Texas Sheriffs, Jails on Immigration Front Line
TexasTribune: With a $6 billion budget and more than 20,000 employees, U.S. Immigration and Customs Enforcement stands poised to seize and deport immigrants — undocumented or not — who commit serious crimes in the United States.
Provided someone else catches them.
The behemoth agency at the center of the nation’s immigration enforcement efforts has no proactive way — watch lists, data mining or the like — to systematically search for dangerous undocumented immigrants, including those who have returned to the United States after being deported for committing crimes.
Instead, if an immigrant criminal is caught and thrown out of the country, the process most likely begins when a local police officer or sheriff’s deputy pulls them over for a traffic stop or arrests them as part of a criminal investigation.
The success of federal deportation policy in Texas and nationwide depends for the most part on a heads up from county sheriffs. They run the jails where people are taken when arrested and where the culling of criminal immigrants begins.
Being at the bottom of the enforcement pyramid places tremendous pressure on them — political, legal and otherwise — sheriffs say, and with federal policy increasingly targeting serious, repeat criminal offenders, their role in the process has grown.
“When some of these sheriffs talk about bringing in an undocumented, it may be one a month,” said Dallas County Sheriff Lupe Valdez. “With us, it’s several a day.”
The legal tool federal authorities use to take custody of immigrants they want is the detainer. Around in some form or fashion since the 1950s, detainers are notices sent to jails asking them to hold on to an immigrant once local authorities are done with them so federal agents can come by and get them.
In its latest incarnation, the detainer is reserved for the most serious convicted immigrant criminals. This new, narrower restriction, imposed in November 2014, has caused the number of detainers to drop. As of October 2015, the latest monthly figure available, 7,117 detainers were issued. That’s down from an all-time monthly high of 27,755 in August 2011, according to voluminous Freedom of Information Act requests made by the Transactional Records Access Clearinghouse at Syracuse University.
Texas is central to the federal agency’s deportation efforts. Nationwide, only eight jails received more than 1,000 detainer requests in the last year, according to clearinghouse data. Four were in Texas — Harris, Travis, Dallas and Hidalgo counties.
A report last year on the federal agency’s enforcement operations shows it plucked 139,368 people from the nation’s jails and prisons during the fiscal year ending Sept. 30, 2015. That accounted for about 59 percent of the total number of people ICE removed from the country that year for a variety of reasons.
Many came from Texas, screened out of state prisons or found among the approximately 71,000 people who are booked into local Texas jails each month, according to the Texas Department of Public Safety. On average, 3,724 undocumented immigrants were detained in Texas jails each month in 2015, according to a Texas Tribune analysis of immigration detainer reports from the Texas Commission on Jail Standards.
Between December 2012 and October 2015, undocumented immigrants who sat in Texas county jails cost taxpayers a total of $210.6 million, according to reports filed with the Texas Commission on Jail Standards that were released to The Texas Tribune.
In 2015, the federal government provided about $12 million to Texas to care for incarcerated undocumented immigrants. Most of that – more than $8 million – went to the Texas prison system, not jails.
Yet for all the statistics, no federal, state or local agency can claim it has a handle on the number of criminal aliens in the country, how many crimes they are responsible for and what share the system catches.
Local options
In Harris, the state’s most populous county, 135,000 inmates each year come through the jailhouse doors. It and the city of Carrollton are the only two Texas jurisdictions that contract with the federal government to have immigration agents stationed at its jail helping pinpoint criminal immigrants. Nine federal officers and nine Harris County deputies schooled in federal procedures comb booking documents and interview inmates suspected of being in the country illegally.
By contrast, in Brewster County, the state’s geographically largest — as in, bigger than some states — things work a bit differently. About 9,200 people live in the West Texas county, and its jail in Alpine has no official policy for handling undocumented immigrants.
How does it strive to alert federal authorities when a criminal immigrant is arrested? “We’ve got a sign on the wall,” jail administrator Lora Nussbaum told the Tribune, referring to a torn ICE flier taped on a jail wall that lists the agency’s phone number.
County jails may be the front line of efforts to keep undocumented immigrants who commit serious crimes from slipping through the cracks, but the state of Texas has no uniform method of going about that task, or measuring the scope of the problem.
To gain a better picture of crimes committed by undocumented immigrants and how counties handle them, the Tribune asked for booking data and immigration procedure policies from 26 Texas counties, including the state’s 10 most populous.
