islamic State group since it was defeated and pushed from Ramadi in western Iraq in December. The extremist group seized Mosul, which was Iraq’s second largest city, after a lightning assault from Syria in 2014.
Meanwhile, the Pentagon was looking into what could have been the first insider attack this year in Afghanistan.
On Wednesday, an assailant reportedly dressed in an Afghan National Army uniform killed an unidentified U.S. servicemember and an American civilian who were working on a NATO mission to train local forces at Camp Morehead in Kabul. Another servicemember and two civilians were also injured.
The assailant was killed during the attack.
Back to Baghdad and who is leading the fight to liberate Mosul:
Baghdad’s Finest: A look at Iraq’s vaunted special forces
WT/BAGHDAD (AP) – Iraq’s special forces, which barreled into a town east of Mosul on Thursday despite a wave of suicide attacks, are the country’s most professional and least sectarian fighting force.
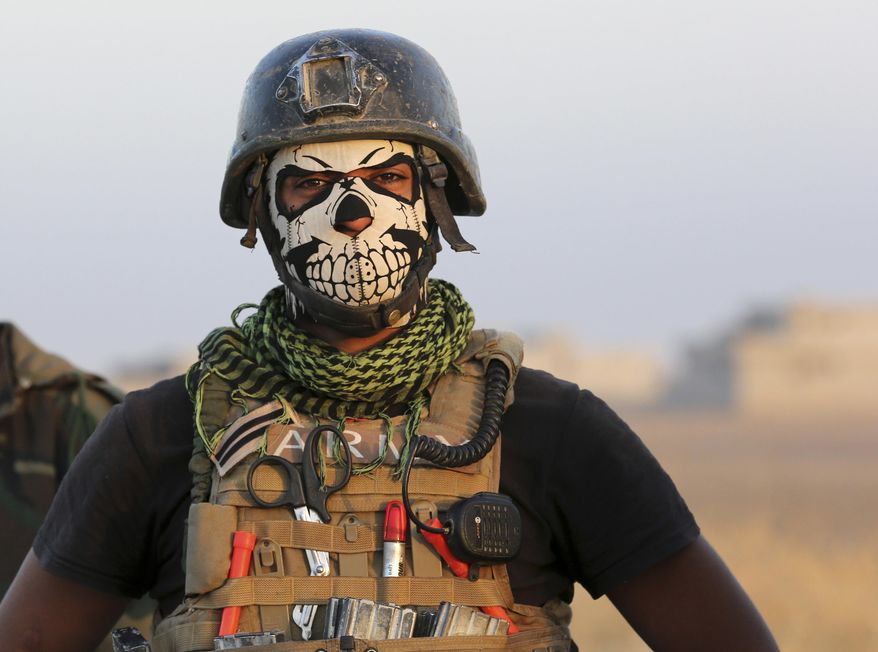
A member of Iraq’s elite counterterrorism forces pauses as they advance towards the city of Mosul, Iraq, Thursday, Oct. 20, 2016. Iraq’s special forces, which barreled into a town east of Mosul on Thursday despite a wave of suicide attacks, are the country’s most professional and least sectarian fighting force. Officially known as the Counter Terrorism Service, the troops have played a key role in wresting back towns and cities from IS, and are expected to lead the charge in Mosul. (AP Photo/Khalid Mohammed)
Officially known as the Counter Terrorism Service, the U.S. trained troops have played a key role in wresting back towns and cities from IS, and are expected to lead the charge in Mosul, their toughest battle yet.
Here is a look at Iraq’s special forces:
MADE IN AMERICA
The CTS was established by the American military shortly after the 2003 invasion as an elite commando unit charged with hunting down top insurgents and carrying out complex raids. They were trained, armed and supplied by U.S. Special Forces, who fought alongside them at the height of the insurgency.
The force proved to be a more reliable partner to the Americans than the mainstream security forces, where corruption was rife and many units were tied to parties or militias. But many Iraqis saw the special forces as the shock troops of an occupying power, and took to referring to them as the “Dirty Division.”
A PRAETORIAN GUARD?
The force grew in size over the years and expanded beyond its commando roots, with some taking part in conventional battles and even mundane tasks like manning checkpoints. Today they number around 12,000 men, including administrators, and up to 2,600 are taking part in the Mosul operation.
The unit was never incorporated into the Defense Ministry and answers directly to the prime minister. In the latter years of Prime Minister Nouri al-Maliki’s rule, many feared the special forces had become a praetorian guard that would cement his grip on power, but those fears were laid to rest when al-Maliki peacefully stepped down in 2014.
FROM “DIRTY” TO “GOLDEN”
When the Islamic State group swept across northern and central Iraq in 2014, Iraq’s security forces crumbled. Officers fled and their soldiers beat a humiliating retreat, many stripping off their uniforms and leaving their weapons and Humvees behind.
But not the special forces, who held their ground and became a source of national pride.
The CTS “retained its organizational cohesion and structure in 2014 when many other units of the Iraqi army fell apart,” said David M. Witty, a retired U.S. Army Special Forces colonel and former adviser to the CTS. “The key leaders of CTS have become central figures in the Iraqi public’s perception of the campaign to destroy IS.”
“Dirty” no more, the 1st Brigade is now widely known as the “Golden Division.”
A NON-SECTARIAN FORCE
The CTS was designed to be a non-sectarian force, with Shiite, Sunni and Kurdish members who were strictly vetted to ensure they had no ties to political factions or militias. In the early years, the force mainly battled Sunni insurgents, but it also played a lead role in a 2008 offensive against Shiite militias. Maj. Gen. Fadhil al-Barwari, who leads the Golden Brigade, is a Kurd.
The force also has a better human rights record than most of the other participants in the Mosul Offensive. An Amnesty International report released this week documenting abuses in Anbar mainly focused on state-sanctioned Shiite militias, and included only passing mention of the CTS.
LEADING THE CHARGE INTO MOSUL
The special forces launched their first assault in the Mosul operation early Thursday, pushing into the town of Bartella with the aid of attack helicopters despite stiff resistance from IS, which unleashed nine suicide truck bombs, one of which struck an armored Humvee. The rest were destroyed before hitting their targets.
“We will lead the charge into Mosul as we are specialized in the battles in urban areas and guerrilla war,” said special forces Brig. Gen. Haider Fadhil. “We are trained to break into towns and cities with fewer casualties.”
The special forces are expected to help drive IS out of Mosul in the coming weeks or months. But they can’t police the country, and will eventually have to hand things off to Iraq’s army and police, as well as Shiite militias and Sunni tribal fighters. It will be left to them to ensure that IS, which has recovered from past defeats, does not return.
___
Associated Press writer Qassim Abdul-Zahra in Bartella, Iraq contributed to this report.



 1930
1930