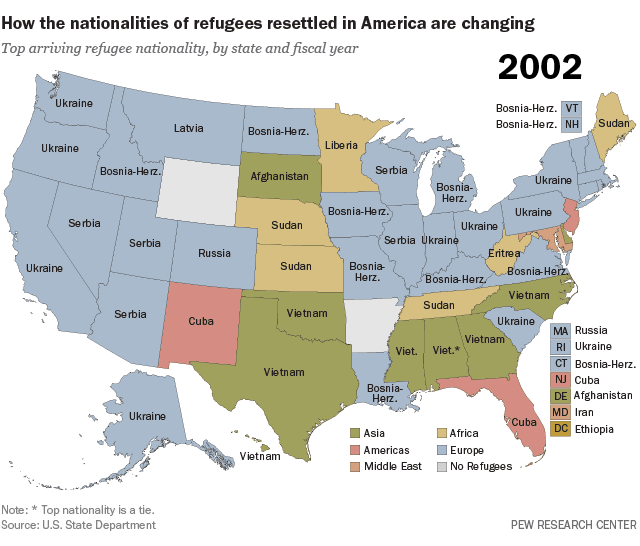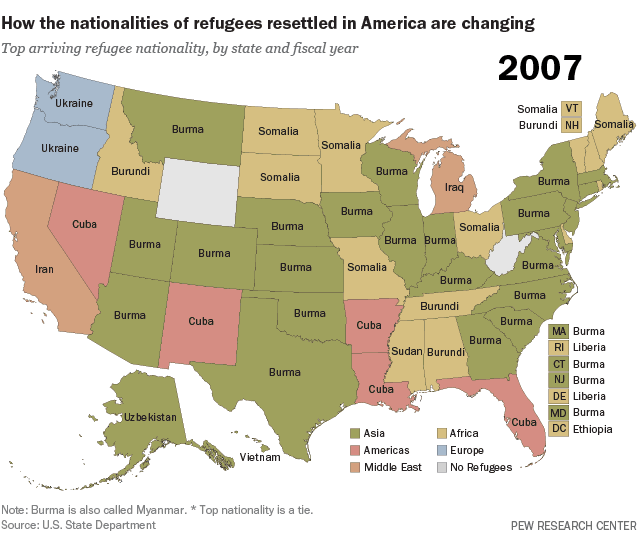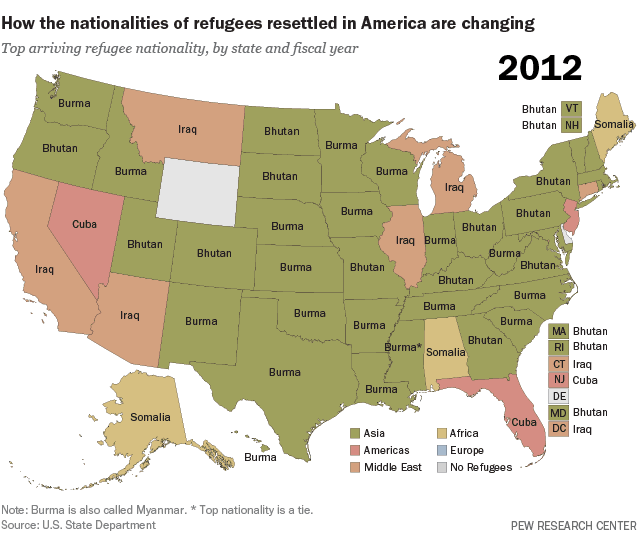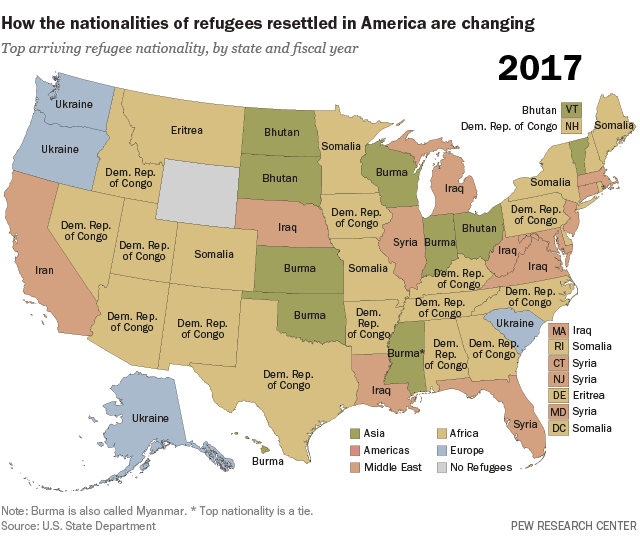
Col. Hiftar hires a DC lobby firm….why? To get money from the U.S. and Russia at the same time perhaps?
Khaled Khalifa Hiftar is restoring Libya to what end and before Russia fully steps in?What about the migrant crisis?
After Hiftar gained political and military legitimacy, Hifter concentrated on fighting Islamists in Benghazi, though with little initial success. His most sworn enemy was Ansar al-Sharia, the dominant terror group in Benghazi at the time, which the United States had already declared a terrorist organization after it was accused of killing the US ambassador in 2012.