Almost none would provide it. Some, like Montgomery and Presidio counties, insisted that providing booking information, including an inmate’s date of birth, violated the inmate’s right to privacy. Harris County claimed that releasing a list of noncitizens was essentially creating new information — something the Texas Public Information Act does not require a governmental body to do.
Some counties argued that that federal law specifically prohibits releasing information about immigrants.
Attorney General Ken Paxton‘s office upheld most of the counties’ arguments, saying state open records laws don’t compel release of the information.
The Dallas County Sheriff’s Office went a step further and insisted that booking records are court records and, as such, are not subject to the state’s open records law. The attorney general’s office agreed, blocking their release.
Five counties responded to the Tribune’s request for booking data: Brewster, Nueces, Fort Bend, Travis and Tarrant. Of those, only Travis responded with enough detailed information to analyze.
“We don’t want to be in a position where somebody loses their life because of something we didn’t do that was legal for us to do.”— Maj. Wes Priddy, chief administrator for Travis County jails
The numbers show that Travis County booked about 20,000 inmates with federal immigration detainers between 2008 and 2015, facing charges that were roughly evenly divided between felonies and misdemeanors. More than 7,000 of those inmates faced drunk driving charges, the most common charge by far. That was followed by family violence-related assault charges, which about 1,900 inmates faced. An estimated 2,400 of the total inmates were repeat offenders.
Maj. Wes Priddy, chief administrator for Travis County jails, said local law enforcement’s primary concern was public safety, not investigating immigration status. But he said that part of keeping dangerous people off the streets involved close cooperation with federal authorities.
“We don’t want to be in a position where somebody loses their life because of something we didn’t do that was legal for us to do,” Priddy said.
After arresting someone, the Department of Public Safety, county sheriffs, and even the Texas Department of Criminal Justice — the nation’s largest prison system — all have to rely on the federal government to inform them who is in the United States illegally.
“What our obligation is, is to provide ICE with the population information,” said Tarrant County Sheriff Dee Anderson. “They go through it. They determine who they’re going to put a hold on and who they’re not, and our people don’t really have a way to further investigate are they truly here legally or not.”
That typically happens during the booking process, when a suspect’s fingerprints are sent to the Federal Bureau of Investigation, a procedure used for every new inmate. If the fingerprints match a profile in the federal database of non-U.S. citizens with previous criminal histories, ICE can decide to ask for a detainer. Texas jail officers do ask arrestees to name their country of birth as a part of the booking process, but an arrested immigrant’s answer is written down without being verified.
The same holds true for inmates in Texas prison. As of Nov. 30, 2015, three-fourths of the 9,135 inmates in the Texas prison system with ICE detainers were in the United States illegally. The remainder include those serving time for crimes who had legal immigration status.
“Ultimately, ICE will make the determination whether that person is in country illegally,” said Texas prisons spokesman Jason Clark. In 2010, the agency began asking for ICE help verifying those among the system’s 148,000 inmates who were illegally in the country.
But the federal tracking system of verifying what law enforcement refers to as “criminal aliens” is less than precise. It relies on someone’s fingerprints being in the system because they have been arrested before. If an undocumented immigrant has never encountered law enforcement, the federal tracking system might not notice their first arrest.
Jumbled numbers
There is no definitive data showing that undocumented immigrants commit crimes at a higher rate than the citizen population, and a few indications that in Texas they do not.
The Pew Research Center estimates undocumented immigrants comprise about seven percent of the Texas population. On average, 3,724 undocumented immigrants were detained in Texas jails each month in 2015, according to a Texas Tribune analysis of immigration detainer reports from the Texas Commission on Jail Standards.
Of the 148,000 inmates held in 100 Texas prison units, about 9,135 inmates have federal detainers asking that they be handed to federal officials when their sentences are complete. Not all were in the country illegally when arrested. Those that were illegal account for about 6 percent of the prison population.
Nationwide, almost 60 percent of immigrants who are deported had some previous criminal charges, according to 2015 numbers from ICE.
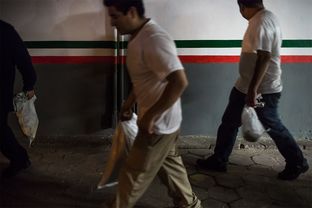 by: Martin do NascimentoA group of undocumented Mexican nationals who were convicted of crimes in the U.S. enter Mexico at the US-Mexico border crossing at Brownsville/Matamoros after being deported from the United States on Nov 4, 2015.
by: Martin do NascimentoA group of undocumented Mexican nationals who were convicted of crimes in the U.S. enter Mexico at the US-Mexico border crossing at Brownsville/Matamoros after being deported from the United States on Nov 4, 2015.The Pew Center, relying on 2012 U.S. Census numbers, estimated that Texas has 1.7 million undocumented immigrants, ranking second in the nation. What portion of that 1.7 million is responsible for crimes is a tougher calculus.
Estimates from the Texas Department of Public Safety, which gets the information from jails, are considered inaccurate because there’s no uniform requirement to verify citizenship during the jail booking process.
In 2014, then-Gov. Rick Perry was criticized for relying on DPS’ first attempts to calculate the impact of crimes committed by immigrants. That year, Perry repeated the department’s claim that “criminal aliens” had committed more than 642,000 crimes in Texas since 2008. It was later revealed that “criminal aliens” referred to all foreign-born immigrants in Texas, not just those in the state illegally, and the “crimes” counted included charges, not convictions, some dating back decades.
One year later, DPS tried to clarify the numbers, but even director Steve McCraw, appearing before the Texas House Committee on State Affairs in December, tried to lower expectations about the “criminal alien statistic” his agency featured on its website.
“It’s an undercount,” McCraw testified on Dec 10. “We acknowledge it woefully undercounts the amount, but it does accurately count the ones who are in fact here and the ones who have committed crimes.”
The DPS statistics continue to confuse both the public and lawmakers.
ICE officials consider a foreign national — here legally or otherwise — a “criminal alien” if they’ve been convicted of a crime. DPS broadens the definition to include foreign nationals who have only been arrested.
“Criminal alien is a foreign national with a criminal record,” explained DPS Assistant Director Skylor Hearn, who oversees the agency’s law enforcement support division, which includes the state’s crime records. “There was probable cause to arrest them for something, and it would apply to the rest of us as well, generally speaking. If you’ve been arrested, you have a criminal record; you are not a criminal, but you have a criminal record.”
By DPS’s count, 177,060 foreign-born individuals were charged with crimes from 2011 through Jan. 31. That’s a much larger number than those foreign nationals actually convicted during the same time frame in Texas: 84,182 non-U.S. citizens. Of those, 58,128 were determined to be in the United States unlawfully.
State Rep. Cesar Blanco, D-El Paso, says the DPS numbers on “criminal aliens” are artificially pumped up by counting the number of criminal charges filed against undocumented immigrants instead of actual convictions. Charges are routinely dismissed for lack of evidence or other reasons, he noted.
But by hyping the number of charges, the agency bolsters the argument for more border security money. Last year, the Texas Legislature approved an additional $800 million for border security.
“When crime rates were higher in this state, did the legislature move this much money?” Blanco asked.
Adding to the mathematical murkiness, immigration status can be fluid. A foreign-born Texas jail inmate could be legally in the country at the time of one arrest but have an expired visa by the next arrest and be undocumented the second time around, further bedeviling Texas’ attempts at measuring unauthorized immigrants’ impact on the state’s criminal justice system.
Attempts by DPS to connect criminal aliens to their crimes also fall short.
The agency’s data, obtained by the Tribune, shows that 177,060 non-U.S. citizens arrested from 2011 through Jan. 31 were charged with 252,083 offenses during that time. This is less than what DPS reports on its own website because the agency counts crimes committed over a U.S. citizen’s lifetime, outside the five-year span.
DPS officials insist that its criminal alien counts, based on federal immigration data, are not an attempt to construe that foreign-born criminals are a greater threat than U.S. citizens.
“The department has not made that statement and does not have information to support that statement,” DPS spokeswoman Summer Blackwell said in a statement. “The Department of Public Safety believes any individual who has committed a violent crime or is party to criminal activities — no matter their citizenship status or country of origin — is considered a potential threat to public safety and the security of Texas.”
Just say no
Even when federal immigration authorities decide they want to take immigrants from the state criminal justice system into custody, there can be obstacles.
Federal records obtained by the Tribune show that in more than 18,000 cases over the past two years, local jails across the country failed to hand over deportable immigrants to federal authorities. Jurisdictions in many states, including Pennsylvania, California and Colorado, have become reluctant to honor the detainers after facing a series of lawsuits from inmates challenging the constitutional legitimacy of the extended detention.
Further information about the outcomes in cases where local officials declined to detain someone — whether those inmates, many with previous criminal histories, had been released to the public — proved difficult to come by, even in Texas, where there were only 146 such cases.