Hifter relied heavily on his tribal connections in eastern Libya and capitalized on the bad security situation in Benghazi. By May 2015, he believed he had enough force to declare war on terror throughout Libya, not just Benghazi, where hundreds of former security officials, army officers and civil and political activists had been assassinated. In a way he was defending himself since he knew that he could be next on the death list.
His offensive in Benghazi stalled for a while since the army fragments he managed to reorganize were few in numbers and lacked training and equipment. Above all, many former professional officers did not join him because neither his motives nor his objectives were clear. More here.
For months, the Kremlin has sought to draw Libya’s eastern potentate General Khalifa Hiftar into its orbit. Hiftar is currently the de facto leader of a bloc of eastern Libyan forces that oppose Libya’s internationally recognized government in Tripoli, the so called Government of National Accord. Negotiations between the two sides are going nowhere and rumors of a potential Hiftar offensive against the Tripoli government have been swirling for months.
Hiftar has been to Moscow and paid a visit to the Russian aircraft carrier Kuznetsov in the Mediterranean, during which he held a video call with Russian Defense Minister Defense Minister Sergei Shoigu. Then, last week, Moscow reportedly deployed troops to a base on Egypt’s northern coast just 60 miles from the border crossing with Libya.
There are a few ways to interpret their latest move: It could just be posturing, part of a Russian hybrid warfare strategy aimed at influencing ongoing negotiations over Libya’s future. But there are plenty of reasons to believe it may be the early phase of a Russian intervention.
Russian President Vladimir Putin is eager to underscore the challenges that U.S. pro-democracy interventions in the Middle East have faced and offer up an alternative Russian strategy that relies on authoritarian leaders that look a lot like Putin himself. The 2011 NATO intervention in Libya has long been a target of Kremlin criticism and the chance to portray Russia as Libya’s savior as Russia has attempted to do in Syria must be more than a little tempting for the Russian president.
Closer ties to Libya would also offer Russia the chance to extend its reach further along the Mediterranean’s southern littoral i.e. NATO’s southern flank. Russia could, for example, seek to deploy advanced anti-access, area-denial systems along the Libyan coast, significantly enlarging the anti-access bubble that it has already established in the Eastern Mediterranean with similar deployments in Syria a bubble that was already raising significant concern with top U.S. military commanders a year ago. More here.
Related reading: What Americans Need To Know If Russia Intervenes in Libya’s Civil War
Related reading: The European Migrant Crisis Includes Libya
Further, what was his relationship with Hillary and Ambassador Cretz? We may never know due to those still missing Hillary emails.
Downfall and exile
Gaddafi put Haftar – recently promoted to field marshal – in charge of the Libyan forces involved in the conflict in Chad in the 1980s. This proved to be his downfall, as Libya was defeated by the French-backed Chadian forces, and Haftar and 300 of his men were captured by the Chadians in 1987.
Having previously denied the presence of Libyan troops in the country, Gaddafi disowned him. This led Haftar to devote the next two decades towards toppling the Libyan leader.
He did this from exile in the US state of Virginia. His proximity to the CIA’s headquarters in Langley hinted at a close relationship with US intelligence services, who gave their backing to several attempts to assassinate Gaddafi.
Return from exile
After the start of the uprising against Gaddafi in 2011, Haftar returned to Libya where he became a key commander of the makeshift rebel force in the east.
With Gaddafi’s downfall, Haftar faded into obscurity until February 2014, when he outlined on TV his plan to save the nation and called on Libyans to rise up against the elected parliament, the General National Congress (GNC), whose mandate was still valid at the time.
His dramatic announcement was made at a time when Libya’s second city, Benghazi, and other towns in the east had in effect been taken over by the local al-Qaeda affiliate, Ansar al-Sharia, and other Islamist groups who mounted a campaign of assassinations and bombings targeting the military, police personnel and other public servants.
Although Haftar did not have the wherewithal to put his plan into action, his announcement reflected popular sentiment, especially in Benghazi, which had become disenchanted with the total failure of the GNC and its government to confront the Islamists.
Haftar’s popularity is not necessarily shared elsewhere in the country where he is remembered more for his past association with Gaddafi and his subsequent US connections.
He is also detested by Islamists who resent him for confronting them in Benghazi and elsewhere in the east.
Operation Dignity
In May 2014 Haftar launched Operation Dignity against Islamist militants in Benghazi and the east. In March 2015 Libya’s elected parliament, the House of Representatives (HoR) – which had replaced the GNC – appointed him commander of the Libyan National Army (LNA).
After a year of little progress, in February 2016 the LNA pushed the Islamist militants out of much of Benghazi. By mid-April this had been followed up by further military action that dislodged the Islamists from their strongholds outside Benghazi and as far as Derna, 250km east of Benghazi.
Operation Swift Thunder
In September 2016, the LNA launched operation “Swift Thunder”, seizing from the Petroleum Facilities Guard – an armed group aligned with the UN-brokered Government of National Accord (GNA) – the key oil terminals of Zueitina, Brega, Ras Lanuf and Sidrah, in the oil-rich heartland locally known as the Oil Cresent.
In recognition of this, the Speaker of the HoR and supreme commander of the armed forces, Agilah Saleh, promoted Haftar from lieutenant-general to field marshal. More here from BBC.