Of the 11 state jails contacted by the Tribune, only one could provide definitive answers about what had happened with declined detainers in its jurisdiction.
In Collin County north of Dallas, where agency records show two declined detainers, one for an inmate with a criminal history, a spokesman for the sheriff’s office said it “would literally be too manpower-intensive and potentially impossible to locate the reasons they were released.”
The Texas county with the most declined detainers — Travis, which had 72 instances, including 33 on inmates with a prior criminal history — referred all questions about the records to the federal government.
“I do not know how ICE came up with those numbers and we do not keep stats for ICE,” Travis County Sheriff’s office spokesman Roger Wade said in an email. “You will have to ask ICE how they arrived at those numbers and what their definition is of declining detainers.”
The federal agency itself could not verify further details about the cases. An ICE official, who lacked authorization to comment and thus spoke on condition of anonymity, said a small number of the cases could be a result of administrative errors at the federal or local level.
But beyond that, the official said it would be “resource-prohibitive” to determine what exactly happened in the individual circumstances.
Step away from the direct cost to jails to house undocumented immigrants — and the troubling lack of standardized record keeping — and there’s the added pressure of keeping up with the federal government’s ever-shifting parameters of who in local jails is eligible for deportation.
On Nov. 20, 2014, ICE’s parent, the U.S. Department of Homeland Security, discontinued a policy known as Secure Communities in favor of a new plan called the Priority Enforcement Program. Secure Communities — which targeted anyone in the United States illegally — had faced fierce pushback from local officials across the country who feared legal liability under the program.
With the new program, the federal agency decided to focus its deportation efforts on undocumented immigrants who committed the most serious crimes.
In congressional testimony and internal documents detailing the new policy’s implementation, ICE officials have stressed the importance of local cooperation. A 2015 memo from the federal immigration agency describes “expansive efforts to encourage state and local law enforcement partners” to collaborate with the agency.
The program was developed to “bring back on board those state and local jurisdictions that had concerns with, or legal obstacles to, assisting us,” said ICE Director Sarah Saldaña in July testimony before a congressional committee.
But the federal agency has opposed requiring local authorities to honor immigration detainers. Homeland Security Secretary Jeh Johnson told members of the House Judiciary Committee in July that it would a “huge setback” to mandate compliance with immigration policy.
“I do not believe that mandating through federal legislation the conduct of sheriffs and police chiefs is the way to go,” he said. “I think it will be hugely controversial. I think it will have problems with the Constitution. I want to see us work cooperatively with state and local law enforcement, and I believe they are poised to do that.”
The voluntary guidelines from federal authorities can leave local officials in a politically precarious position — often, no matter what decision they make will land them in hot water.
Jurisdictions in Democratically controlled urban areas face intense pressure from activists critical of federal immigration policy to cease any cooperation with ICE.
“Our ideal situation would be for there to be no ICE collaboration whatsoever,” said Carolina Canizales, the San Antonio-based deportation defense director of United We Dream, a national immigrant rights organization, which regularly stages protests at jails in the state, in an October interview. “I think they shouldn’t condemn thousands of undocumented immigrants for one crime that has been committed.”
At the same time, state lawmakers are on the watch for any sign that county sheriffs are failing to hold unauthorized immigrants singled out by ICE for deportation until federal ICE officers can pick them up and return them to their home country.
Take the case of Dallas County Sheriff Valdez, who throughout her time in office has most often found herself in the crosshairs of immigrant rights activists. She currently faces a lawsuit alleging her jail has held immigrants for unconstitutionally long periods of time even after they received bond.
But recently, she has become better known for the harsh public denunciation she received from Gov. Greg Abbott, who wrote her a letter saying that what he viewed as lacking enforcement of federal immigration policy posed a “serious danger to Texans.”
Abbott’s letter came after Valdez told reporters in October she would review federal detainers placed on inmates in her jail on a case-by-case basis and would not hold immigrants arrested for minor crimes for up to 48 hours for ICE officers.
Her comments seemed to mirror ICE’s changed focus on the most serious immigrant criminals — but before she had a chance to clarify, Abbott blasted her stance and threatened to cut off grants to any sheriff’s office choosing to not abide by federal immigration detainers.
Valdez said late last year that her statement was taken out of context.
“What I said was, when there’s a disagreement (over whether a jail inmate was undocumented or not) we look at it case-by-case,” Valdez told the Tribune in December. “But in this whole time we haven’t had a disagreement … The feds and I are great. ICE and I are fine.”









